![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
178 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What portion of thalamus relays:
Somatosensory from body |
VPL
|
|
|
What portion of thalamus relays:
Cerebellum and basal ganglia-->motor cortex |
VL
|
|
|
What portion of thalamus relays:
Trigeminothalamic and taste-->somatosensory cortex |
VPM
|
|
|
What portion of thalamus relays:
Mamillothalamic tract-->cingulate gyrus |
Anterior nucleus
|
|
|
What portion of thalamus relays:
Integration of visual, auditory, and somesthetic input |
Pulvinar (sp)
|
|
|
What portion of thalamus relays:
Memory loss if destroyed |
Medial dorsal
|
|
|
What portion of thalamus relays:
Brachium of inferior colliculus-->primary auditory cortex |
Medial geniculate body
|
|
|
Tumor marker for:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HBV and HCV patients) |
AFP
|
|
|
Tumor marker for:
Ovarian cancer |
CA125
|
|
|
Tumor marker for:
Melanoma |
CA199, CEA
|
|
|
Tumor marker for:
Colon cancer |
CEA
|
|
|
Tumor marker for:
Astrocytoma |
S100
|
|
|
A 70 year-old patient develops pneumonia.
Organism? |
Strep pneumo
H flu |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of disulfiram?
What other drugs have a disulfiram reaction? |
Inhibits acetaldehyde DH
Metronidazole Procarbazine 1st generation sulfonylureas Cephalosporins |
|
|
MOA of:
Protease inhibitors |
Inhibit viral assembly by inhibiting protease enzyme
|
|
|
MOA of:
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors |
Nucleic acid analog inhibits reverse transcriptase and prevents integration of viral DNA into host genome
|
|
|
MOA of:
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors |
Inhibit reverse transcriptase by binding non-competitively (and directly) to enzyme
IRREVERSIBLE |
|
|
MOA of:
Fusion inhibitors |
Bind viral gp41 and inhibit fusion with CD4 cells
|
|
|
What are the common circumstances when passive immunity is required?
|
testanus, botulinum, HBV, rabies, RSV
|
|
|
Which nerve is damaged:
Loss of forearm pronation |
Median
|
|
|
Which nerve is damaged:
Loss of arm and forearm flexion |
Musculocutaneous
|
|
|
Which nerve is damaged:
Trouble initiating arm abduction |
Suprascapular n
|
|
|
Which nerve is damaged:
Unable to raise arm above horizontal |
Long thoracic, spinal accessory
|
|
|
Which abnormality:
Boot-shaped heart |
RVH
|
|
|
Which abnormality:
Continuous machine-like murmur |
PDA
|
|
|
Which abnormality:
Tendon xanthomas |
Familial hyperchol
|
|
|
Which abnormality:
Subluxation of lenses |
Marfan's
|
|
|
Which abnormality:
Cafe-au-lait spots |
Neurofibromatosis type I
McCune-Albright Syndrome |
|
|
Which abnormality:
Tuft of hair on lower back |
Occult spina bifida
|
|
|
What adult cell types arise from neural crest cells?
|
ANS
DRG Melanocytes Adrenal chromaffin cells (make catechols) Pia, arachnoid cells Bone to skull Etc....... |
|
|
Metastasis to brain commonly comes from __________.
|
Lots of bad stuff kills glia
Lung Breast Skin (melanoma) Kidney (RCC) GI tract cancers |
|
|
Metastasis to liver commonly comes from __________.
|
Cancer sometimes penetrates benign liver.
Colon, stomach, pancreas, breast |
|
|
Metastasis to bone commonly comes from __________.
|
PT barnum loves kids
Prostate Thyroid Breast Lungs Kidney |
|
|
What are the 4 types of epithelial cell junctions?
|
Zona occludens--tight jns
Zona adherens--intermediate jn w/actin and e-cadherin Macula adherens--desmosomes Gap jns |
|
|
What are the 4 proteins involved in non-epithelial adhesion mechanisms?
|
Selectins, integrans, i-cams, cadherins
|
|
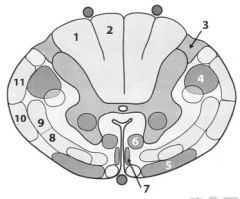
Label
|
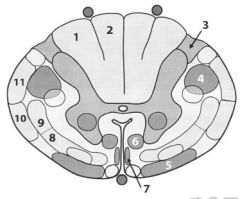
1. Vesiculus cuneatus
2. Vesiculus gracilis 3. Lissauer's tract 4. Lateral corticospinal tract 5. Vestibulospinal tract 6. Reticulospinal tract 7. Anterior (ventral) corticospinal tract 8. Anterior (ventral) spinothalamic tract 9. Lateral spinothalamic tract 10. Anterior (ventral) spinocerebellar tract 11.Posterior (dorsal) spinocerebellar tract |
|
|
Which pathology:
Psammoma bodies |
PSMM
Papillary adenoca of thy Serous cystadenoca of ovary Meningioma Mesothelioma |
|
|
Which pathology:
Posterior cervical adenopathy |
EBV-->mono
Cat scratch Acute otitis media |
|
|
Which pathology:
Lytic bone lesions on x-ray |
Multiple myeloma
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Thyroid-like appearance of kidney |
Chronic bacterial pyelonephritis
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Low serum ceruloplasmin |
Wilson's dz
|
|
|
Drug class:
Azathioprine |
Immunosuppress
|
|
|
Drug class:
Probenecid |
Used for gout, inhibits uric acid reabsorption
|
|
|
Drug class:
Primaquine |
Anti-malarial
|
|
|
Drug class:
Cefprozil |
2nd gen cephalosporin
|
|
|
Drug class:
Lamivudine |
NRTI
|
|
|
Drug class:
Tobramycin |
Aminoglycoside
|
|
|
Drug class:
Losartan |
ARB
|
|
|
Drug class:
Indinavir |
HIV protease inhibitor
|
|
|
Drug class:
6-mercaptopurine |
Anti-cancer
|
|
|
Drug class:
Rofecoxib |
COX2 inhibitor
|
|
|
Drug class:
Carmustine |
Nitrosylurea
|
|
|
Drug class:
Doxycyline |
Tetracycline
|
|
|
Drug class:
Timolol |
Beta-blocker
|
|
|
Drug class:
Methotrexate |
Inhibitor of DHF reductase
|
|
|
Drug class:
Cimetidine |
H2RA
|
|
|
Drug class:
Mefloquine |
Anti-malarial
|
|
|
What is the MOA of N-acetylcysteine when given as an antidote for acetaminophen overdose?
|
Regenerates glutathione
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Stimulates bone and muscle growth |
GH via IGF-1
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Stimulates milk production and secretion |
PL
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Stimulates milk secretion during lactation |
Oxytocin
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Responsible for female secondary sex characteristics |
Estrogen
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Stimulates metabolic activity |
T4
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Increases blood glucose level and decreases protein synthesis |
Glucocorticoids--cortisol
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Responsible for male secondary sex characteristics |
T
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Prepares endometrium for implantation/maintenance of pregnancy |
PG
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Stimulates adrenal cortex to synthesize and secrete cortisol |
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Stimulates follicle maturation in females and spermatogenesis in males |
FSH
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Increases plasma calcium, increases bone resorption |
PTH
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Decreases plasma calcium, increases bone formation |
Calcitonin
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Stimulates ovulation in females and testosterone synthesis in males |
LH
|
|
|
Which hormone:
Stimulates thyroid to produce T4 and uptake iodine |
TSH
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Growth hormone |
Anterior Pit
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Thyroid hormone |
Thy
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Glucocorticoids |
Zona fasciulata of adrenal cortex
Glucocorticoids = CORTISOL |
|
|
Secreted from where:
Progesterone |
Ovaries
Placenta |
|
|
Secreted from where:
Prolactin |
Ant pituitary
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Oxytocin |
Made in hypothal (paraventricular nuclei) but stored in posterior pituitary
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Atrial natriuretic hormone |
Heart
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Glucagon |
alpha cells in pancreas
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Testosterone |
Testis in males
Ovaries in females Zona reticularis of adrenal cortex |
|
|
Secreted from where:
Follicle stimulating hormone |
Anterior pituitary
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Vasopressin |
Hypothal (supraoptic nuc) stored in post pit
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Calcitonin |
Parafollicular C cells of thyroid
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Thyroid stimulating hormone |
Ant pit
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Epinephrine and norepinephrine |
Chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Insulin |
beta cells of pancreas
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Estradiol |
Ovaries
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Estriol |
Placenta
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Estrone |
Fat cells via peripheral conversion
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Estrogen in males |
Testis
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Parathyroid hormone |
Parathyroid
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Somatostatin |
D cells of Pancreas
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Luteinizing hormone |
Ant pit
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Mineralocorticoids |
Zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
|
|
|
Secreted from where:
Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
Ant pit
|
|
|
Which hormones utilize cAMP pathways?
|
FLAT CHAMP
FSH LH ACTH TSH CRH hCG ADH (V2 receptor) MSH PTH (anything from ant pit) Calcitonin GHRH glucagon |
|
|
Which hormones utilize cGMP pathways?
|
Think vasodilators:
ANP NO (EDRF) |
|
|
Which hormones utilize IP3 pathways?
|
GOAT
GnRH Oxytocin ADH (V1 receptor) TRH |
|
|
Which hormones bind receptors in the nucleus?
|
T3/T4
|
|
|
Which hormones bind receptors in the cytosol?
|
VET CAP
Vitamin D Estrogen Testosterone Cortisol Aldosterone Progesterone |
|
|
Which hormones utilize a tyrosine kinase pathway?
|
Insulin
IGF-1 FGF PDGF (GROWTH FACTORS) |
|
|
Posterior pituitary:
AKA Embryonal derivation of _____ Hormones |
AKA Neurohypohysis
Arises from neuroectoderm Stores vasopressin (ADH) and oxytocin |
|
|
Anterior pituitary:
AKA Embryonal derivation of _____ Hormones |
Adenohyphophysis
Surface ectoderm (Rathke's pouch) FLAT PiG FSH LH ACTH TSH PL GH ALL ACT VIA cAMP!--except GH, acts via tyrosine kinase |
|
|
POMC:
Precursor of ______ |
ACTH
MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone) |
|
|
The alpha-subunit is common to these hormones.
Which subunit determine hormone specificity? |
TSH
LH FSH hCG beta-subunit determines hormone specificity |
|
|
Effect of TRH on pituitary
|
Hypothal releases TRH and causes TSH & PL release
|
|
|
Effect of DA on pituitary
|
Inhibits PL release
|
|
|
Effect of CRH on pituitary
|
Releases ACTH
|
|
|
Effect of GHRH on pituitary
|
Releases GH
|
|
|
Effect of somatostatin on pituitary
|
Inhibits GH, TSH
|
|
|
Effect of GnRH on piuitary
|
Releases FSH, LH
|
|
|
Effect of prolactin on pituitary
|
Inhibits GnRH release
|
|
|
Bromocriptine:
MOA |
DA agonist at pituitary to decrease PL release
|
|
|
Hyperprolactinemia:
Causes Presentation |
Causes:
Pregnancy/nipple stimuln Stress Prolactinoma (associated with bitermporal hemianopsia) DA antagonists: antipsychotics (haloperidol, respiridone), methyldopa Presentation: Premenopausal females: hypogonadism-->infertility, oligo/amenorrhea, rarely galactorrhea Postmenopausal female: none since already hypogonodal Male syx: hypogonadism (low T), dec'd libido, impotence, infertility (low sperm count), gynecomastia, rarely galactorrhea |
|
|
Pituitary adenoma:
Presentation Treatment |
Most commonly a prolactinoma
Presents w/features of hyperprolactinemia, also w/bilateral hemianopsia (tumor impinges on optic chiasm) Tx: bromocriptine, cabergoline |
|
|
Sheehan's Syndrome:
Pathophys Presentation |
Postpartum hypopituitarism due to inc'd risk of infarction
Fatigue Anorexia Poor lactation Loss of pubic/axillary hair (lack all of pituitary hormones!) |
|
|
Acromegaly:
Pathophys Presentation Treatment |
Excess GH
Large tongue, deep furrows Indentions along tongue due to pressure of teeth against large tongue Large hands, feet Coarse facial features Insulin resistance Pituitary resection, octreotide |
|
|
Somatostatin:
Produced by Effects Examples of analogues Uses |
Made by D cells in pancreas and GI tract
Effects: Dec'd splanchnic blood flow, dec'd GI motility and GB contraction, inhibits secreiton of most GI hormones Uses: Acromegaly, ACTH-secreting tumors (will dec endocrine/exocrine secretions in CNS/PNS) Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, carcinoid syndrome, VIPoma, glucagonoma Portal HTN Ex: Octreotide, lamreotide |
|
|
50 year-old female complains of double vision, amenorrhea, headaches.
Cause? |
Prolactinoma suppressing optic chiasm
|
|
|
MRi reveals replacement of tissue in sella turcica with CSF.
Clinical presentation? |
Empty Sella Syndrome (pituitary normally sits in sella)
No unusual presentation bc normally have some residual pituitary tissue, but sometimes have deficiency in one or more hormones. |
|
|
What hormones arise from the anterior pituitary?
|
FSH
LH ACTH TSH PL GH MSH |
|
|
Which hormones share a common alpha-subunit?
|
TSH
LH FSH beta-hCG |
|
|
PTH:
Stimulus for release Released by Effects |
Hypocalcemia-->PTH release
Comes from parathyroid chief cells F/X: Inc'd renal absorption of calcium Inhibits phosphate reabsorption (phosphate trashing hormone) Inc'd production of 1,5-OH Vit D-->inc'd GI absorption of Ca2+ Directly stimulates oblasts, indirectly stimulates oclasts-->inc'd bone resorption -->inc'd serum Ca2+ |
|
|
Vitamin D2 vs Vitamin D3:
Sources What becomes of these? |
Vitamin D2 from plants, Vitamin D3 from Sun
-->25-OH vitamin D in liver -->1,25-OH2 vitamin D in kidney via 1-alpha-hydroxylase (activated by PTH)-->bone/GI tract |
|
|
What non-parathyroid condition results in hypercalcemia?
How? |
Sarcoidosis
Granulomas-->macs produce active vitamin D |
|
|
Calcitonin:
Source Embryonic origin Function Regulation |
Source: parafollicular C cells of thyroid
Derived from NCC Decreases bone resorption of calcium High serum Ca2+ causes calcitonin secretion CalciTONin TONes down Ca2+ levels |
|
|
Hyperparathyroidism:
Primary vs Secondary vs Tertiary-- Pathophys Lab values Examples |
Primary (Stones, bones, and groans): usually adenoma; hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria (renal stones), hypophosphatemia, often asyx, but may present with weakness and constipation (groans)
Ex: osteitis fibrosa cystica Secondary: secondary hyperplasia due to dec'd gut Ca2+ absorption and inc'd phosphorus, most often in chronic renal disease (low active vitamin D)--HYPOCALCEMIA, hyperphosphatemia, high alk phos, high PTH Ex: Renal osteodystrophy Tertiary: refractory hyperpara; results from chornic renal dz; HIGH HIGH PTH, high Ca2+ |
|
|
Which diuretics result in increased urinary excretion of calcium?
|
Loops lose calcium
Thiazides don't (dec'd renal calcium stones) |
|
|
Hypoparathyroidism:
Causes Presentation |
CAused by accidental surgical excision (thyroid sx), autoimmune destructions, or DiGeorge syndrome
Presentation: Chvostek's sign--Tap cheek-->contraction of facial muscles Trousseau's sign--occlusion of brachial artery with BP cuff-->carpal spasm |
|
|
What is pseudohypoparathyroidism?
|
Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy--autosomal-dominant kidney unresponsiveness to PTH
leads to hypocalcemia, shortened 4th/5th digits, short stature PTH WILL BE HIGH |
|
|
What are the 3 functions of vitamin D?
|
Increases GI absorption of Ca2+
Increases GI absorption of PO4 Increases bone resorption of Ca2+ and PO4 |
|
|
How does PTH affect calcium?
|
Increases serum Ca2+
Increases renal absorption of Ca2+ at DCT |
|
|
How does PTH affect phosphate?
|
Pulls PO4 from bone and excretes it in urine
|
|
|
What cells secrete calcitonin?
|
Parafollicular C Cells of thyroid
|
|
|
What are two signs of hypocalcemia?
|
Chvostek's (tap cheek)
Trousseau's (tighten cuff-->carpal spasm) |
|
|
What are the two most common causes of primary hyperparathyroidism?
|
Solitary parathyroid adenoma or parathyroid hyperplasia
|
|
|
What is the underlying cause of renal osteodystrophy? How will serum Ca, Phos, Alk Phos, and PTH levels compare to normal levels?
|
Dec'd nephron loss
Phosphate elevated Calcium low PTH elevated ALP elevated or normal |
|
|
What agents can be used to treat osteoporosis?
|
Ca2+, vit D
Bisphosphonates*** Pulsatile PTH Calcitonin E2 Tamoxifen, raloxifene T |
|
|
In osteomalacia and Rickets, how will serum Ca, Phos, Alk Phos, PTH, urine Ca, and urine Phos compare to normal values?
|
Vitamin D Deficiency-->
Calcium low PTH high ALP increases as PTH increases Phosphate low Urine phsophate inc'd (kidneys still fnal!) Urine calcium dec'd |
|
|
Which hormones work via tyrosine kinase second messengers?
|
Insulin
IGF-1 PDGF FGF Prolactin GH (growth related!) |
|
|
Which cancers are associated with hypercalcemia?
|
SquamousCC (anywhere)
Renal CC Multiple myeloma Breast Ca Mets |
|
|
A young woman is found to have short stature and shortened 4th and 5th metacarpals.
Diagnosis? |
Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy--pseudohypopara
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of bisphosphonates?
|
Inhibit oclast, simulate oblast (or just lets them stay fnal)
|
|
|
What are some possible causes of hypocalcemia?
|
Hypopara due to Thyroid Sx
Autoimmune disorder, DiGeorge Syndrome |
|
|
T3/T4:
Sources of each Function Regulation |
T4 formed by thyroid follicles
T3 formed in blood by peripheral conversion T3 functions: Brain maturation, bone growth, beta-adrenergic f/x (inc'd CO, HR, SV< contractility), inc'd Basal metabolic rate (inc'd Na/K/ATPase-->inc'd O2 consumption, body temp, RR) Inc'd glycogenolysis, glucneo, lipolysis Regulation: TRH from hypothal stimulates TSH at pituitary; negative feedback by T3 to anterior pituitary |
|
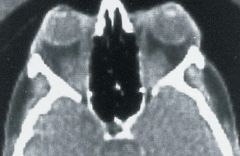
|
Extraocular muscle enlargement-->Graves' Disease
|
|
|
TBG:
Role |
Binds free T3/T4 (inactive when bound)
Only unbound is active |
|
|
Hypothyroidism vs Hyperthyroidism:
Symptoms Lab findings |
Hypothy:
Syx: Cold intolerance Weight gain, dec'd appetite Hypoactivity Constipation Hyporeflexia Labs: Inc'd TSH, dec'd T4, dec'd T3 uptake Hyperthy: Heat intolerance Weight loss, inc'd appetite Hyperactive Diarrhea Hyperreflex Dec'd TSH (if primary), inc'd T4, inc'd T3 reuptake |
|
|
Hashimoto's thyroiditis:
Pathophys Presentation |
Autoimmune thyroid disorder
Most common cause of hypothy (may start out as hyperthy though) |
|
|
Hurthle cells:
What are they? Pathognomonic of? |
enlarged epithelial cells w/excess eosinophilic granules in cytoplasm
Seen in Hashimoto's thyroiditis |
|
|
Cretinism:
Pathophys Presentation |
Fetal hypothy
May be due to iodine deficiency; defect in T4 formation (or failure to form thyroid) Pot bellied, protuberant tongue, pale, puffy face, protruding umbilicus MR |
|
|
Subacute thyroiditis:
Pathophys Presentation |
Self-limited hypothy following flu-like illness
Hypothyroid |
|
|
Riedel's thyroiditis:
Pathophys Presentation |
Thryoid replaced by fibrous tissue
Hypothyroide Fixed, har, rock-like, painless goiter |
|
|
Graves' Disease:
Pathophy Presentation Hypersens Rxn Type? |
Autoimmune hyperthyroidism; due to ab's activating TSH receptor
Proptosis TYPE II HYPERSENS (Ab mediated) |
|
|
Thyroid storm:
What is it? Causes Treatment |
aka thyrotoxicosis
Stress-induced catechol surge leading to death by arrhythmia; seen as serious complication of Graves' and other hyperthy disorders Tx: Propranolol |
|
|
Propylthiouracil:
MOA Use |
Inhibits iodination and coupling of thyroid hormone synthesis
Decreases peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 Use in hyperthy LESS BIRTH DEFECTS, OKAY IN PREGNANCY |
|
|
Methimazole
MOA Use |
Inhibits iodination and coupling of thyroid hormone synthesis
(NO EFFECT ON PERIPHERAL CONVERSION) Use in hyperthy Possibly a teratogen!! |
|
|
Cause of hyperthyroidism:
Extremely tender thyroid gland |
de Quervain's thyroiditis (subacute thyroiditis)
|
|
|
Cause of hyperthyroidism:
Pretibial myxedema |
Graves'
|
|
|
Cause of hyperthyroidism:
Pride in recent weight loss, medical professional |
Thyroid hormone abuse
|
|
|
Cause of hyperthyroidism:
Palpation of single thyroid nodule |
Toxic thyroid adenoma
|
|
|
Cause of hyperthyroidism:
Palpation of multiple thyroid nodules |
Toxic multinodular goiter
|
|
|
Cause of hyperthyroidism:
Recent study using IV contrast dye (iodine) |
Jod-Basedow phenomenon--thyrotoxicosis if pt w/iodine deficiency goiter is made iodine replete
|
|
|
Cause of hyperthyroidism:
Proptosis, edema, injection |
Graves'
|
|
|
Cause of hyperthyroidism:
History of thyroidectomy or radio-ablation of thyroid |
Too much exogenous thyroid hormone
|
|
|
Most common form of thyroid cancer.
Histologic features? |
Papillary carcinoma--excellent prognosis, ground glass nuclei (Orphan Annie)
Psammoma bodies, inc'd risk w/childhood irradiation |
|
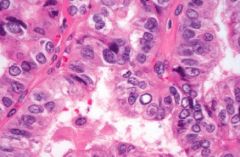
|
Papillary cancer of thyroid--note Orphan Annie nuclei
|
|
|
A 35 year-old female presents with diffuse goiter and hyperthyroidism.
What are her TSH and T4 levels like? |
This is probably Graves
Low TSH High T4 |
|
|
A 48 year-old woman has suffered from progressive lethargy and extreme sensitivity to cold.
Diagnosis? |
Hypothy--Hashimoto's most common cause
|
|
|
Type of thyroid cancer:
Most common type of thyroid cancer (75%) |
Papillary
|
|
|
Type of thyroid cancer:
Second most common type of thyroid cancer (10%) |
Follicular
|
|
|
Type of thyroid cancer:
Activation of receptor tyrosine kinases |
Papillary/Medullary
|
|
|
Type of thyroid cancer:
Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a risk factor |
Lymphoma
|
|
|
Type of thyroid cancer:
Cancer arising from parafollicular C cells |
Medullary
|
|
|
Type of thyroid cancer:
Commonly associated with either a RAS mutation or a PAX8-PPAR gamma1 rearragnement |
Follicular
|
|
|
Type of thyroid cancer:
Commonly associated with rearrangements in RET oncogene or NTRK1 |
Papillary
|
|
|
Type of thyroid cancer:
Most common mutation in BRAF gene (serine/threonine kinase) |
Papillary
|

