![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
aVR vs aVF vs aVL:
Vectors |
aVR: heart to right arm
aVF: heart to feet aVL: heart to left arm |
|
|
Lead I vs Lead II vs Lead III:
Vectors |
Lead I: Right arm to left arm
Lead II: Right arm to left leg Lead III: Left arm to left leg |
|
|
Left Axis Deviation:
EKG signs Causes |
Positive QRS in aVL and aVR
Causes: Inferior wall MI Left anterior fascicular block L BBB LVH (sometimes) High diaphragm |
|
|
Right Axis Deviation:
EKG signs Causes |
Positive QRS in limb lead III
RVH Acute right heart strain (massive pulm embolism) R BBB Dextrocardia |
|
|
Quick way to determine normal axis.
|
Positive QRS in Limb Lead I and II
|
|
|
1 tiny box =
1 big box = |
1 small box = 0.04 s
1 big box = 0.2s |
|
|
How wide is a normal QRS complex?
What if it's longer? |
3 small boxes
If longer-->ventricular-generated rhythm |
|
|
Peaked T wave indicates _____
|
High potassium levels
|
|
|
Flat T wave indicates ______.
|
Low potassium levels
|
|
|
Torsades de Pointes:
What is it? Cause Risks |
Ventricular tach that can progress to V-fib
Cause: anything that prolongs QT interval Very fast, wide QRS |
|
|
What drugs place patients at risk of Torsades de pointes?
How? |
These drugs prolong QT interval can can cause Torsades
Marolides (thromycin) Chloroquine, methoquine Haloperidol Risperidol Methadone Proteas Inhibitors |
|
|
Torsades de pointes:
Treatment |
Mg2+
|
|
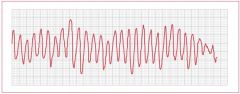
|
Torsades de pointes--
Rapid sinusoidal waveforms Prolonged QT interval |
|
|
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome:
Pathophys EKG characteristics Risk Treatment |
Accessory conduction PW from atria to ventricle (bundle of Kent), bypassing AV node.
Thus, ventricles begin to partially depol earlier, giving rise to characteristic delta wave on ECG. Tx: amiodarone, procainamide Risk: Supraventricular tachycardia |
|

|
WPW delta wave
|
|

|
WPW delta wave
|
|
|
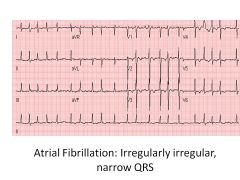
Atrial fibrillation:
Predisposing factors Risks Treatment |
Enlarged atria, SA nodes depolarize at different times-->irregularly irregular rhythm
Blood can pool-->clots-->emboli Tx: If less than 48 hours-->cardiovert (defib) If over than 48 hours-->do not cardiovert (risk of embolus): -Heparin -Clot assessment -Rate control (digoxin, beta-blockers, CCB) OR -Rhythm control (sotalol, amiodarone--K+ blockers) |
|

|
Atrial fibrillation--irregularly irregular
|
|

|
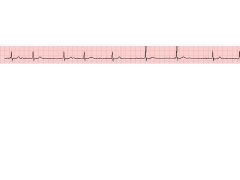
Atrial flutter--sawtooth pattern
|
|
|
1st degree AV block:
EKG characteristics Cause |
PR interval >.200sec
Borelli burgdorferi (Lyme) |
|
|
2nd Degree Heart Block:
Mobitz I vs II-- EKG Characteristics |
Mobitz I: Progressive lengthening of PR until beat is dropped (P wave not followed by QRS)
Usually asyx Mobitz II: Dropped beats not preceded by change in length of PR interval; can progress to 3rd degree heart block |
|
|
3rd Degree Heat Block:
EKG Characteristics |
Atria and ventricles beat independently of each other
Both P and QRS are present, although P waves bear NO RELATION to QRS complexes Usually treated with pacemaker; can by caused by Lyme dz |
|
|
How do you determine rate on EKG?
|
Count big boxes:
300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 |
|
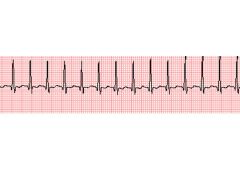
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
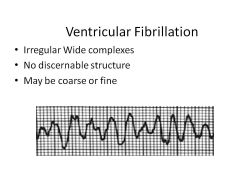
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
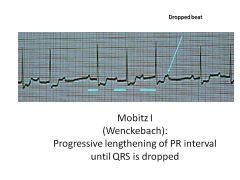
|
|
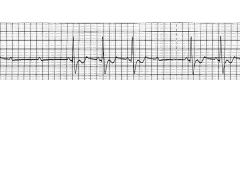
|

|
|
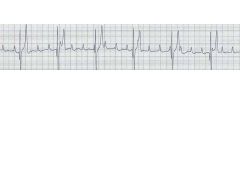
|

|
|
|
Describe the JGA response to low BP
Is this a long-term or short-term response? |
JG releases Renin
Renin converts angiotensinogen (from liver) to AgI ACE from lungs: Ag1-->Ag2 Ag2--> -vasoconstriction at vasc SM -adrenal production of aldosterone-->favorable gradient for Na+ and H2O reabsorption (retention) LONG TERM RESPONSE (takes a while to retain water and sodium) |
|
|
Baroreceptors:
Location Stimuli and Effects |
Located in carotid sinus (glossopharyngeal, responds to dec'd and inc'd BP) and aortic arch (vagus; detects inc'd BP only)
Baroreceptor: 1) Hypotn-->dec'd arterial pressure-->dec'd stretch-->dec'd afferent firing to medulla (via vagus) Results in inc'd efferent symp firing and dec'd efferent parasymp stimuln Results in vasoconstriction, inc'd HR, inc'd contractiliy, inc'd BP Important for response to hemorrhage! 2nd stimulus: Carotid massage-->inc'd pressure on carotid artery-->inc'd stretch-->inc'd afferent firing-->dec'd HR |
|
|
Chemoreceptors:
Location Stimuli and Effects |
Located in carotid sinus (glossopharyngeal, responds to dec'd and inc'd BP) and aortic arch (vagus; detects inc'd BP only)
1) Peripheral stimulus (detected by ABG)--carotid and aortic bodies respond to PO2 <60mmHg, inc'd PCO2, and dec'd pH of blood 2) Central stimulus--respond to changes in pH and PCO2 of brain interstitial fluid (influenced by arterial CO2). Doesn't directly respond to PO2. Inc'd intracranial pressure constricts arterioles-->cerebral ischemia-->HTN (symp response)-->reflex bradycardia and respiratory depression |
|
|
Pulmonary Cap Wedge Pressure:
Approximates what? Example of an abnormal finding |
Measures LA pressure
If PCWP>LV diastolic pressure-->Mitral stenosis |
|
|
Describe how the following factors affect the Starling forces of fluid movement through capillaries.
Heart failure Liver failure Infections and toxins Lymphatic blockage |
Heart failure: build up of fluid (?) osmotic pressure??
Liver failure: dec'd oncotic pressure due to lack of proteins Infections, Toxins: Increase cap perm Lymphatic blockage:: protein retention in capillaries, draw fluid in (nonpitting edema) |
|
|
What are the two different types of second degree AV block and how do they differ?
|
Mobitz 1: progressive prolonged PR intervals, dropped beat
Mobitz 2: Dropped beat without progressive elongation of PR interval |
|
|
What are normal BPs in the right and left ventricles?
|
RV:
Systolic <25, diastolic<5 LV: Systolic <130, diastolic <10 |
|
|
What substances act on smooth muscle myosin light-chain kinase?
How does this affect blood pressure? |
CCBs
Epinephrine at beta-2 receptors PGE2 All will relax vascular SM |
|
|
Describe the chain of events by which hypotension causes a reflex tachycardia.
|
Carotid sinus senses low BP (aortic arch doesn't sense despression)
Results in less stimuln of baroreceptor at carotid sinus Less stimuln of glossopharyngeal nerve Glossoph signals to solitary tract of medulla, resulting in dec'd inhibition of sympathetic output; less excitation of psymp Results in reflex tach |
|
|
What is pre-hypertension?
|
BP >130/85
|
|
|
Leading cause of HTN.
|
Primary causes (essential--familial); related to inc'd CO and inc'd TPR
|
|
|
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy:
Cause Associated heart sound Effects |
Caused by chronic HTN
Requires more oxygen, becomes stiffened S4 heart sound LV can't fill as well (les volume bc thickened muscle takes up space) Can lead to MI |
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Paroxysms of increased sympathetic tone Anxiety Palpitations Diaphoresis |
Pheochromocytoma
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Age of onset between 20 and 50 |
Primary or essential HTN
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Elevated serum Cr Abnormal urinalysis |
HTN due to renal dz
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Abdominal bruit |
Renal artery stenosis
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
BP in arms>legs |
Coarctation of aorta
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Family history of HTN |
Primary or essential HTN
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Tachycardia Heat intolerance Diarrhea |
Hyperthy
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Hyperkalemia |
renal failure
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Episodic sweating and tachycardia |
pheo
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Abrupt onset in patient younger than 20 or older than 50 Suppressed serum K+ levels |
Hyperaldosteronism
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Central obesity Moon facies Hirsutism |
Cushing's
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Normal urinalysis Normal serum K+ |
Primary or essential HTN
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Young individual with acute onset tachycardia |
Stimulant abuse: coke, amphetamines
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Hypokalemia |
Hyperaldost or Renal Artery Stenosis
|
|
|
Cause of HTN:
Proteinuria |
Renal Dz
|
|
|
Essential HTN:
Treatment |
First line:
HCTZ or thiazide (retain Ca2+, can redue risk of osteoporosis, prevents calcium renal stones) Or ACE-i |
|
|
CHF:
Treatment |
Loop diuretics (lose Ca2+, inc'd Ca2+ in urine): Furosemide
ACE-inhibitor, aldosterone antagonist, beta-blockeres (if compensated) |
|
|
DM HTN:
Treatment |
ACE-i or ARB
CCB Diuretics, beta-blockers BUT CAN MASK SIGNS OF HYPOGLYCEMIA |
|
|
Hydralazine:
MOA Use |
Inc'd cGMP-->SM relaxation
Vasodilation of arterioles > veins Afterload reduction Use: Severe HTN, HTN crisis, safe in pregnancy |
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drugs are safe in pregnancy?
|
Hydralazine
Nifedipine Labetalol Methyldopa |
|
|
Dihydropyridine CCBs:
Examples Use How do they differ from verapamil? |
-dipines (nifedipine, amlodipine, etc)
Act like nitrates; dilate veins, dec'd preload verapamil does not do this! Used in HTN, angina, |
|
|
Which calcium channel blockers act at vascular smooth muscle?
|
Nifedipine>Diltiazem>Verapamil
|
|
|
Which calcium channel blockers act at the heart?
|
Verapamil > diltiazem > nifedipine
|
|
|
Nitroglycerin:
MOA Other drugs with same MOA Use |
Vasodilate by releasing NO in smooth muscle, causing inc'd cGMP and SM relaxation
Dilate veins >> arteries; dec preload Other drugs: isosorbide, dinitrate Use in angina |
|
|
Nitroprusside:
MOA AE Use |
Short acting inc cGMP via direct release of NO for both veins and arteries
Can cause cyanide toxicity Use in malignant HTN |
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
First dose orthostatic hypotension |
alpha-1 blockers (zosin)
|
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Ototoxic, especially with aminoglycosides |
Loop diuretics
|
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Hypertrichosis |
Minoxidil--Rogaine
|
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Cyanide toxicity |
Nitroprusside
|
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Dry mouth, sedation, severe rebound HTN |
Clonidine
|
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Bradycardia Impotence Asthma exacerbation |
beta-blockers
|
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Reflex tachycardia |
nitrates
hydralazine dihydropyridine CCBs Anything that vasodilates! |
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Cough |
ACE-i (excess bradykinin)
|
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Avoid in patients with sulfa allergy |
Loop and thiazide diuretics are actually sulfa drugs
|
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Possible angioedema |
ACE-i (bradykinin)
angioedema = swollen face; lips to larynx |
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Possible development of drug-induced lupus |
Hydralazine
|
|
|
Which anti-hypertensive drug:
Hypercalcemia, hypokalemia |
Thiazide (HCTZ)
|
|
|
Which antihypertensives are safe for use in pregnancy?
|
Methyldopa
Labetalol Hydralazine Nifedipine |
|
|
While on an ACE inhibitor, a patient develops a cough.
What is a good replacement drug and why doesn't it have the same side effects? |
ARB (sartan)
Not inhibiting enzyme, they're inhibiting receptor; bradykinin is broken down |

