![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Type 1 Hypersens:
Describe Examples Diagnostics |
Free Ag crosslinks IgE on mast cells and basophils
Triggers release of histamine-->inc'd vasc perm, tissue edema WHEAL & FLARE Anaphylaxis Takes 15 mins Test = scratch test |
|
|
Type 2 Hypersens
Describe Examples Diagnostics |
Ab's against self-->macs will start eating away
Mac-mediated tissue damage Complement Nphils Test: Coombs Ex: Hemolytic anemia (Ab mediated, pernicious anemia, erythroblastosis fetalis, Graves' Dz, Myasthenia gravis |
|
|
Type 3 Hypersens
Describe Examples Diagnostics |
Ab's against Ag's; Ab-Ag complex gets deposited in tissues
Mac-mediated tissue damage Ex: Serum sickness SLE RA Arthus rxn (swelling and inflammn following tetanus vaccine)--takes 5-12 hours, not 15 mins like Type 1 |
|
|
Type 4 Hypersens
Describe Examples Diagnostics |
Sensitized T-cell causes mac activation
4th = last, thus delayed reaction Takes 24-48 hours! T lymphocytes Transplant rejections TB skin tests Touching (contact dermatitis--poison ivy, oak, nickel, belt buckle) Ex: Type 1 DM MS Guillain-Barre Hashimoto's thyroiditis Graft vs Host PPD |
|
|
Erythroblastosis fetalis:
Pathophys Treatment Presentation of neonate |
Maternal Abs (Rh-D) to fetal RBC Ag
In Rh(-) mom (lack Rh-D) will develop Rh-D when exposed to baby with RhD (but won't attack until second pregnancy with RhD positive baby) Tx: Rhogam (Anti-RhD Immunoglobulin) at 28 weeks, any traumatic event (MCA), and within 3rd week of delivery Neonate presents with: -Hemolytic anemia due to maternal Ab -Jaundice (possible kernicterus) -Hydrops fetalis -IU death Note: mom can also be exposed to RhD during miscarriage/abortion |
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis |
III
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Asthma |
I
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Rheumatic Fever |
II
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Tb skin test |
IV
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Hay fever |
I
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Polyarteritis nodosa |
III
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Serum sickness |
III
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
ABO blood type incompatibility |
II
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Poison ivy |
IV
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Eczema |
I
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Contact dermatitis |
IV
|
|
|
Type of hypersens rxn:
Goodpasture's Syndrome |
II (anti-Glomerular BM Ab's)
|
|
|
Anti-nuclear Ab
|
SLE
Nonspecific! Sjogren's RA Juvenile arthritis |
|
|
Andi-dsDNA Ab
|
SLE (specific)
|
|
|
Anti-smith Ab
|
SLE (specific)
|
|
|
Antihistone Ab
|
Drug-induced lupus
|
|
|
Anti-IgG Ab
|
Scleroderma (RA)
Anti-IgG = Rheumatoid Factor; note: this is IgM attacking IgG |
|
|
Anticentromere Ab
|
CREST Scleroderma
C for CREST and centromere |
|
|
Anti-Scl-70 Ab
|
Scleroderma (diffuse)
ANti-Scl-70 = anti-DNA topoisomerase I |
|
|
Anti-DNA topoisomerase I Ab
|
Diffuse scleroderma
|
|
|
Antimitochondrial Ab
|
Primary biliary cirrhosis
|
|
|
Antigliadin Ab
|
Celiac dz
|
|
|
Anti-basement membrane Ab
|
Goodpasture's Syndrome
|
|
|
Anti-desmoglein Ab
|
Pemphigus vulgaris
|
|
|
Anti-microsomal Ab
|
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
|
|
|
Antithyroglobulin Ab
|
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
|
|
|
Anti-Jo-1 Ab
|
Polymyositis
Dermatomyositis |
|
|
Anti-SS-A Ab
|
Sjogren's
SS-A = Anti-Ro |
|
|
Anti-SS-B Ab
|
Sjogren's
SS-B = anti-La |
|
|
Anti-U1 RNP Ab
|
Mixed connective tissue dz
|
|
|
Anti-smooth muscle Ab
|
Autoimmune hepatitis
|
|
|
Anti-glutamate decarboxylase Ab
|
Type 1 DM
|
|
|
c-ANCA Ab
|
Wegener's granulomatosis
Microscopic polyangitis Churg Strauss Syndrome ANCA = anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody |
|
|
p-ANCA
|
Other vasculitides
|
|
|
MPO-ANCA
|
Pauci-immune crescentic glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
Anti-TSH receptor Ab
|
Graves'
|
|
|
Anti-ACh receptor Ab
|
Myasthenia Gravis
|
|
|
What processes elevate ESR?
|
Polymyalgia rheumatic
Temporal arteritis Disease activity in RA, SLE Infection, inflammation (osteomyelitis) Malignancy Never diagnostic of anything! |
|
|
Which complement is responsible for neutrophil chemotaxis?
|
C5a
|
|
|
Bruton's Agammaglobulinemia:
Describe |
B for boys (X-liniked)
B cell deficiency-->defective tyrosine kinase Low levels of all Igs Recurrent Bacterial infections after 6 months (once passive immunity wears off) |
|
|
Thymic Aplasia:
Describe |
AKA DiGeorge
Failure of 3rd, 4th pouches to develop No thymus-->No T cells No PTH-->low Ca2+-->tetany Congenital defects in heart/great vessels Recurrent viral, fungal, protozoal infections Tap cheek: (Chvostek's sign) and spasms Trousseau's sign (where tighten BP cuff and get carpal spasm) |
|
|
22q11 deletion
|
90% of DiGeorge (detect with FISH)
|
|
|
Severe combined immunodeficiency:
Describe |
Defect in early stem cell diff
Gene defects result in adenosine deaminase deficiency Last defense is NKCs Presentation: 1)Severe recurrent infections -Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis -Fatal or recurren RSV, VZV, HSV, measles, flu, parainfluenza, PCP pneumonia 2) Chronic diarrhea 3) Failure to thrive (no thymic shadow on newborn CXR) |
|
|
No thymic shadow on newborn CXR
|
DiGeorge
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency |
|
|
Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis:
Describe |
T cell dysfn against Candida albicans
Tx: ketoconazole |
|
|
Which immunodeficiencies are X-linked?
|
WBC
Wiskott-Aldrich Bruton's Agammaglobulinemia Chronic Granulomatous Dz (+/- doesn't have to be X-linked) Hyper-iGM syndrome (3 types)--high IgM, low Ig's: If X-linked-->No CD-ligand If AR-->no CD40 |
|
|
Wiskott-Aldrich Immunodeficiency:
Describe |
WAITER
Wiskott Aldrich Immunodeficiency Thrombocytopenia (and purpura) Eczema Recurrent pyogenic infections No IgM against capsular polysaccharides of bacteria Low IgM, high IgA X-linked |
|
|
Truncal Eczema
|
Wiskott Aldrich (WAITER)
|
|
|
Ataxia-telangectasia:
Describe |
IgA deficiency
cerebellar Ataxia Poor smooth pursuit if moving target w/eyes Telangiectasias of face Inc'd risk of lymphoma, leukemia Radiation sensitivity Age of death ~25 alpha-fetoprotein usually elevated beyond 8 months (can be helpful with diagnosis) |
|
|
IgA deficiency:
Describe |
Most appear healthy
Sinus and lung infections 1/600 European descent have this Assocd w/atopy (eczema), asthma Possible anaphylaxis to blood transfusions and blood products!! |
|
|
Nitroblue tetrazolium dye test
|
Chronic granulomatous dz
Phagocytes will engulf dye and will not be able to oxidize (no yellow to blue oxidation; will stay yellow) |
|
|
Chronic granulomatous disease:
Tx |
Prophylactic TMP-SMX
|
|
|
Defective LYST gene
|
LYST = lysosomal transport
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome |
|
|
Job Syndrome:
Pathophys Presentation |
Hyper-IgE syndrome
Deficiency of IFN-gamma-->nphils fail to respond to C5a, LTB4 Leads to high levels of IgE and ephils Triad: Eczema Recurrent cold (staph aureus abscesses--think of biblical Job with boils)--not warm bc not generating inflammatory response Frontal bossing, deep set eyes, doughy skin 2 rows of front teeth (retain primary teeth) |
|
|
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency syndrome:
Pathophys |
Abnormal integrins-->inability of phagocytes to exit circulation
Delayed separation of umbilicus |
|
|
Young child presents with tetany from hypocalcemia and candidiasis from immunosuppression.
|
DiGeorge
T cell deficiency |
|
|
Young child has recurrent lung infections and granulomatous lesions.
|
Chronic Granulomatous Dz
Deficiency of NADPH oxidase |
|
|
2 year-old child presents with multiple viral and fungal infections. Found to be hypocalcemic.
|
DiGeorge
|
|
|
Child has immune disorder with repeated Staph abscesses. IFN-gamma fails to mobilize neutrophils.
|
Job's Syndrome (Hyper IgE)
|
|
|
This embryonic germ cell gives rise to the thymus.
|
Endoderm
|
|
|
Define syngeneic graft.
|
Graft from twin or clone
|
|
|
Define allograft.
|
Graft from nonidentical individual of same species
|
|
|
Define xenograft.
|
Graft from different species
|
|
|
Hyperacute transplant rejection:
What is it? When does it occur? |
TYpe II hypersens rxn (Ab mediated) due to presence of preformed antidonor Abs in transplant recipient.
Occurs w/in minutes after transplanation. Occludes graft vessels-->ischemia, necrosis |
|
|
Acute transplant rejection:
What is it? When does it occur? |
Cell mediated due to cytotoxic T cells reacting x foreing MHCs.
Occurs weeks after transplantation. Tx w/immunosuppressant (cyclosporine and OKT3) |
|
|
Chronic transplant rejection:
What is it? When does it occur? |
T-cell and Ab-mediated vascular damage (obliterative vascular fibrosis)
Months to years post-transplantation. irreversible. Class I-MHC non-self perceived by CTLs as class I-MHC self presenting non-self antigen. |
|
|
Graft-vs-Host Disease:
What is it? Presentation? |
Grafted immunocompetent T cells proliferate in irradiated immunocomp'd host and reject cells w/foreign proteins-->severe organ dysfn
Syx: Maculopapular rash Jaundice HSM Diarrhea Usually in BM and liver transplant |
|
|
Cytokine which:
Promotes B cell growth, differentiation |
IL-4,5
|
|
|
Cytokine which:
Produced by Th1 cells |
IL-2, IFN-gamma
|
|
|
Cytokine which:
Produced by Th2 cells |
IL-4,5,10
|
|
|
Cytokine which:
Secreted by T helper cells and activates macs |
IFN-gamma
|
|
|
Cytokine which:
Pyogens secreted by by monocytes and macs |
IL-1,6, TNF-alpha
|
|
|
Cytokine which:
Enhances synthesis of IgE and IgG |
IL-4
|
|
|
Cytokine which:
Enhances synthesis of IgA |
IL-5
|
|
|
Cytokine which:
Released by virally infected cells |
IFN-alpha, beta
|
|
|
Patient suffers from recurrent Neisseria infections:
Relevant complement proteins |
Can't make MAC so C5-9 deficiency
|
|
|
45-year old female complains of malar rash and arthritis:
Relevant antibodies |
Anti-dsDNA, Anti-Sm
ANA too but non-specific |
|
|
After BM transplantation, patient suffers from dermatitis, enteritis, hepatitis.
|
Graft vs Host Dz
|
|
|
Infant with failure to thrive
HSM Neurodegeneration |
Niemann-Pick (genetic sphingomyelinase deficiency)
Cherry red spots on macula |
|
|
Infant with hypoglycemia
Failure to thrive Hepatomegaly |
Cori's dz (debranching enzyme deficiency)
Glycogen in the liver can't undergo glycogenolysis |
|
|
Infant with microcephaly
Rocker-bottom feet Clenched hands Structural heart defect |
Edwards' Syndrome (Trisomy 18)
|
|
|
Jaundice
RUQ pain Fever |
Charcot's triad (ascending cholangitis)
|
|
|
Keratin pearls on skin biopsy
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
Large rash with bull's eye appearance
|
Erythema migrans from ixodes tick bite (Lyme dz: Borrelia)
|
|
|
Lucid interval after traumatic brain injury
|
Epidural hematoma (middle meningeal artery rupture)
"hit with a softball, knocked out, were lucid, and passed out again" |
|
|
Male child
Recurrent infecitons No mature B cells |
Bruton's dz (x-linked agammaglobulinemia)
|
|
|
Mucosal bleeding
Prolonged bleeding time |
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia (defect in platelet agg due to lack of GpIIb/IIIa)
|
|
|
Multiple colon polps
Osteomas/soft tissue tumors Impacted/supernumerary teeth |
Gardner's syndrome (subtype of FAP)
Garden of excess tissue! |
|
|
Necrotizing vasculitis (lungs)
Necrotizing glomerulonephritis |
Wegener's (c-ANCA poz)
Goodpasture's (anti-BM ab's) |
|
|
Neonate with arm paralysis following difficult birth
|
Erb-Duchenne palsy (superior trunk--C5-C6--brachial plexus injury)-->waiter's tip
|
|
|
No lactation postpartum
Absent menstruation Cold intolerance |
Sheehan's syndrome (pituitary infarct)
|
|
|
Nystagmus
Intention tremor Scanning speech Bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia |
MS
|
|
|
Oscillating slow/fast breathing
|
Cheyne-Stokes respirations (central apnea in CHF or inc'd intracranial pressure)
|
|
|
Painful blue fingers/toes
Hemolytic anemia |
Cold agglutinin dz (autoimmune hemolytic anemia caused by mycoplasma pneumoniae, infections mononucleosis, EBV)
IgM Ab's precipitating together-->thrombosis-->hemolytic anemia |
|
|
Painful, pale, cold fingers/toes
|
Raynaud's syndrome (vasospasm in extremities)
|
|
|
Painful, raised red lesions on palms and soles
|
Osler's node (infective endocarditis)
|
|
|
Painless erythematous lesions on palms and soles
|
Janeway lesions (infective endocarditis)
|
|
|
Painless jaundice
|
Cancer of pancreatic head obstructing bile duct
|
|
|
Palpable purpura
Joint pain Abdominal pain (child) |
Henoch-Schonlein purpura (IgA vasculitis affecting skin and kidneys)
|
|
|
Pancreatic, pituitary, parathyroid tumors
|
Wermer's syndrome (MEN I)
|
|
|
Polyostic fibrous dysplasia
Precocious puberty Cafe au lait spots Short stature |
McCune Albright
|
|
|
Draw brachial plexus.
Label nerves, innervations, and effects of injury. |
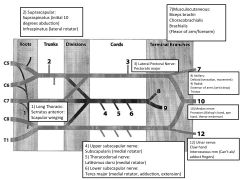
|

