![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
175 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the side effects of amiodarone?
|
Pulm fibrosis
Hepatotox Hypo/hyperthy Corneal deposits Photosensitivity |
|
|
Which protozoal/helminth:
Undercooked fish Inflammation of biliary tract |
Clonorchis
|
|
|
Which protozoal/helminth:
Most common protozoal infection in US |
Giardia
|
|
|
Which protozoal/helminth:
Cause of Chagas' Dz |
T cruzi
|
|
|
Which protozoal/helminth:
Most common helminthic infection in US |
Enterobius pernicularis (Pinworm)
|
|
|
Which protozoal/helminth:
Snail host Swimmer's itch |
Schistosoma mansoni
|
|
|
Which protozoal/helminth:
Diarrhea in campers and hikers |
Giardia
|
|
|
Which protozoal/helminth:
Raw meat Infected cat feces |
Toxoplasma
|
|
|
Thyroid cells with optically clear nuclei
|
Papillary Carcinoma of Thyroid (orphan Annie nuclei)
|
|
|
Anemia with hypersegmented neutrophils
|
Megaloblastic anemia
|
|
|
Branching rods on oral infection
|
Actinomyces israeli
|
|
|
Eczema
Recurrent Infections Thrombocytopenia |
Wiskott-Aldrich
|
|
|
Hemosiderinuria
Thrombosis |
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
|
|
|
Dermatitis
Dementia Diarrhea |
Pellagra (Niacin deficiency)
|
|
|
Treatment:
Trichomonas |
Metro
|
|
|
Treatment:
Gardnerella |
Metro
|
|
|
Treatment:
Plasmodium vivax/ovale |
Chloroquine + Primaquine
|
|
|
Treatment:
Hookworm, pinworm, roundworm |
-bendazole
|
|
|
Treatment:
Pediculosis capitis or pubis |
Permethrin
Pyrethrin (these are insecticides) |
|
|
What are the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia?
|
pos:
Hallucinations, delusions, strange behavior, loose assocns neg: flat affect, social withdrawal, poor motivation/grooming |
|
|
Which immunodeficiency:
Neutrophils fail to respond to chemotactic stimuli |
Job's syndrome (Hyper IgE) or Leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome
|
|
|
Which immunodeficiency:
Adenosine deaminase deficiency |
SCID
|
|
|
Which immunodeficiency:
Failure of endodermal development |
DiGeorge
|
|
|
Which immunodeficiency:
Defective tyrosine kinase gene |
Bruton's agamma
|
|
|
Which immunodeficiency:
High levels of IgE |
Hyper IgE (Job's)
|
|
|
Which organism:
Cat scratch |
Baronella
|
|
|
Which organism:
Dog/cat bite |
Pasturella
|
|
|
Which organism:
Cat feces |
Toxo
|
|
|
Which organism:
Puppy feces |
Yersinia
|
|
|
Which organism:
Animal urine |
Leptospira (spirochete)
or Hantavirus |
|
|
Name 7 teratogens.
|
ACE-i
EtOH Alkylating agents Aminoglycosides Cocaine DES Folate agonists Iodide |
|
|
Which lipid-lowering agent:
SE: Facial flushing |
Niacin
|
|
|
Which lipid-lowering agent:
SE: elevated LFTs, myositis |
Fibrates, statins
|
|
|
Which lipid-lowering agent:
SE: GI discomfort, bad taste |
Bile acid binding resins
|
|
|
Which lipid-lowering agent:
Best effect on HDL |
Niacin
|
|
|
Which lipid-lowering agent:
Best effect on TGs/VLDL |
Fibrates
|
|
|
Which lipid-lowering agent:
Best effect on LDL/cholesterol |
Statins
|
|
|
Which lipid-lowering agent:
Binds C. diff toxin |
Cholestyramine
|
|
|
Diastolic murmurs
|
Mitral/tricuspid stenosis
Aortic/pulmonic regurgitation |
|
|
Systolic murmurs
|
Aortic/pulmonic stenosis
Mitral/tricuspid regurgitation |
|
|
These murmurs worsen with inspiration.
|
Tricuspid murmurs (because atria are filling upon inspiration)
RIGHT SIDED |
|
|
These murmurs worsen with expiration.
|
Mitral murmurs
LEFT SIDED |
|
|
Holosystolic murmur
|
Mitral regurgitation (blood flowing through valve during systole--BAD)
|
|
|
Murmur:
Loudest at apex Migrates toward axilla |
Mitral regurgitation
|
|
|
Causes of mitral regurgitation.
|
Mitral valve prolapse
Ischemid heart dz Endocarditis Rheumatic fever |
|
|
Systolic murmur heart over right sternal border
Radiates to carotids |
Aortic stenosis
|
|
|
Aortic stenosis:
Causes |
Bicuspid aortic valve after age 40
Senile/degenerative calcification Chronic rheumatic valve dz Congenital unicuspid aortic valve Syphilis |
|
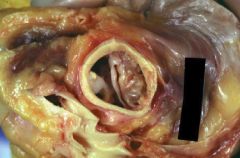
|
Bicuspid aortic valve; cause of aortic stenosis
|
|
|
Draw thorax and areas to place stethoscope.
Associated murmurs in these ares? |
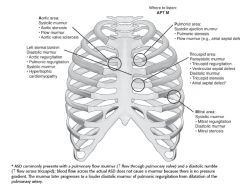
|
|
|
Systolic murmur with mid-systolic click
|
Mitral prolapse; only problematic if there's regurgitation
|
|
|
Murmurs associated with Rheumatic heart disease.
|
Mitral regurg/stenosis
Aortic regurg/stenosis |
|
|
What heart sounds are considered benign when there is no incidence of disease?
|
Split S1
Split S2 on inspiration S3 in patient under 40 Early quiet systolic murmur |
|
|
Identify defect:
Crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur heard in 2nd-3rd right interspace close to sternum |
Aortic stenosis
|
|
|
Identify defect:
Early diastolic decrescendo murmur heard along left side of sternum |
Pulmonic regurgitation
|
|
|
Identify defect:
Late diastolic decrescendo murmur head along left side of sternum |
Tricuspid stenosis
|
|
|
Identify defect:
Pansystolic murmur heard at apex and radiates to left axilla |
Mitral regurg
|
|
|
Identify defect:
Late systolic murmur preceded by mid-systolic click |
Mitral prolapse
|
|
|
Identify defect:
Cresceno-decrescendo systolic murmur best heard in 2nd-3rd left interspaces close to sternum |
Pulmonic stenosis
|
|
|
Identify defect:
Pansystolic murmur heard at 4th-6th left interspace |
Tricuspid regurg or VSD
|
|
|
Identify defect:
Continuous machine-like murmur |
PDA
|
|
|
Identify defect:
High-pitched diastolic murmur with widened pulse pressure |
Aortic regurg (classic widening of pulse pressure)
|
|
|
Murmur heard best in left lateral decubitus position.
|
MR
MS Left sided S3/S4 |
|
|
80 year-old man presents with systolic crescendo-decrescendo murmur.
Cause? |
Aortic stenosis
|
|
|
Signs of right-sided heart failure.
|
Lower extrem edema, HSM
|
|
|
Signs of left-sided heart failure.
|
Dyspnea on exertion, orthopnea, pulmonic syx
|
|
|
What medications are used to treat chronic heart failure?
Acute heart failure? |
Chronic: Digoxin, beta-blockers, ACE-i, diuretics (hyperact of renin)
Acute: LMNOP: Lasix, morphine, nitrates, oxygen, positioning/pressors |
|
|
Signs of endocarditis
|
Bacterioa FROM JANE:
Fever New murmur Roth spots on retina (rare) Osler's nodes (raised lesions on fingertips; painful) Janeway lzns (non-tender lesions on palms/soles) Splinter hemorrhages |
|
|
Bacteria causing endocarditis.
|
75% staph aureus (rapid onset)
Strep viridens (subacute) on abnl valves (TOF, prosthesis), esp bc of dental procedures Enterococci Staph epidermidis (IV drug user!!) Strep bovis (COLON CANCER) |
|
|
Culture-negative endocarditis:
Causes |
HACEK organisms
Haemophilus Actinobacillus Cardiobacterium Eikenella Kingella |
|
|
Left-sided vs Right-sided endocarditis:
Risks |
Left side: stroke
Right side: PE (bc throw emboli) |
|
|
Libman-Sacks endocarditis:
Pathophys |
Sterile vegetations on both sides of heart
COMMON CAUSE = SLE; SLE CAUSES LSE |
|
|
Hypovolemia effects on SVR, CO.
Treatment? |
SVR inc
CO inc Tx: IV fluid and blood |
|
|
Heart failure effects on SVR, CO.
Treatment? |
SVR inc
CO dec (cardiogenic shock!) Tx: LMNOP |
|
|
Sepsis/anaphylaxis effects on SVR, CO.
Treatment? |
SVR low (leaky vasculature)
CO inc Tx: Abx, iv fluids, NE |
|
|
Earliest sign of sepsis.
|
Tachycardia
|
|
|
Neurogenic effects on SVR, CO.
Treatment? |
SVR dec
CO dec Tx: IV fluids, high dose steroids for traumatic SC injuries |
|
|
Causes of hypovolemic shock.
|
Trauma (blood loss)
Severe burns |
|
|
Causes of cardiogenic shock.
|
Heart failure
MI Life-threatening arrhythmias PE Tension pneumo Cardiac contusion |
|
|
Rheumatic fever:
Pathophys Lab findings |
Immune-mediated (type II hypersens) consequence of pharyngeal infection with Grab A strep (pyogenes)
Elevated ASO (anti-streptolysin O) ab's |
|
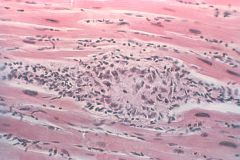
|
Aschoff body-->Rheumatic heart dz
|
|
|
Pulsus paradoxus:
What is it? Disease association? |
Exaggerated dec in amplitude of pulse during inspiration
Seen in cardiac tamponade, asthma (exagg'd inspiration) |
|
|
EKG finding of cardiac tamponade.
|
Electrical alternans--beat to beat variation of QRS complex
|
|
|
Kussmaul's sign:
What is it? Associated disease? |
Inspiration-->JVD
Due to dec'd capacity of RV Dz: Constrictive pericarditis |
|
|
Syphilitic heart disease:
Effects |
Calcification of aortic root and ascending aortic arch--"tree bark" appearance of aorta
Can result in aneurysm |
|
|
Most common cardiac tumor
|
Myxomas
|
|
|
Myxoma:
Most common site Effect |
Atria (mostly left atrium)
Assocd w/syncopal episodes (obstruction of valve) |
|
|
Most common cardiac tumor in kids.
|
Rhabdomyomas--assocd w/tuberous sclerosis
|
|
|
Most common metastases to heart.
|
Melanoma
|
|
|
IV drug user presents with chest pain, dyspnea, tachycardia, and tachypnea.
Cause? |
Bacterial endocarditis--could be right-sided with embolization to PA
|
|
|
Patient in MVA presents with chest pain, dyspnea, tachycardia, and tachypnea.
Cause? |
Tension pneumothorax (lung collapse)
|
|
|
Post-op patient presents with chest pain, dyspnea, tachycardia, and tachypnea.
Cause? |
Pulmonary embolism
|
|
|
Young girl with congenital valve disease given PCN prophylactically. In ER, bacterial endocarditis is diagnosed.
Next step in management? |
IV vancomycin until culture comes back
|
|
|
Under what circumstances might you see pulsus paradoxus?
|
Tamponade
Croup Asthma |
|
|
Diffuse myocardial inflammation with necrosis and mononuclear cells
|
Myocarditis
|
|
|
Focal myocardial inflammation with multinucleate giant cells
|
Rheumatic fever--these are Aschkoff cells
|
|
|
Fever
IV drug abuse New heart murmur |
Bacterial endocarditis
|
|
|
Chest pain and coarse rubbing heart sounds in patient with Cr of 5.0
|
Uremic pericarditis
|
|
|
Tree-barking of aorta
|
Syphilis
|
|
|
Child with fever, joint pain, cutaneous nodules
4 weeks after throat infection |
Rheumatic fever
|
|
|
ST elevations in all EKG leads
|
Pericarditis
|
|
|
Disordered growth of myocyte
|
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
EKG shows electrical alternans
|
Cardiac tamponade
|
|
|
Raynaud's
Treatment |
ASA
Dihydropyridine CCB Sildenafil (vasodilation) |
|
|
Wegener's granulomatosis:
Presentation Presentation Lab-findings Treatment |
Necrotizing vasculitis
Necrotizing granulomas in lung and upper airway (even in the hard palate!) Necrotizing glomerulonephritis Presentation: Hemoptysis Hematuria Perforation of nasal septum** Lab: c-ANCA positive! Tx: Steroids |
|
|
Microscopic polyanitis:
Presentation |
Same as Wegener's but p-ANCA positive (P! not C!)
(Necrotizing vasculitis Necrotizing granulomas in lung and upper airway (even in the hard palate!) Necrotizing glomerulonephritis) |
|
|
Churg-Strauss Syndrome:
Presentation |
Granulomatous vasculitis
Eosinophilia Asthma, atopic dermatitis Peripheral neuropathy (wrist/foot drop) p-ANCA positive |
|
|
c-ANCA vs p-ANCA diseases
|
c-ANCA: Wegener's
p-ANCA: Churg-Strauss, microscopic polyangitis, Pauci-immune crescentic glomerulonephritis, polyarteritis nodosa |
|
|
Pauci-immune crescentic glomerulonephritis:
Pathophys |
Vasculitis limited to kidney; paucity of antibodies
|
|
|
Sturge-Weber Disease:
Presentation |
Port-wine stain on face
Seizures, early-onset glaucoma |
|
|
Henoch-Schonlein purpura:
Presentation |
Skin rash on buttocks and legs (palpable purpura)
Arthralgia Abdominal pain/melena IgA immune complexes |
|
|
Burger's disease:
Presentation |
Vasculitis fo small and medium peripheral vessels in HEAVY SMOKERS
|
|
|
Kawasaki disease:
Presentation |
Acute vasculitis in Asian children/infants (self-limiting)
Fever, conjunctivitis, strawberry tongue, peeling of skin/desquamation of skin on palms/soles Coronary aneurysms Treat with high dose ASA, forget Reye's! |
|
|
Polyarteritis nodosa:
Presentation |
Immune-complex mediated vasculitis in patients with Hep B
|
|
|
Temporal arteritis:
Presentation Diagnosis Treatment |
MOST COMMON VASCULITIS
Elderly females with unilateral headache, jaw claudication (hurts so much to chew) Impaired vision, irreversible blinndess Elevated ESR to screen Temporal biopsy for confirmatory Tx: high dose steroids |
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Weak pulses in upper extremities |
Takiyasu's
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Necrotizing granulomas of lung and necrotizing glomerulonephritis |
Wegener's
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Necrotizing immune complex inflamman of visceral/renal vessels |
Wegener's
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Young male smokers |
Buerger's
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Young Asian women |
Takiyasu's
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Asthmatics |
Churg-Strauss
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Infants and young children Involved coronary arteries |
Kawasaki
|
|
|
Most common vasculitis
|
Giant cell (Temporal) arteritis
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Associated with Hepatitis B infection |
Polyarteritis nodosa
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Occlusion of ophthalmic artery can lead to blindness |
Temporal arteritis
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Perforation of nasal septum |
Wegener's
|
|
|
Which vasculitis:
Unilateral headache Jaw claudication |
Temporal arteritis
|
|
|
Which vascular tumor:
Benign raised red lesion about size of mole in older patients |
Cherry hemangioma
|
|
|
Which vascular tumor:
Raised, red area present at birth, increases in size initially, regresses over months to years |
Strawberry hemangioma
|
|
|
Which vascular tumor:
Lesion caused by lymphoangiogenic growth factors in infected HIV patient |
Kaposi's sarcoma
|
|
|
Which vascular tumor:
Polypoid red lesion found in pregnancy or after trauma |
Pyogenic granuloma
|
|
|
Which vascular tumor:
Benign, painful, red-blue tumor under fingernails |
Glomus tumor
|
|
|
Which vascular tumor:
Cavernous lymphangioma associated with Turner's Syndrome |
Cystic hygroma
|
|
|
What is the classic presentation of a patient with temporal arteritis?
What lab findings help diagnose temporal arteritis? |
Jaw claudication
Unilateral HA Blindness/impaired vision ESR would help Temporal bx is definitive |
|
|
Which vascular tumor:
Skin papule in AIDS patient caused by Bartonella |
Bacillary angiomatosis
|
|
|
Hypochromic, microcytic anemia
|
Fe def anemia
Pb poinoning Thalassemia Anemia of chronid disease (micro CLIT) |
|
|
What are the differences between acute and subacute bacterial endocarditis?
|
Acute: staph aureus; rapid onset, can affect normal valves
Subacute: Strep viridans with pre-existing damage; insidious onset |
|
|
Increased alpha-fetoprotein in amniotic fluid/maternal serum
|
Anencephaly
Spina bifida (NT defects) |
|
|
What are the Jones criteria for the diagnosis of acute rheumatic fever?
|
JONES:
Joints--polyarteritis O (<3): Pancarditis--endo/myo/pericarditis N: nodules subcut E: Erythema marginatum S: Sydenham's chorea |
|
|
Increased uric acid levels
|
Gout
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Tumor lysis syndrome Loop, thiazide diuretics |
|
|
Why do the kidneys retain fluid in CHF patients?
|
Kidneys sense poor perfusion-->Renin via JGA-->AgII-->Aldosterone-->Na+ and H2O retention
|
|
|
Intranuclear eosinophilic droplet-like bodies
|
Cowdry type A (HSV or yellow fever)
|
|
|
Which defect:
Crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur best heard in 2nd-3rd right interspace close to sternum |
Aortic stenosis
|
|
|
Large lysosomal vesicles in phagocytes
Immunodeficiency |
Chediak-Higashi dz
|
|
|
Which defect:
Rumbling late diastolic murmur with opening snap |
MS
|
|
|
Low serum ceruloplasmin
|
Wilson's dz
|
|
|
Which defect:
Pansystolic murmur best heard at 4th-6th left intercostal spaces |
TR or VSD
|
|
|
Lumpy-bumpy appearance of glomeruli on immunofluorescence
|
Poststrepp GN (immune complex deposn)
|
|
|
Which defect:
Continuous machine-like murmur |
PDA
|
|
|
Lytic bone (hole-punched) lesions on x-ray
|
Multiple myeloma
|
|
|
What are the common causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy?
|
Sarcoid
Amyloid Hemochromatosis Laughler's Dz Post-radiation fibrosis |
|
|
Mammary gland (blue-domed) cyst
|
Fibrocystic change of breast
|
|
|
What is Dressler's syndrome?
|
Pericarditis following MI/heart surgery (though to be auto-immune process)
|
|
|
Monoclonal antibody spike
|
1. Multiple myeloma (M protein--usually IgG or IgA)
2. Monoclonal gamopathy of undet'd significance (MGUS) 3. Waldenstrom's (M protein = IgM) macroglobulinemia 4. Primary amyloidosis |
|
|
What are the most common complications after an MI?
|
Arrhythmia (Vfib = deadly)
LVF-->pulm edema |
|
|
Monoclonal globulin protein in blood/urine
|
Bence Jone proteins (multiple myeloma--kappa or lambda Ig light chains in urine); Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
|
|
|
Evolution of an MI:
0-4 hours 4-24 hours 2-4 days 5-10 days 10+ days |
0-4 hours: no visible change
4-24 hours: contraction bands, necrotic cells, enzymes spill 2-4 days: acute inflamn, nphils, dilated vessels, hyperemia 5-10 days: macs, risk of free wall rupture, pap mm rupture, septal rupture 10+ days: contracted scar, absence of myocytes; risk of aneurysms |
|
|
Mucin-filled cell with peripheral nucleus
|
Signet ring (gastric carcinoma)
|
|
|
What are the most common locations for atherosclerosis?
|
Abdominal aorta
Coronary arteries Popliteal arteries Carotid arteries (TIAs, Strokes, dementia) |
|
|
Narrowing of bowel lumen on barium radiograph
|
String sign--Crohn's dz
|
|
|
An adult patient with a history of hypertension presents with sudden sharp, tearing pain radiating to the back.
What do you expect to see on CXR? |
Aortic dissection causing widening of mediastinum
|
|
|
Needle-shaped, negatively birefringent crystals
|
Gout (hyperuricemia)
|
|
|
On auscultation of a patient, you hear a pansystolic murmur at the apex with radiation to the axilla.
Cause? |
MR
|
|
|
Nodular hyaline deposits in glomeruli
|
Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules (diabetic nephropathy)
|
|
|
A 25 year-old pregnant woman in her 3rd trimester has a normal BP when standing and sitting.
When supine, her BP drops to 90/50. Diagnosis? |
Compression of inferior vena cava, less pre-load to heart, less stroke volume out of heart
|
|
|
Nutmeg appearance of liver
|
Chronic passive congestion of liver due to RHF
|
|
|
Onion-skin periosteal reaction
|
Ewing sarcoma of bone
|
|
|
Onion skin periosteal reaction
|
Ewing's sarcoma (malignant round-cell tumor)
|
|
|
Pseudopalisading tumor cell arragnement
|
Glioblastoma multiforme (most common brain tumor)
|
|
|
Periosteum raised from bone, creating triangular area
|
Codman's triangle on x-ray (osterosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, pyogenic osteomyelitis)
|
|
|
Elevated serum uric acid
|
Gaut
L-N syndrome Diuretics (loop, thiazides) |
|
|
Podocyte fusion on EM
|
Minimal change dz (child w/nephrotic syndrome)
|
|
|
Polished, ivory-like appearance of bone at cartilage erosion
|
Eburnation (osteoarthritis resulting in bony sclerosis)
|
|
|
Protein aggregates in neurons from hyperphosphorylation of protein tau
|
Neurofibrillary tangles (AD, CJD)
|
|
|
Pseudopalisading tumor cells on brain biopsy
|
Glioblastoma multiforme
|
|
|
RBC casts in urine
|
Acute GN
|

