![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Seronegative spondyloartrhopathies:
What is it? Examples? |
Arthritis without rheumatoid factor (anti-IgG antibody)
Strong association with HLA-B27 PAIR: Psoriatic arthritis Ankylosing spondylitis Inflammatory bowel dz Reactive arthritis (Reiter's; can't see, can't pee, can't climb a tree) |
|
|
Ankylosing spondylitis:
Pathophys Diagnostics Presentation |
Chronic inflammatory dz of spine, sacroiliac joints-->ankylosis (stiff spine due to fusion of joints), uveitis, aortic regurgitation
Stiffness that is relieved with activity x-ray: bamboo spine |
|
|
Reiter's Arthritis:
Presentation |
Conjunctivitis, anterior uveitis
Urethritis Arthritis ASSOCIATED WITH POST-GI or chlamydia infections |
|
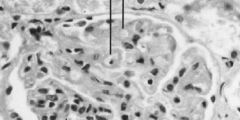
|
Lupus GN--wire-loop thickening occurs as result of immune complex deposition
|
|
|
Lupus:
Lab tests Complement levels |
Antinuclear antibodies (not specific), but good for ruling out
Anti-dsDNA--very specific, poor prognosis Anti-Smith--very specific, not prognostic Antihistone--drug-induced lupus Dec'd C3/C4 |
|
|
Sarcoidosis:
Pathophys Presentation |
Immune-mediated widespread NONCASEATING GRANULOMAS, elevated ACE
B/L hilar LAD Gammaglobulinemia Rheumatoid arthritis ACE increase Interstitial fibrosis Noncaseating granulomas (GRAIN) Hypercalcemia too! |
|
|
Polymyalgia Rheumatica:
Presentation Risks Labs |
Pain and stiffness in shoulders, hips
Fever, malaise Associated with temporal arteritis! Elevated ESR, NORMAL CK (no muscle dz) |
|
|
Dermatomyositis vs Polymyositis:
Presentation Labs |
Polymyositis--symmetric proximal weakness caused by CD8+ cell injury to myofibers. Most often involves shoulders. Perifascicular inflammn is diagnostic.
Dermatomyositis--similar to polymyositis, but also involves malar rash, heliotrope rash, inc'd risk of malignancy! Labs are the same: elevated CK, positive ANA, anti-Jo-1 |
|
|
Lambert-Eaton syndrome:
Pathophys Associations |
Autoab's to presynaptic Ca2+ channels-->dec'd ACh release-->proximal muscle weakness
Syx improve with muscle use; no eversal of syx w/AChE-i (opposite of myasthenia gravis) Assocd w/small cell lung ca. |
|
|
Scleroderma:
Pathophys Presentation Diffuse vs CREST |
Excessive fibrosis and collagen deposition throughout body
Commonly sclerosis of skin, manifesting as puffy, and taut skin w/absence of wrinkles. Also in renal, pulm, cv, and GI systems. Diffuse: widespread involvement of skin, rapid progression, Anti-Scl-70 Ab CREST: Calcinosis Raynaud's Esophageal dysmotility Sclerodactyly Telangiectasia Limited skin vinvolvement, often confined to skin on fingers and face. Anti-Centromere antibody (C for CREST) |
|
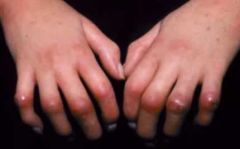
|
Tight skin-->scleroderma
|
|
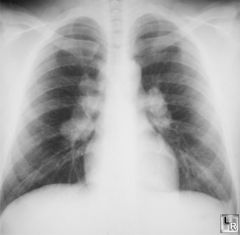
|
b/l hilar LAD-->sarcoidosis
|
|
|
A patient has difficulty swallowing, distal cyanosis in cold temperatures, and anti-centromere antibodies.
What else would you expect to see in this patient? |
Calcinosis
Sclerodactly Telangiectasias |
|
|
A patient presents with photosensitivity, arthritis, renal disease, and recurrent oral ulcers is taking primaquine and NSAIDs.
What type of check-up should she receive twice a year? |
Lupus! Must check for renal dz-->proteinuria, serum Cr level, Anti-dsDNA
|
|
|
A 30 year-old woman presents with low grade fever, a rash across her nose that gets worse when she is out in the sun, and widespread edema.
What blood test would you order to confirm your clinical suspicion? |
ANA to screen
|
|
|
A 75 year-old man presents with acute knee pain and swelling. An x-ray reveals absence of erosion of the joint space and calcium deposits in the menisci.
What is the diagnosis and what would you find on aspiration of the joint? |
Pseudogout-->calcium pyrophosphate crystals
|
|
|
What drugs cause a lupus-like syndrome?
|
SHIPP
Sulfasalazine Hydralazine Isoniazid Procainamide Phenytoin |
|
|
Dermatologic term:
Flat discoloration <1 cm, >1cm |
<1 cm = macule
>1 cm = patch |
|
|
Dermatologic term:
Elevated skin lesion <1cm, >1cm |
<1cm = papule
>1cm = plaque |
|
|
What is a keloid?
|
Irregular, raised lesion resulting from scar tissue hypertrophy (follows trauma to skin, esp. in African-Americans)
|
|
|
Allergic contact dermatitis:
Hypersens type |
IV
|
|
|
Psoriasis:
Hypersens type Presentation |
Type IV rxn
Papules and plaques with silvery scales, bleed when scraed off. Associated with nail pitting and psoriatic arthritis. |
|
|
Seborrheic keratosis:
Presentation |
Flat, greasy, pigmented squamous epithelial proliferation w/keratin-filled cysts (horn cysts). Looks "pasted on".
Occur on head, trunk, extremities. Common benign neoplasm of older persons. |
|
|
Acne:
Pathophys Treatment |
Hyperkeratosis--tx w/ Retinoic Acid (vitamin A analog), isotretinoin
Sebum overproduction--tx w/isotretinoin, sprinolactone, OCPs Propionibacterium acnes proliferation--Tx: Erythromycin, Tetracycline, topical clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide Inflammation--Tx with injected steroids (acute only!) |
|
|
Impetigo:
Pathophys Presentation |
Superficial skin infection with Staph aureus OR Strep pyogenes
HONEY COLORED CRUST HIGHLY CONTAGIOUS |
|
|
Pemphigus vulgaris:
Pathophys Presentation |
IgG Abs x Desmosomes (Desmoglein)--connect cell to cells
Acantholysis; separatin of epidermis upon stroking of skin |
|
|
Bullous pemphigoid:
Pathophys Presentation |
IgG ab's x Hemidesmosomes (Epidermal BM; 'bullow' the epidermis)
Presents with tense bullae (vesicles) |
|
|
Erythema Multiforme:
Pathophys |
Associated with infections (Mycoplasma, HSD), drugs (sulfa, beta-lactams, phenytoin)
|
|
|
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome:
Pathophys Presentation |
Fever, bulla formation and necrosis, sloughing of skin, high mortality rate
Assocd w/adverse drug rxn: -Seizure drugs -Sulfa -PCNs -Allopurinol Note: becomes toxic epidermal necrolysis when 30% of more of skin sloughs off |
|
|
Lichen Planus:
Presentation |
Pruritic, purple, polygonal papules
Assocd w/Hep C |
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma of skin:
Presentation Histologic features |
Sun-exposed lesion (red, ulcerative)
Rarely mets Keratin pearls |
|
|
Basal cell carcinoma:
Presentation |
Locally invasive, never mets
Rolled edges with central ulceration in sun-exposed areas |
|
|
Melanoma:
Presentation Predictor of metastasis Tumor marker |
Dark with irregular borders in sun-exposed areas
Depth Tumor marker: S100 |
|
|
Why can't acetaminophen be used as an anti-inflammatory drug?
|
Inactivated peripherally so has no anti-inflamm ability
Only antipyretic and analgesic |
|
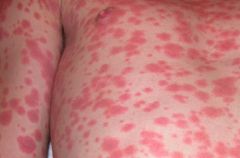
|
Erythema multiforme (drug-induced)
|
|
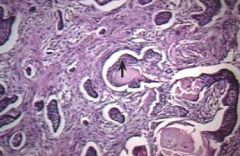
|
Keratin pearl-->Squamous CC
|
|
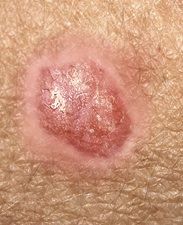
|
Basal cell carcinoma (rounded; non-ulcerative)
|
|
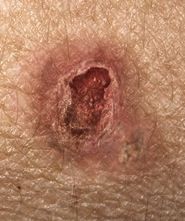
|
Squamous cell carcinoma--ulcerative
|
|
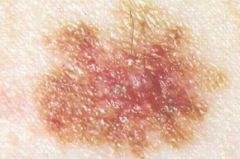
|
Melanoma
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Pruritic, purple, polygonal papules |
Lichen planus
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Life threatening rash with bulla |
Steven-Johnson
Pemphigus |
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Pruritis associated with asthma |
Atopic dermatitis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Pruritic vesicles associated with Celiac Disease |
Dermatitis herpetiformis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Allergy to nickel |
Type IV Hypersens; contact dermatitis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Antibodies against epidermal basement membrane |
Bullous pemphigoid
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Antibodies against epidermal cell surface |
Pemphigus vulgaris
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Parakeratotic scaling |
Psoriasis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Keratin-filled cysts |
Psoritic(?) Keratosis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Pruritic, purple, polygonal papules |
Lichen planus
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Life threatening rash with bulla |
Steven-Johnson
Pemphigus |
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Pruritis associated with asthma |
Atopic dermatitis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Pruritic vesicles associated with Celiac Disease |
Dermatitis herpetiformis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Allergy to nickel |
Type IV Hypersens; contact dermatitis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Antibodies against epidermal basement membrane |
Bullous pemphigoid
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Antibodies against epidermal cell surface |
Pemphigus vulgaris
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Parakeratotic scaling |
Psoriasis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Keratin-filled cysts |
Psoritic(?) Keratosis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Sand paper, predisposition to squamous cell carcinoma |
Actinic keratosis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Skin rash and proximal muscle weakness |
Dermatomyositis
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Honey crusting lesions near the nose and lips |
Impetigo
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Hyperkeratosis, koilocytosis |
Veruchi (HPV)
|
|
|
Which skin disorder:
Histology showing palisading nuclei |
Basal cell carcinoma
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Fragments DNA, toxicity = Pulmonary Fibrosis |
Bleomycin
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Blocks purine synthesis, metabolized by xanthine oxidase |
6-Mercaptopurine
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Folic acid analog that inhibits dihydrofolate reductase |
MTX
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
Prevents tubulin disassembly |
Taxols
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
DNA alkylating agents used in brain cancer |
Nitrosylureas (nitro on a mustang--mustines!)
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug:
SERM-blocks estrogen binding to ER+ cells |
Tamoxifen, raloxifen
|
|
|
What are the manifestations of CREST scleroderma?
|
Calcinosis
Raynaud's Esophageal dysmotility Sclerodactyly Telangiectasia |
|
|
What are the manifestations of sarcoidosis?
|
GRUELING
Granulomas RA Uveitis Erythema nodosum LAD--hilar, b/l Idiopathic Not TB Gammaglobulinemia ACE is inc'd, as is vitamin D |
|
|
What are the classic symptoms of Sjögren's syndrome?
|
Dry eyes, mouth, arthritis
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Signet ring cells in ovary |
Krukenberg tumor (stomach mets to ovary)
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Smudge cell |
CLL
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Spike and dome of glomerulus on EM |
Membranous GN
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Tram track of glomerulus on light microscopy |
Membranoprolif GN
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Strawberry tongue |
Scarlet fever
Kawasaki Dz |
|
|
Which pathology:
Most common location of tophi |
External ear
|
|
|
Which pathology:
Signet rings in RBCs |
Trophozoites--seen in malaria
|
|
|
What drugs can be used in the treatment of gout?
|
Acute: NSAIDs, colchicine, steroids
Chronic: Colchicine, NSAID, allopurinol, probenecid |
|
|
What is the mechanism of treating acetaminophen overdose?
|
N-acetylcysteine to regenerate glutathione
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for osteoporosis?
What measures can be taken to prevent osteoporosis? |
RIsk factors:
Age, smoking, steroids, heparin, white, thin, not exercising, poor Ca2+, low T, low E2 Prevention: weight bearing exercise, calcium and vit D intake, not smoking, addressing hypogonadism |
|
|
What drugs are known for causing drug-induced lupus?
|
Sulfonamides
Hyrdralazine Isoniazid Phenytoin Procainamide |
|
|
Silver-staining spherical aggregation of tau proteins in neurons
|
Pick bodies (similar to AD)
|
|
|
Soap bubble in femur or tibia on x-ray
|
Giant cel tumor of bone--generally benign
|
|
|
Spikes on basement membrane, dome-like endothelial deposits
|
Membranous GN (may progress to nephrotic syndrome)
|
|
|
Stacks of RBCs
|
Rouleaux formation (high ESR, multiple myeloma)
|
|
|
Stippled vaginal epithelial cells
|
Clue cells--Gardnerella vaginalis
|
|
|
Rectangular, crystal-like, cytoplasmic inclusions in Leydig cells
|
Reinke crystals (lydig cell tumor)
|
|
|
Renal epithelial casts in urine
|
Acute toxic/viral nephrosis
|
|
|
Rhomboid crystals, positively birefringent
|
Pseudogout (calcium pyrophophate dihydrate)
|
|
|
Rib notching
|
Coarcation of the aorta
|
|
|
Sheets of medium-sized lymphoid cells (starry sky appearance on histology)
|
Burkitt's lymphoma (t(8;14)
|
|
|
Tennis racket shaped cytoplasmic organelles in Langerhans cells
|
Birbeck granules
|
|
|
Thrombi made of white/red layers
|
Lines of Zahn (arterial thrombus, layers of PLTs/RBCs)
|
|
|
Thumb sign on lateral x-ray
|
Epiglottitis (H. flu)
|
|
|
THyroid-like appearance of kidney
|
Chronic bacterial pyelonephritis
|
|
|
Tram track appearance of kidney
|
Chronic bacterial pyelonephritis
|
|
|
Triglyceride accumulation in liver cell vacuoles
|
Fatty liver disease
|
|
|
WBCs that look smudged
|
CLL (almost always B cell; affects the elderly)
|
|
|
Wire loop glomerular appearance on light microscopy
|
Lupus nephropathy
|
|
|
Yellow CSF
|
Xanthochromia--subarachnoid hemorrhage
|

