![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Streak ovaries
Congenital heart disease Horseshoe kidney |
Turner Syndrome (XO, short stature, webbed neck, lymphedema)
|
|
|
Sudden swollen/painful big toe joint
Tophi |
Gout/podagra (hyperuricemia)
|
|
|
Swollen gums
Mucous bleeding Poor wound healing Spots on skin |
Scurvy--vitamin C deficiency (can't hydroxylate proline/lysine for collagen synthesis)
|
|
|
Swollen, hard, painful finger joints
|
Osteoarthritis (osteophytes on PIP--Bouchard's nodes; DIP--Heberden's nodes)
|
|
|
Systolic ejection murmur
|
Aortic Valve Stenosis
|
|
|
Thyroid and parathyroid tumors
Pheochromocytoma |
MEN2A
|
|
|
Toe extension/fanning upon plantar scrape
|
Babinski's sign (UMN lesion)
|
|
|
Unilateral facial drooping involving forehead
|
Bell's palsy (LMN CN VII palsy)
|
|
|
Urethritis
Conjunctivitis Arthritis in a male |
Reiter's syndrome (reactive arthritis assocd w/HLA-B27)
Can't pee, can't see, can't climb a tree |
|
|
Vascular birthmark--port-wine stain
|
Hemangioma (benign, but assocd w/Sturge-Weber syndrome)
|
|
|
Vasculitis from exposure to endotoxin causing glomerular thrombosis
|
Shwartzman reaction following second exposure to endotoxin
|
|
|
Vomiting blood following esophagogastric lacerations
|
Mallory-Weiss syndrome--alcholic and bulimic pts
|
|
|
Waxy casts with very low urine flow
|
Chronic end stage renal dz
|
|
|
WBC casts in urine
|
Acute pyelonephritis
|
|
|
Weight loss
Diarrhea Arthritis Fever Adenopathy |
Whipple's dz (Tropheryma whippelii)
|
|
|
Worst headache of my life
|
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
|
|

Label all critical structures.
|

|
|
|
Pineal gland:
Role |
Makes melatonin
Regulates circadian rhythm |
|
|
Superior colliculi:
Role |
Conjugate vertical gaze (your eyes are above your ears)
|
|
|
Inferior colliculi:
Role |
Auditory (your eyes are above your ears)
|
|
|
What is Parinaude syndrome? Cause?
|
Paralysis of conjugate vertical gaze due to lesion in superior colliculi (pinealoma)
|
|

|

|
|

|
Langhnans' Giant cell (TB)
|
|
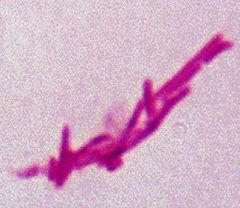
|
Acid fast stain--TB
|
|

|
Miliary TB--hematogenous spread
|
|
|
Primary tubcerculosis:
Who does it affect? Effects? |
Primary TB affects nonimmune host--usually child
Effects: Hilar node calcification Ghon focus (calcified scars of lower lobes) If both-->Ghon complex This can then lead to: -Healing by fibrosis, immunity, and PPD poz -Progressive lung dz (HIV) -Severe bacteremia-->miliary TB -Dormancy |
|
|
Secondary tuberculosis:
Who does it affect? When does it arise? |
Affects partially immune hypersensitized host (adult)
Reactivates-->fibrocaseous cavitary lesion (upper lobes) |
|
|
PPD + vs PPD -
(Interpretations) |
PPD +: current infection, past exposure, BCG vaccinated
PPD -: no infection, anergic (can't mount immune response--steroids, malnutrition, immunocomp'd) |
|
|
What is Pott's disease?
|
Tb involvement of vertebral bodies
|
|
|
What is a Ghon complex?
Primary or secondary Tb? |
Primary Tb exposure--
Chon complex = Ghon focus (lower lobe calcifications) + lobar/Hilar LN involvement |
|
|
Leprosy:
AKA Bacterial name Treatment Lepromatous vs Tuberculoid |
Leprosy = Hansen's Dz
Acid-fast!! M. leprae Tx: Long-term oral dapsone Lepromatous = diffuse skin involvement, communicable (weak T-cell immunity) Tuberculoid: Hypoesthetic skin nodules (intact T cell response) LEpromatous is LEthal |
|
|
Water contaminated with animal urine
|
Leptospira
Hantavirus |
|
|
Lyme Disease:
Bacteria Reservoirs Treatment Presentation |
Borrelia burgdorferi
Mice = impt reservoir; deer required for tick life cycle Tx: Doxycycline (early Lyme), ceftriaxone (late Lyme) Presentation: Bake a Key Lyme Pie Bilateral Bell's palsy Arthritis Kardiac block Erythema migrans |
|
|
Syphilis:
Bacteria Treatment Stages (1-3) |
Treponema pallidum (spirochete)
Tx: PCN G Stage 1: painless chancre Stage 2: Constitutional Syx, rash on PALMS AND SOLES; condyloma lata, shiny bald spot Stage 3: tabes dorsalis--Neurosyphilis (dorsal columns obliterated) GUMMA (chronic granulomas) |
|
|
What bacteria make up the spirochetes?
Characteristic features? |
Spiral-shaped bacteria with axial filaments
BLT: Borrelia (Lyme) Leptospira Treponema (Syphilis) |
|
|
Positive Romberg
Broad-based ataxia |
No proprioceptive info-->neurosyphilis (tertiary)
|
|
|
Anterior bowing of tibia
Flattened nasal bridge Frontal bossing Blood-tinged nasal secretions |
Congenital syphilis (newborn)
|
|
|
Testing for syphilis.
|
Screen: VDRL
Confirm: FTA-Abs |
|
|
Causes of VDRL False positives
|
Viruses (mono, hepatitis)
Drugs Rheumatic Fever Lupus, Leprosy |
|
|
What is a clue cell?
|
Vaginal epithelial cell covered w/bacteria
|
|

|
Granulated-looking cell = Clue Cell; sign of bacterial vaginosis (overgrowth of bacteria)
|
|
|
Gardnerella vaginalis:
Method of spread Presentation Treatment |
Can be sexual, but not STI
FISHY SMELL Clue Cells Tx w/metronidazole |
|
|
Rickettsiae:
Diseases Presentation Treatment |
Coxsackie
Rocky Mtn Spotted Fever Presentation: classic triad--HA, fever, rash (vasculitis) Tx: Doxycyline |
|
|
Rickettsia rickettsii vs Rickettsia typhi:
Presentation |
Rickettsia on wRists (rash)
Typhus on Trunk (rash) |
|
|
Q fever:
Cause Presentation Treatment |
Coxiella burnetti (atypical rickettsia transmitted by aerosol)
NO rash, no vector, negative Weil-Felix. Tx: Doxycyline |
|
|
Weil-Felix Reaction:
Utility |
When pt serum mixed with Proteus antigens, antirickettsial Abs cross-react to Proteus O Ag's and agglutinate
EXCEPTION = COXIELLA |
|
|
Pneumonia
Bird owner |
Chlamydia psittaci (avian reservoir)
|
|
|
Chlamydia:
Treatment |
doxycyline
|
|
|
Bacterial cause of ectopic pregnancy.
How? |
Chlamydia--causes scarring of fallopian tubes; egg doesn't make it to uterus
|
|
|
What is walking pneumonia?
How does it present? |
Walking pneumonia = atypical pneumonia
Insidious onset HA Nonproductive cough Diffuse interstitial infiltrate--x-ray looks worse than patient |
|
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae:
Presentation Lab tests Treatment |
Walking pneumonia
COld agglutinins (IgM) Tx: Tetracycline, erythromycin |
|
|
What oragnisms can be treated with tetracyclines?
|
VACUUM the BedRoom
Vibrio cholera Acne Chlamydia Ureoplasma urealyticum Mycoplasma pneumonia Tularemia H pylori Borrelia burgdorferi Rickettsia |
|
|
Which Rickettsial sp has properties unique from other Rickettsial organisms?
What are those unique properties? |
Coxielle burnetii
Negative Weil-Felix Aerosol transmission (instead of lice, ticks, fleas) Endospore NO RASH |
|
|
What infections are caused by Chlamydia?
Treatment? |
C. psittaci--birds
C. pneumoniae--walking pneumonia C. trachomatis--Pelvic inflamm dz, neonatal conjunctivitis Tx: Erythromycin or macrolides |
|
|
Which mycobacteria sp:
Leprosy |
M. leprae
|
|
|
Which mycobacteria sp:
Pulmonary TB-like symptoms in COPD pts |
M. knasasii
|
|
|
Which mycobacteria sp:
Cervical lymphadenitis in children |
M. scrofulaceum
|
|
|
Which mycobacteria sp:
Disseminated disease in AIDS pts |
M. avium intracellulare/complex (MAI, MAC)
|
|
|
Which mycobacteria sp:
Hand infection in aquarium |
M. marinum
|
|
|
What is the Rickettsial triad of symptoms?
|
HA
Fever Rash |
|
|
25 year-old with mycoplasma atypical pneumonia exhibits anemia due to cryoagglutinins.
What type of immunoglobulins are responsible for the anemia? |
IgM
|
|
|
Homeless alcoholic patient vomited while intoxicated and subsequently developed foul-smelling sputum.
Organism causing infection? |
Klebsiella
Anaerobic pneumonia |
|
|
Antibiotic for:
Mycoplasma pneumoniae |
Tetracyline or erytrhomycin
|
|
|
Antibiotic for:
Rocky Mtn Spotted Fever |
Tetracycline
|
|
|
Antibiotic for:
Early Lyme Dz |
Doxycycline
|
|
|
Antibiotic for:
Late Lyme Dz |
Ceftriaxone
|
|
|
Antibiotic for:
Syphilis |
PCN G
|
|
|
Antibiotic for:
Leprosy |
Daponse
|
|
|
Antibiotic for:
Bacterial vaginosis |
Metronidazole
|
|
|
Ethambutol:
Use Side Effects |
Part of tx for M. tuberculosis
AE: E for Eye-->optic neuritis |
|
|
What drug cocktail is used in treatment of tuberculosis?
|
RIPE for Tx:
Rifampin INH Pyrazinamide Ethambutol |
|
|
What is the only agent used as solo prophylaxis in TB?
|
INH
|
|
|
What antibiotic is used for prevention of MAI in AIDS patients?
When should prophylaxis begin? |
Azitrhomycin
|
|
|
Isoniazid:
MOA AEs |
Dec'd synthesis of mycolic acids; bacteria catalase-peroxidase needed to convert INH to active metabolite
AE: INH Injures Neurons and Hepatocytes (INH)--neuro and hepatotoxicity; Lupus Pyridoxine (vit B6) prevents neurotoxicity!! |
|
|
Drug-Induced Lupus:
Causes |
HIPP; it's not HIPP to have Lupus
Sulfonamides Hydralazine Isoniazid Procainamide Phenytoin |
|
|
Rifampin:
Uses |
M. tuberculosis
Meningococcal prophylaxis Chemoprophylaxis in contacts of children w/H. flu B |
|
|
What are the R's of rifampin?
|
RNA polymerase inhibitor
Revs up P450 Red/orange body fluids Rapid Resistance if used alone |
|
|
What drugs induce cytrochrome P450?
|
Quinidine
Barbiturates Phenytoin Rifampin Griseofulvin Carbamazepine |
|
|
What drugs inhibit cytochrome P450?
|
Protease Inhibitors
INH Cimetidine Ketoconazole Erythromycin Grapefruit Juice Sulfonamides |
|
|
Prophylaxis for:
Gonorrhea |
Ceftriaxone
|
|
|
Prophylaxis for:
Syphylis |
PCN G
|
|
|
Prophylaxis for:
Recurrent UTIs |
TMP-SMX
|
|
|
Prophylaxis for:
P. jiroveci pneumonia |
(PCP)
TMP-SMX |
|
|
Prophylaxis for:
Exposure to meningococcal meningitis |
PCN
|
|
|
Prophylaxis for:
Exposure to H. flu type-B meningitis |
Rifampin
|
|
|
Prophylaxis for:
Endocarditis prevention in patient with turbulent flow heart disease |
PCN
|
|
|
Which cell wall inhibitor:
Next step in treatment of otitis media if resistant to amoxicillin |
Amoxicillin w/Clavulanic acid
|
|
|
Which cell wall inhibitor:
Prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis |
PCN V
Amoxicillin, ampicillin, cefalexin |
|
|
Which cell wall inhibitor:
Increases nephrotoxicity |
Cephalosporins
|
|
|
Which cell wall inhibitor:
Sufficient for treatment of syphilis |
PCN G
|
|
|
Which cell wall inhibitor:
Single dose treatment for gonorrhea |
Ceftriaxone
|
|
|
Clinical uses:
1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th generation cephalosporins |
1st generation:
PEKC Proteus, E coli, klebsiella pneumonia, gram poz cocci 2nd gen: HEN PEK: H flu, Enterobacter, Neisseria Proteus, E coli, Klebsiella; and Gram poz cocci 3rd gen: Pseudomonas, neisseria (gram poz) 4th gen: gram poz and neg |
|
|
Clinical uses for macrolides
|
PUS
Pneumonias (atypical)--legionella, mycoplasma, chlamydia URIs--Strep throat (S pyogenes) STDs: Chlamydia, gonorrhea |
|
|
Side effects of aminoglycosides
|
NOT:
Nephrotoxicity Ototoxicity Teratogenic |
|
|
Drugs with photosensitivity reactions
|
SAT for photo:
Sulfonamide Amiodarone Tetracycline |
|
|
Drug class:
Minocycline |
Tetracycline
|
|
|
Drug class:
Gentamycin |
Aminoglycoside
|
|
|
Drug class:
Erythromycin |
Macrolide
|
|
|
Drug class:
Tobramycin |
Aminoglycoside
|
|
|
Drug class:
Azithromycin |
Macrolide
|
|
|
Drug class:
Doxycyline |
Tetracycline
|
|
|
Drug class:
Amikacin |
Aminoglycoside
|
|
|
Drug class:
Neomycin |
Aminoglycoside
|
|
|
Drug class:
Clarithromycin |
Macrolide
|
|
|
Drug class:
Clindamycin |
It's its own drug category!
|
|
|
Drug class:
Which drugs exhibit a disulfiram reaction? |
Inhibition of acetyl dehydrogenase (?);
Metronidazole Some cephalosporins Procarbazine 1st generation sulfonylureas Disulfiram |

