![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
PCN G vs PCN V
|
PCN V = oral
PCN G = IV |
|
|
|
PCN:
MOA Uses AE |
Binds pcn-binding protein
blocks cross-linking of cell wall (via blocking transpeptidases) Activates autolytic enzymes Use: -Gram poz organisms (S. pneumo, S. pyogenes, actinomyces, GBS; clostridium, listeria, bacillus) -Syphilis -Neisseria AE: Hypersens rxn |
|
|
|
Penicillinase:
AKA Activity Where is it produced? |
AKA beta-lactamase
PCNase breaks beta-lactam ring of PCNs Produced in periplasm of bacteria |
|
|
|
Which beta-lactam drugs are penicillinase resistant?
AE? |
Methicillin
Nafcillin Dicloxacillin AE: Hypersens rxns |
|
|
|
Staph aureus:
Treatment |
Nafcillin (naf for staph!)
|
|
|
|
What about MRSA makes it resistant to methicillin?
|
Altered PCN-binding protein target site
|
|
|
|
Clavulanic acid:
Drug Class Use |
beta-lactamase inhibitor
Combine with aminopenicillin (AMoxicillin; AMpicillin) |
|
|
|
Aminopenicillin vs PCN:
General |
Aminopenicillin is sensitive to PCNase (just like PCN), but has wider spectrum
Also can be combined with PCNase inhibitors |
|
|
|
Sulbactam:
Drug Class Use |
beta-lactamase inhibitor
Combine with aminoPCN |
|
|
|
Tazobactam:
Drug class Use |
beta-lactamase inhibitor
Combine with aminoPCN |
|
|
|
HELPS mnemonic
|
Ampicillin/amoxicillin HELPS kill enterococci.
H. flu E. coli Listeria Protes mirabilis Salmonella and Enterococci |
|
|
|
Most common cause of mononucleosis.
|
EBV
|
|
|
|
Most common cause of pseudomembranous colitis.
|
C. diff
|
|
|
|
What pencillins are antipseudomonals?
|
TCP: Tace Care of Pseudomonas
Ticarcillin Carbenicillin Pipieracillin Susceptible to PCNase! |
|
|
|
Cephalosporins:
MOA Examples by generation Uses |
MOA: Beta-lactm drugs that inhibit cell wall synthesis; less susceptible to PCNase
1st gen: Cephalexin Cefazolin 2nd Gen: Cefprozil Cefuroxime 3rd Gen: Cefdinir Ceftriaxone 4th Gen: Cefipime Uses: 1st gen: PEcK--Proteus mirabilis, E coli, Klebsiella 2nd gen: HEN PEcKS: H flu, Enterobacter aeorgenes, Neisseria, Proteus mirabilis, E Coli, Klebsiella, Serratia 3rd Gen***: Ceftriaxone: meningitis, gonorrhea |
|
|
|
What cephalosporin has the longest half-life?
|
Ceftriaxone--gonorrhea, meningitis
|
|
|
|
What is a disulfiram-like reaction?
What drugs cause this? |
Disulifram-like reaction:
Accumuln of aldehyde Results in flushing, sweating, nausea, HA, hypotn Drugs: Certain cephalosporins Metro 1st generation sulfonylureas Procarbazine |
|
|
|
Aztreonam:
Drug class Use |
Monobactam resistant to beta-lactamases
Inhibits cell wall synthesis Use on gram neg rods ONLY (E coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Serratia) |
|
|
|
Imipenem:
MOA Use |
Broad-spectrum, beta-lactamase resistant carbapenem.
ALWAYS administered w/cilastatin (inhibitor of renal dihydropeptidase I) to dec ianctivtn of drug in renal tubulrs Use: life-threatening infections (not sure of what cause is), or after failure of other drugs. |
|
|
|
Meropenem:
MOA Use |
Broad-spectrum, beta-lactamase resistant carbapenem.
Use: life-threatening infections (not sure of what cause is), or after failure of other drugs. Less seizure risk than imipenem |
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Causes red man syndrome |
Vanco
|
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Next step in tx of otitis media if resistant to amoxicillin |
Augmentin (amocillin and clavulanic acid) or
Cefdinir |
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis |
Aminopcns
First gen cephalosporinss |
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Increases nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides |
Cephalosporins
|
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Aminoglycoside pretender |
Aztreonam
|
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Inpatient treatment for MRSA |
Vanco
|
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Sufficient for treatment of syphilis |
PCN G (IV)
|
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Single doe treatment for gonorrhea |
Ceftriaxone
|
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Hospitalized patient with new gram poz cocci in clusters in blood |
Staph aureus!
Vanco |
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Treatment for C diff colitis |
Oral vanco
Metro |
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Broad spectrum coverage for appendicitis |
Meropenem
Impienem/cilastatin |
|
|
|
ID the drug:
Cell wall inhibitors effective against pseudomonas |
Cefepine (4th generation cephalosporin)
Ticarcillin Cerbenicillin Piperacillin |
|
|
|
Cilastatin:
MOA Use |
Inhibitor of renal dihydropeptidase I to dec inactivation of imipenem
|
|
|
|
Vancomycin:
MOA Use AEs |
Inhibits cell wall formation by binding D-ala D-ala of cell wall precursors.
Gram poz--serious multi-drug resistant organisms, including MRSA AEs: does N.O.T. have many problems: nephrotoxicity ototoxicity thrombophlebitis Diffuse flushing (red man syndrome)--can avoid by pretreat with histamine |
|
|
|
Draw gram negative algorithm.
|
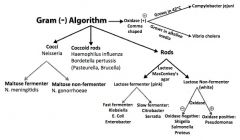
|
|
|
|
This agar tests for lactose fermentation.
Which bacteria are lactose fermenters? |
Lactose is KEE, test with MacConKEE's (maconKey's)
KEE'S: Klebsiella E coli Enterobacter Serratia |
|
|
|
Gram neg diplococci
|
Neisseria
|
|
|
|
Gram poz diplococci
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
|
Gram poz clusters
|
Staph aureus
|
|
|
|
Sexually active individual
Urethritis Arthritis |
Neisseria
|
|
|
|
Urethritis
Epididymitis or Cervicitis |
Neisseria gonorrhea or Chlamydia trachomatis
|
|
|
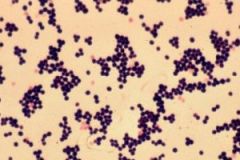
Identify bug.
|
Gram poz cluster;
Staph aureus |
|
|
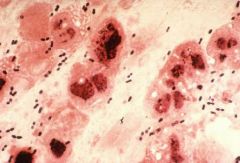
Identify bug.
|
Gram poz chain,
Strep pneumo |
|
|
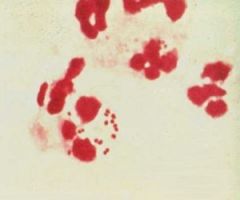
Identify bug.
|
Gram negative, diplococci;
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
|
|
|
Gonococci vs Meningococci:
Capsule Maltose fermentation Vaccine (yes/no) Transmission Effects |
Gonocci = gonorrhea
No polysaccharide capsule No maltose fermentation No vaccine (rapid Agenis variation of pilus prots) Sexually transmitted Causes gonorrhea, septic arthritis, neonatal conjunctivitis (all neonates must receive erythromycin eye drops) Meningococci: Polysacch capsule Maltose fermentation Vaccine present Resp and oral spread Causes meningococcemia, meningitis, Waterhouse-Fredrichsen syndrome Rifampin prophylaxis |
|
|
|
Pediatric epiglottitis:
Cause Management |
Cause: likely Haemophilus influenzae (which is NOT the flu!)
Don't do anything! Make child comfortable, because if child becomes upset, can lose airway. Have ability to rapidly intubate. |
|
|
|
H. influenza:
Growth requirements (agar) |
Chocolate agar
Factors V, X (when child has flu, mom goes to five and dime--V and X--to buy chocolate) |
|
|
|
Silver stain
|
Legionella
|
|
|
|
Infected water supply
|
Legionella
|
|
|
|
Legionella:
Growth requirements (agar) |
Think of a French legionnaire (soldier) with his silver helmet, sitting around a campfire (charcoal) with his iron dagger--he is no sissy (cysteine).
Grow on charcoal yeast extract with iron and cysteine. |
|
|
|
Cystic fibrosis
Pneumonia |
Pseudomonas
|
|
|
|
Pseudomonas:
Effects Aerobic/Anaerobic |
PSEUDO
Pneumonia (esp in cystic fibrosis) Sepsis (black lzns on skin) External otitis (swimmer's ear) UTI Drug Use and Diabetic Osteomyelitis AERuginosa: AERobic--water! Burn victims! |
|
|
|
Hot tub folliculitis
|
Pseudomonas
|
|
|
|
List the 4 types of E. coli, their toxins, mechanism, and presentation.
|
EIEC (invasive; dysentery--bloody diarrhea): shiga-like toxin invades intestinal mucosa-->necrosis and inflammn
ETEC: Traveler's diarrhea (watery): labile toxin/stable toxin; no inflammn/invasion EPEC: Pediatric diarrhea; no toxin, adheres to apical surface, flattens villi, prevents absorption EHEC: Dysentery, does not ferment sorbitol; Shiga-like toxin (necrosis/inflammn), hemolytic-uremic syndrome |
|
|
|
E. coli:
Treatment |
TMP-SMX
Fluoquinolones (-floxacin) |
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of gram negative sepsis?
|
E. coli
|
|
|
|
Protease spp.:
Effects |
UTI
Urease causes ammonium-magnesium-phosphate stones-->staghorn calculi |
|
|
|
Staghorn calculi
|
Protease spp. (maribilis, vulgarus)
|
|
|
|
Lobar pneumonia in alcoholics
|
Klebsiella (aspirated)
|
|
|
|
Klebsiella:
Effects |
4A's
Aspiration pneumonia Abscess in lungs Alcoholics di-A-betics |
|
|
|
4A's mnemonic
|
Effects of Klebsiella:
Aspiration pneumonia Alcoholics Abscesses in lungs di-A-betics |
|
|
|
Red currant jelly sputum
|
Klebsiella
|
|
|
|
Salmonella vs Shigella:
General Effects Transmission |
Both are non-lactose fermenters; both invade intestinal mucosa and cause bloody diarrhea
Salmonella: Salmon swim! Motile, flagellated Can cause typhoid fever (salmonella typhi) Transmitted via Food, Fingers, Feces, Flies Shigella: More virulent Causes dysentery--watery diarrhea followed by bloody diarrhea w/mucus |
|
|
|
Grows at 42°C
|
Campylobacter jejuni
Bloody diarrhea in children |
|
|
|
Rice water diarrhea
|
Vibrio cholerae
|
|
|
|
Bacteria that increases likelhood of cancer.
|
H pylori (lymphoma, adenocarcinoma)
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Cat scratch |
Bartonella
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Cat feces |
Toxoplasmosis
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Puppy feces |
Yersinia enterocolitica
|
|
|
|
Borrelia burgdorferi
|
Lyme dz from ticks that live on deer and mice
|
|
|
|
22-year old presents with burning feeling in gut after meals
Biopsy of gastric mucosa shows gram (-) rods What's the organism? |
H pylori
|
|
|
|
50-year old male smoker presents with new cough, flu-like symptoms
Gram stain of sputum shows no organism What's the organism? |
Legionella pneumophila
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Osteomyelitis in a patient with DM |
Pseudomonas
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Sepsis DIC Adrenal hemorrhage |
WF Syndrome; N. meningitidis sepsis
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
5 year old with pharyngitis Drooling X-ray revelas thumb sign |
H. flu type B (epiglottitis; not really seen anymore due to immunization)
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Osteomyelitis in patient with Sickle Cell |
Salmonella
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Aspiration pneumonia in alcoholic |
Klebsiella
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Child with new puppy develops severe abdominal pain |
Yersinia enterocolitica
|
|
|
|
What enzymes do obligate anaerobes lack?
|
Lack catalase and superoxide dismutase
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Burn wound infeciton |
Pseudomonas
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Motile, causes UTI |
Proteus mirabilis
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Traveler's diarrhea |
ETEC
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Life-threatening meningitis Purpura |
N. meningitidis
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Common cause of UTI and pneumonia |
Klebsiells pneumoniae
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Corneal infections in contact lens wearers |
Pseudomonas
|
|
|
|
ID the bug:
Septic arthritis in young, sexually active patients |
N. gonorrhoeae
|
|
|
|
40 year-old female
Acute unilateral knee pain Bilateral Bell's palsy |
Lyme Dz via Ixodes Tick caused by Borrelia
|
|
|
|
Treatment of N. gonorrhoeae.
|
Single dose ceftriaxone
|
|
|
|
Post-amoxicillin
Toxic megacolon Diarrhea |
C. diff overgrowth
|
|
|
|
Protein synthesis inhibitors:
MOA |
Target smaller bacterial ribosome (70S made of 30S and 50S subunits)--leaves human 80S ribosome unaffected
|
|
|
|
30S vs 50S inhibitors:
List Bacteriostatic/Bacteriocidal? |
Buy AT 30, CCELL (sell) at 50
30S inhibitors: Aminoglycosides (cidal) Tetracyclines (static) 50S: C: chloramphenicol, clindamycin (static) E: Erythromycin (static) L: Lincomycin (static) L: Linezolid (variable) |
|
|
|
Aminoglycosides:
MOA List Use |
MOA: cidal; inhibit formation of initiation complex and cause misreading of mRNA; require O2 for uptake so can't kill anaerobes
Aminoglycosides-->AMINO-->Mean GNATS canNOT kill anaerobes Gentamicin Neomycin Amikain Tobramycin Streptomycin Use: severe gram negative rods, and work synergistically w/beta-lactams |
|
|
|
These drugs are both ototoxic and nephrotoxic.
|
Aminoglycosides (-mycins)
Vancomycin Loop diuretics Cisplatin |
|
|
|
Tetracyclines:
MOA List Use |
Static--bind 30S, prevents attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA
DOn't take with milk, antacids, or iron-containing preparations (will block absorption in gut) Cyclines: tetracycline, doxycycline, demelocycline, minocycline Use: Borrelia burgdorferi, H pylori, M pneumoniae Rickettsia, Chlamydia |
|
|
|
This tetracycline is safe in those with renal failure. Why?
|
Doxycyline--because it's fecally eliminated
|
|
|
|
This drug causes a blue pigmentation of the skin.
|
Minocycline
|
|
|
|
What drugs are associated with photosensitivity reactions?
|
SAT for a photo
Sulfonamides Amiodarone Tetracyclines |
|
|
|
Macrolides:
MOA List Use |
Static; Inhibit protein synthesis by binding rRNA of 50S subunit
Erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin Use: Atypical pneumonias (mycoplasma, chlamydia, legionella), URIs, STDs (PUS) |
|
|
|
This drug prolongs QT interval.
|
Macrolides, esp erythromycin
|
|
|
|
Gray baby syndrome
|
Chloramphenicol
|
|
|
|
Chloramphenicol:
Uses AEs |
Meningitis: H flu, Neisseria, Strep pneumo
AEs: Dose-dependent anemia Dose-dependent aplastic anemia Gray baby syndrome (bc lack liver UDP-gluornyl transferase) |
|
|
|
Gray man syndrome
|
Amiodarone
|
|
|
|
Clindamycin:
Uses AEs |
Anaerobic infections--bacteroides, c. perfringens in aspiration pneumonia
AE: pseudomembranous colitis (C. diff overgrowth) |
|
|
|
Nitrofurantoin:
MOA Uses |
Bacteriocidal--inactivates bacterial ribosomes
Uses: UTI cystitis (not pyelonephritis) by E coli or Staph saprophyticus (not proteus) |
|
|
|
What organisms most commonly cause UTIs?
|
E coli***
Proteus miarbilis (staghorn calculi) Klebsiella pneumonia Staph saprophyticus |
|
|
|
Sulfonamides:
MOA List Uses |
Bacterial folic acid inhibitors (inhibit folic acid synthesis)
SMX, sulfasoxazole, sulfadiazine Uses: UTIs |
|
|
|
What drugs can cause Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
|
Seizure drugs (ethosuximide, carbamazepine, phneobarbital, phenytoin)
Sulfa drugs PCN drugs Allopurinol |
|
|
|
TMP-SMX:
AEs |
These drugs both work by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis, however, there is also some inhibition of host folic acid synthesis-->megaloblastic anemia (tx: folic acid supplementation)
Oh, and don't forget SULFA allergies. |
|
|
|
Patients with sulfa allergies should not take _________.
|
Thiazide diuretics
Acetazolamide Furosemide Celecoxib Probenecid |
|
|
|
Fluroquinolones:
MOA List AEs |
MOA: inhibits DNA gyrase; CIDAL. don't take antacids
-floxacins AE: Tendonitis and tendon rupture "fluoroquinoLONES hurt attachments to your BONES" |
|
|
|
Metronidazole:
MOA Uses AE |
MOA: forms free radical toxic metabs in bact cells that damage DNA. CIDAL
Get gap on the METRO Giardia Entamoeba Trichomonas Gardenella Anaerobes (bacteroides, clostridium) H. pylori Disulifram-like reaciton! |
|
|
|
What drugs treat anaerobic infections?
|
Metro
Clindamycin Imipenem/cilastatin Meropenem |
|
|
|
This drug acts like a detergent and disrupts bacterial cell membranes.
|
Detergents get MIXed
Polymyxin |
|
|
|
What drugs are effective against pseudomonas?
|
Polymyxins
Fluorquinolones Cefepime Aztreonam Aminoglycosides Extended-spectrum PCNs (Pipercillins) |
|

