![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Live attenuated vaccine:
MOA Indications Examples |
Humoral and cell-mediated immunity (but have reverted to virulence on rare occasions)
No booster required Dangerous to immunocomp'd pts or their close contacts Ex: Live! See small yellow chickens get vaccinated with Sabin's and MMR! Smallpox Yellow fever Chickenpox (VZV) Sabin's Polio virus MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella) |
|
|
Killed vaccines:
MOA Examples |
Humoral immunity only, but stable
RIP Always SalK = Killed Rabies INfluenza Salk Polio HAV |
|
|
Which live attenuated vaccine can be given to HIV-positive patients?
|
MMR
|
|
|
Which vaccines are recombinant?
|
HBV
HPV--6,11,16,18 |
|
|
Which vaccines are egg-based?
|
Flu
Yellow fever |
|
|
HSV-1:
Presentation |
Cold sores
Gingivostomatitis Temporal lobe encephalitis Esp. during times of stress |
|
|
HSV-2:
Presentation |
Multiple genital PAINFUL lesions
|
|
|
VZV:
Presentation |
Primary: Chickenpox
Secondary reaction: Shingles--grouped vesicles in dermatomal pattern (DOES NOT CROSS MIDLINE) |
|
|
EBV:
Presentation Diagnosis |
Infectious Mono***--fever, pharyngitis, ~strep throat
Burkitt's lymphoma (Infects B cells) Monospot: agglutinates with sheep RBCs |
|
|
Mononucleosis
Negative Monospot |
CMV
(listeria possible but less commonly) |
|
|
Owl's eye cellular inclusions
|
EBV
|
|
|
HHV-6:
Presentation |
aka sixth disease
High grade fever, young kids Can be followed by full body rash |
|
|
HHV-8:
Presentation |
Kaposi Sarcoma in HIV patients
(not a true malignancy)--purple looking rash |
|
|
Acyclovir
MOA Use |
Mono-phosphorylated by THYMIDINE KINASE to activate it-->inhibits DNA polymerase
HSV VZV EBV NO CMV |
|
|
Ganciclovir:
MOA Use |
THymidine kinase activates it to Inhibits viral DNA polymerase
Used for CMV, esp in IC'd |
|
|
Foscarnet:
MOA Use |
Viral DNA polymerase inhibitor that doesn't require kinase activation
Used in CMV when ganciclovir fails |
|
|
Hepadnavirus:
Describe Example |
Hepatic DNA virus; Hep B virus
|
|
|
HBV:
Virus Type Transmission MOA Effects |
DNA virus--cellular RNA polymerase transcribed RNA from viral DNA template
Sexual transmission Hepatocellular carcinoma; alpha-fetoprotein is a marker of it! |
|
|
HCV:
Virus Type Transmission MOA Effects Treatment |
Flavivirus
Transmitted through blood, carriers. Prominent amont IVDU's. Cirrhosis, Carcinoma Tx: Ribavrin, IFN-alpha |
|
|
HDV:
Transmission |
Defective virus; requires HBsAg to infect
|
|
|
HAV:
Virus type Transmission Presentation |
Picornavirus (RNA)
Fecal-oral transmission Asyx usually; acute, no chronic carriers |
|
|
HEV:
Virus Type Transmission Presentation |
RNA virus
Enteric transmission; water-borne epidemics ~HAV in course; high MORTALITY RATE in PREGNANT WOMEN |
|
|
HBsAg:
Indication of |
Indication of active dz
|
|
|
Anti-HBsAg Ab:
Indication of |
-Recovered from active dz
-Have been immunized |
|
|
Anti-HBcAg Ab:
Indication of IgG vs IgM |
Active disease
If IgG--chronic If IgM--acute |
|
|
HBeAg:
Indication of |
Transmissibility; can spread (DNA replication)
|
|
|
Anti-HBeAg:
Indication of |
Low transmissibility
|
|
|
Adenovirus:
Presentation |
Conjunctivitis***
Pharyngitis Pneumonia |
|
|
Parvovirus:
Presentation |
B19, classic crisis of sickle cell dz
Fifth Dz, cranial nerve 5, slapped cheek |
|
|
This DNA virus is double-stranded and linear.
|
Adenovirus
|
|
|
HPV:
Presentation |
1,6,11: warts
16,18: CIN-->cervical cancer, penile cancer too! |
|
|
Poxvirus:
Presentation |
Smallpox
Cowpox (milkmaid's blisters) Molluscum contagiosum--flesh-colored dome lesions with central pimple |
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Erythema infectiosum |
Parvovirus B19
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Heterophil-positive mononucleosis |
EBV
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Can cause conjunctivitis or diarrhea |
Adenavirus
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Enlarged cell with owl's eye inclusions |
CMV
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Identified with Pap smear |
HPV-16,18
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Milkmaid's blisters |
Cowpox
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
EBV
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Gingivostomatitis |
HSV-1,2
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Hides in sensory ganglia of S2 and S2 |
HSV-2
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Hides in trigeminal ganglia |
HSV-1
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Hides in dorsal root ganglia |
VZV
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Viral family of JC virus |
Polyomavirus (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in HIV)
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Downey cells |
EBV
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Human progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy |
JC Virus
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Oral hairy leukoplakia |
EBV
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Multinuclear giant cells on Tzank test |
HSV-1,2
VZV |
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Only DNA virus that's not double-stranded |
Parvovirus
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Roseola |
HSV-6
|
|
|
Which DNA virus:
Heterophil-negative mononucelosis |
CMV
|
|
|
Reoviruses:
Presentation |
Colorado tick fever--flu-like illness
|
|
|
Rotavirus:
Presentation |
Fatal watery diarrhea in children
Winter months, Infantile gastroenteritis |
|
|
Picornaviruses
|
Enteroviruses:
Polio Echovirus Rhinovirus Coxsackie Hep A |
|
|
Polio
|
Affects motor neurons of anterior horns (paralysis)
|
|
|
Echovirus
|
Asceptic meningitis and myocarditis--commonly transmitted in swimming pools
|
|
|
Coxsackievirus
|
Asceptic meningitis
Myocarditis Hand, food, and mouth dz |
|
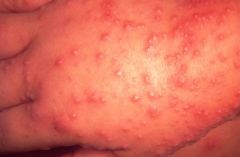
|
Coxsackie enxanthem (hand-foot-mouth dz)
|
|
|
Rhinovirus
|
Cold
|
|
|
Flaviruses
|
Flavi = yellow; so anything causing jaundice
HCV Yellow fever Dengue West Nile |
|
|
Yellow fever virus
|
Mosquitoes in Africa/South America
High fever, hemorrhagic dz (bloody diarrhea, hematuria, ecchymoses), jaundice (liver dz) |
|
|
Dengue virus
|
Most prevalent mosquito dz
"Break bone fever": Retro-orbital pain Muscle/joint pain HA Hemorrhagic fever |
|
|
West Nile Virus
|
Bird reservoir
Mosquito vectors Humans are incidental hosts Sx: HA, malaise, back pain, myalgia, anorexia (flu-like) Meningitis +/- encephalitis including muscle weakness and flaccid paralysis (anterior horn involvement) |
|
|
Togaviruses
|
Rubella
|
|
|
Coronavirus
|
Common cold
|
|
|
Influenza virus:
Virus type Antigens, role of Ag's |
ss-RNA virus with segmented genome
Ag's: Hemagglutinin (promotes viral entry), neuraminidase (promotes progeny virion release) Often superinfected with strep pneumo |
|
|
Genetic drift vs Genetic shift
Which virus exhibits this? |
Sudden Shift is more deadly than GraDual Drift ("Oh shift!"--dangerous)
Drift (epidemic): minor (antigenic drift) changes based on random mutation Shift (pandemic): reassortment of viral genoma (such as when human flu A virus recombines with swine flu A virus) Exhibited by influenza |
|
|
Croup:
Virus family Symptoms |
Parainfluenza = Croup
Barking seal cough, resp distress ~asthma, inspiratory stridor Tx: cool mist humidifier, recemic epinephrine, dose of dexamethasone, supportive, O2 as needed |
|
|
RSV bronchiolitis:
Symptoms Treatment |
Bronchiolitis ±pneumonia
Characteristic brassy cough, wheezing, resp distress ~asthma Tx: Ribavirin not used in children, adults only Albuterol or racemic epinephrine |
|
|
Rubeola:
Symptoms Risks |
MEASLES
Kopplik spots due to immune reactions Rash due to immune reactions --not seen in immunocompromised pts Cough Choriza (rhinitis, nasal congestion) Conjunctivitis Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis |
|
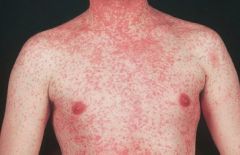
|
Measles
|
|
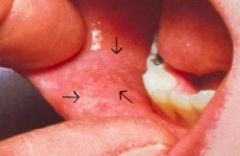
|
Koplik spots
Measles |
|
|
Which RNA virus:
Asthma-sounding infection in infants |
RSV
|
|
|
Which RNA virus:
Meningitis in summer months |
Echo
Coxsackie Enterovirus |
|
|
Which RNA virus:
Tourniquet test helps diagnose hemorrhagic disease |
Dengue
|
|
|
Which RNA virus:
Infects motor neurons of the anterior horn |
Polio
West Nile Virus |
|
|
45-year old male with squamous cell carcinoma of penis.
Virus? |
HPV 16, 18
|
|
|
20 year-old college student presents with LAD, fever, HSM.
Serum agglutinates sheep RBCs. What cell type is infected? |
EBV-->B Cells (Downy Cells)
|
|
|
how does rabies virus travel through the CNS so that it can cause fatal encephalitis with seizures?
|
Retrograde fashion up axons
|
|
|
What is the characteristic shape of rabies virus?
|
Bullet-shaped
|
|
|
Amantadine:
MOA Use |
MOA: Block viral penetration/UNCOATING
Use: Flu, PD "A man to dine" takes off his coat. Because used in PD, must cross BBB, so expect CNS side effects. |
|
|
Mumps:
Symptoms |
Parotitis
Orchitis (inflammn of testes) Viral meningitis (Coxsackie, echo too, just a side note) |
|
|
Rabies virus:
Presentation |
Bullett-shaped (Old Yeller shot with a bullet)
Fever, malaise-->agitaiton, photophobia, hydrophobia-->paralysis, coma |
|
|
Bullett-shaped capsid
|
Rabies (Old Yeller)
|
|
|
Which RNA virus:
Hand, foot, mouth disease |
Coxsackie
|
|
|
Which RNA virus:
Break bone fever |
Dengue
|
|
|
Which RNA virus:
Barking seal cough |
Croup/parainflu
|
|
|
Which RNA virus:
African hemorrhagic fever |
Ebola
|
|
|
Which RNA virus:
Common cold |
Rhino
Corona |
|
|
Which RNA virus:
Fever Jaundice Black vomit |
Yellow fever
|
|
|
Which RNA virus:
Childhood diarrhea in winter months |
Rotovirus
|
|
|
Zanamivir:
MOA Use |
Inhibit influenza neuraminidase, decreasing release of progeny virus
Flu |
|
|
Oseltamivir:
MOA Use |
Inhibit influenza neuraminidase, decreasing release of progeny virus
Flu |
|
|
Ribavirin:
MOA Use |
Inhibits synthesis of gunaine nucleotides by competitively inhibiting IMP dehydrogenase
Use: RSV, HCV (along with IFN-alpha) |
|
|
Which antiviral:
Prophylaxis for influenza A |
Zanamivir
Oseltamivir |
|
|
Which antiviral:
Inhibits CMV DNA polymerase |
Foscarnet
|
|
|
Which antiviral:
Used in treatment for chronic HCV |
Ribavirin + IFN-alpha
|
|
|
Which antiviral:
First-line for HSV or EBV |
Acyclovirs (ganciclovir, etc)
|
|
|
Which antiviral:
Blocks viral penetration and uncoating |
Amantadine
|
|
|
Which antiviral:
Treats both influenza A and B |
Zanamivir
Oseltamivir |
|
|
Which antiviral:
Second-line for CMV retinitis |
Foscarnet
|
|
|
Which antiviral:
Derivative of amantadine with fewer side effects |
Ramantidine
|
|
|
Which antiviral:
Inhibits viral DNA polymerase when phosphorylated by viral thymidine kinase |
Acyclovir (all cyclovirs)
|
|
|
Tzanck Test:
Utility |
Tests for multinucleated giant cells
Can dx: HSV-1/2, VZV |

