![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three functions of the cranial meninges?
|
1) Protect the brain
2) Act as scaffolding for arteries, veins, and venous sinuses (dural folds) 3) Form boundaries of subarachnoid space (contains CSF) |
|
|
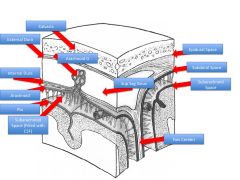
Beginning with skin, name the 5 layers of scalp.
What layers comprise the scalp proper? |
Skin
Dense Connective tissue Aponeurosis (for occipitofrontalis) Loose CT Periosteum Scalp Proper = SCA |
|
|
Which layer of the scalp is also known as the "danger area"?
|
Loose CT
|
|
|
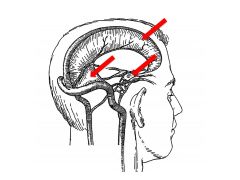
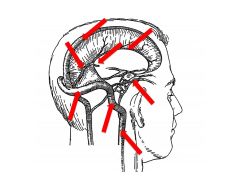
What CN innervates the dural folds?
What are three functions of the dural folds? |
All three branches of CN V (trigeminal)
Functions: 1) Compartmentalizes cranial cavity 2) Offers some protections during head injury 3) Acts as scaffolding for VENOUS sinuses |
|
|
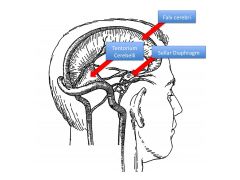
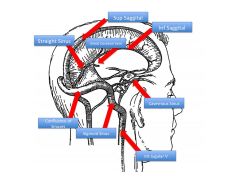
What is the function of the sellar diaphragm?
|
Helps brain stay above pituitary; also isolates pituitary
|
|
|
What is the function of the venous sinuses?
|
Drain blood of brain
|
|
|
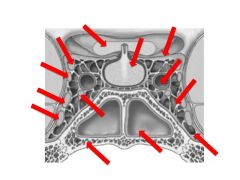
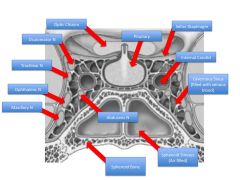
Which cranial nerves and arteries does the sella turcica contain?
|
CN III, IV, V-1, V2, VI
Internal Carotid |
|
|
How do the contents of the sphenoid and cavernous sinuses differ?
|
Sphenoid: Air-filled
Cavernous: Blood-filled |
|
|
What is the function of arachnoid granulations?
|
Site of CSF transfer to venous blood
|
|
|
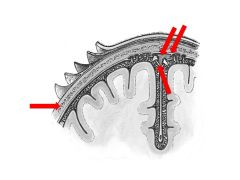
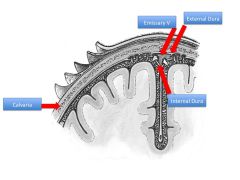
What are the three cranial meningeal spaces?
Where is each located? Which are potential spaces and which are actual spaces? |
1) Epidural Space: between calvaria and dura (potential)
2) Subdural Space: between dura mater and arachnoid mater (potential) 3) Subarachnoid space: between arachnoid and pia (actual space) |
|
|
Compare epidural hematomas with subdural hematomas.
-How they occur -Timeline of Symptoms -Artery vs Vein -Cause of Onset -Etc. |
Epidural (extradural):
Associated with fractures ARTERIES involved (usually middle meningeal) Can be due to accel-decel trauma to Pterion but limited to sutures (dura tight there) Symptoms appear in first hour; can see midline shift Subdural hematoma: No fractures associated Involved veins (BRIDGING VEINS): especially in elderly/alcoholics (cerebral atrophy causes vv to traverse longer space, become brittle, break) Also caused by accel-decel trauma (Shaken Baby Syndrome) Symptoms onset after a few DAYS |
|
|
What region of bones does the MMA sit over?
What bones comprise this region? |
Pterion:
Parietal Frontal Sphenoi Temporal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

