![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
210 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
WBC differential from highest to lowest.
|
NLMEB
Nphils Lymphocytes Monocytes Ephils Bhpils |
|
|
Spectrin:
Role |
Allow for biconcave shape of RBCs
|
|
|
What is the source of energy for RBCs?
|
Glucose and only glucose.
|
|
|
Anisocytosis vs Poikilocytosis
|
Anisocytosis = varying sizes
Poikilocytosis = varying shapes |
|
|
What are causes of polycythemia?
|
Renal Cell Carcinoma
HCC Pheochromocytoma Hemangioblastoma Chronic hypoxia (COPD, high altitude, obstructive sleep apnea) Down Syndrome (65% at birth) Polycythemia vera (excess RBCs despite low EPO) |
|
|
What is the lifespan of platelets?
Where are they stored? |
PLT lifespan = 8-10 days
Stored in spleen |
|
|
This cell mediates type I hypersensitivity reactions.
|
Mast cells
|
|
|
Cromolyn:
MOA Use |
Prevents mast cell degeneration; used to tx asthma
|
|
|
What are the causes of eosinophilia?
|
D NAAACP
Drugs Neoplasm Allargy, Asthma (Churg-Straus) Addison's (adrenal insuff) AIN Collagen vasc dz Parasites (Loeffler's ephilic pneumonitis due to Ascaris lumbricoides) |
|
|
Type of phagocyte in:
Brain Liver Joints |
Brain-microglia
Liver-Kupffer cell Joints-A cells |
|
|
B cells:
CD Markers Role |
CD19, CD20
When antigen encountered, diff into plasma cells and produce antibodies. Exhibit memory. Can function as APC via MHC II |
|
|
What organelle is most prominent in plasma cells?
Why? |
Plasma cell needs to make a lot of protein which is to be exported (immunoglobulins), therefore, has abundant RER.
|
|
|
T lymphocytes:
CD Markers |
Th: CD3, CD4
Tc: CD3, CD8 |
|
|
What clotting factor initiates the extrinsic pathway?
|
VII
|
|
|
What clotting factor initiates the intrinsic pathway?
|
XII
|
|
|
Which coagulation pathway forms kallikrein and bradykinin?
|
Intrinsic PW (XII)
|
|
|
Hemophilia A vs B:
General |
Hemophilia A: Ate--Eight--deficiency in VIII
Hemophilia B: Benign--Nine--deficiency in IX |
|
|
What is the effect of IV citrate on cogaulation?
|
IV citrate = calcium binder
Calcium is essential to coagulation Dec'd available Ca2+-->Dec'd coaguln |
|
|
What is the role of antithrombin?
AKA? |
Antithrombin = Factor IIIa (activated)
Factor III inhibits thrombin (factor IIa), IX, X, XI, XII |
|
|
What is the result of a vitamin K deficiency on coagulation factors?
|
Dec'd synthesis of factors II, VII, IX, X, Protein C, protein S
|
|
|
Heparin:
MOA Use AE Antitode |
Cofactor for activation of antithrombin (IIIa); decreases thrombin, and Xa (short half-life)
Use: Immediate anticaoag for PE, stroke, acute coronary syndrome, MI, DVT Safe in pregnancy AE: HIT, osteoporosis Antidote: Protamine sulfate (positively charged molecule that will bind negatively charged heparin) |
|
|
Enoxaparin:
Drug Class MOA Use AE |
LMW Heparin; acts more on Xa; better avaoilability and longer half-life
RIsk HIT, not easily reversible |
|
|
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia:
Pathophys Tx |
Heparin binds PLT factor IV-->leads to Ab production-->activates PLTs leading to their clearance and resulting in thrombocytopenic, hypercoag state (it's paradoxical)
Tx: Lepirudin or bivalirudin in addition to warfarin |
|
|
Leiprudin:
MOA Use |
Directly inhibit thrombin; used as alternative to heparing for anticoagulating pts with HIT
|
|
|
Warfarin:
MOA Use Labs to monitor it AE Antidote |
Interferes with synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX, X, protein C, protein S (DiSCo started in 1972--10(X),9(IX),7(VII),2(II))
Has effect on extrinsic PW, increasing PT (WEPT); use INR to standardize PT values AE: TERATOGEN, bleeding Antidote: IV Vitamin K, fresh frozen plasma |
|
|
What are the effects of bradykinin?
|
Inc'd vasodilation
Inc'd perm Inc'd pain Angioedema--swelling from lips to larynx (DANGEROUS) |
|
|
What thrombogenic factors are located inside vascular endothelial cells?
|
vWF
Thromboplastin tPA PGl2 |
|
|
vWF:
Cells that synthesize it Functions Signs of deficiency |
Made by endothelial cells and megakaryocytes
Fn: Complexes with and stabilizes Factor VIII (deficiency-->inc'd PTT) PLT adhesion to vessel wall and to other platelets (deficiency-->Inc'd bleeding time) |
|
|
Describe the steps required to achieve platelet adhesion and aggregation.
Begin with endothelial cell damage. |
Endothelial cell damage-->Release vWF-->binds exposed collagen
vWF binds GpIb on PLT (adhesion of PLT) PLT is activated and now secretes ADP, PDGF, thromboxane A2 (vasoconstriction, PLT agg), Calcium (for coag pw), and thrombin (fibrinogen-->fibrin) Aggregation of PLT via GpIIb/IIIa |
|
|
How exactly does ASA affect the coagulation cascade?
|
Inhibit COX-->dec'd TXA2 synthesis and thus dec'd PLT aggregation
|
|
|
What is the effect of clopidogrel on the coagulation cascade?
What other drug has this same effect? |
Clopidogrel and ticlopidine:
Irreversibly inhibit ADP receptors required to insert GpIIb/IIIa receptor into PLT cell membrane (thus, dec'd agg) |
|
|
What is the effect of abciximab on the coagulation cascade?
|
Abciximab directly inhibit GbIIb/IIIa to dec PLT agg
|
|
|
What allows RBCs to change shape as they pass through vessels?
|
Spectrin
|
|
|
What are some of the different causes of polycythemia?
|
Excess EPO:
-RCC -Pheo -Hemangioblastoma -Chronix hypoxia (COPD, OSA) Polycythemia vera Down Syndrome |
|
|
What coagulation factor is deficient in hemophilia A?
|
VIII
|
|
|
What coagulation factor is deficient in hemophilia B?
|
IX
|
|
|
What clotting factors require vitamin K for synthesis?
|
X, IX, VII, II
C, S DiSCo started in 1972 |
|
|
What are the treatments for overdose of heparin and warfarin?
|
Heparin--protamine sulfate
Warfarin--FFP, vitamin K |
|
|
What lab value is used to monitor the following medications: heparin, warfarin, enoxaparin?
|
Heparin: PTT
Warfarin: PT/INR Enoxaparin: Xa |
|
|
What is the treatment for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
|
Lepirudin or bivalirudin
|
|
|
Schistocyte vs Spherocyte::
Appearance Cause |
Schistocyte: helmet cell; seen in DIC, TTP/HUS, traumatic hemolysis
Spherocyte = round; hereditary spherocytosis, autoimmune hemolysis |
|
|
Which RBC form:
Lead poisoning |
Basophilic stippling
|
|
|
Which RBC form:
G6PD deficiency |
Heinz bodies, bite cells
|
|
|
Which RBC form:
DIC |
Schistocyte (helmet cell)
|
|
|
Which RBC form:
Abetalipoproteinemia |
Acanthocytes (spur cell)--also seen in liver dz (acantho = spiny)
|
|
|
Which RBC form:
Asplenia |
Howell-Jolly BOies
|
|
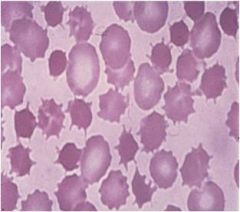
|
acanthocyte (spur cell): seen in liver dz, abetalipoproteinemia
|
|
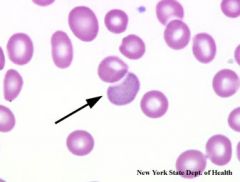
|
Basophilic stippling--Baste the ox TAIL
Thalassemias Anemia of chronid dz Iron def Lead poisoning |
|
|
Hb C vs Hb S:
Structure |
Hb C: alpha2-beta2; glu-->lys in beta chain
Hb S: alpha2-beta2: glu-->val in beta chain |
|
|
Hg Bart vs Hb H:
Structure |
Hg Bart: gamm-4; no alpha chains (severe alpha-thal)
Hb H: beta-4; no alpha chains (severe alpha-thal) |
|
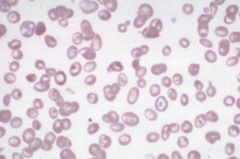
|
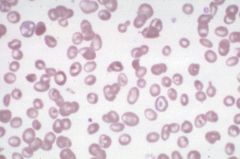
Target cells--due to increase in SA:V ratio from Fe def anemia (dec'd cell volume) or in obstructive liver dz (inc'd cell membrane)
|
|
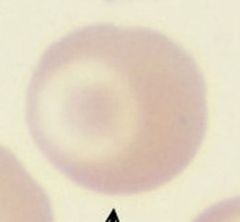
|
Target cell
|
|
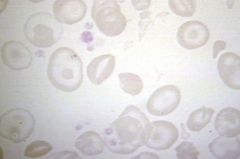
|
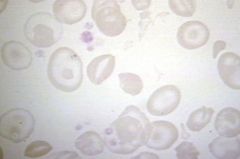
Thalassemia major--blood disorder caused by defect in beta-chain synthesis in Hgb. Note presence of target cells.
|
|
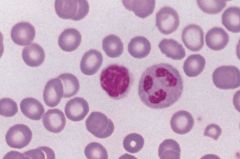
|
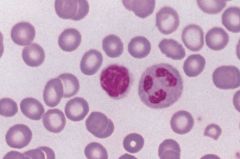
Fe def anemia; microcytosis and hypochromia can be seen
|
|
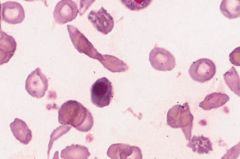
|
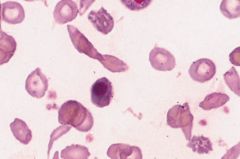
Sickle cell anemia--note sickled cells as well as anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, and nucleated RBCs
|
|
|
alpha-thalassemia:
Subtypes |
–a–aa: silent carrier
– – -aa: alpha-thalasssemia trait – – - –a: HbH – – - – –: Hydrops fetalis (Hb Barts) |
|
|
beta-thalasemia:
Subtypes |
-b: beta-thal minor; usually asyx
- -: beta-thal major; severe anemia requiring blood transfusion (worry about secondary hemochromatosis), skeletal deformities |
|
|
Lead poisoning:
Affected enzyme Presentation Treatment |
Affected enzyme: Ferrochelatase, ALA dehydratase (aminolevulinic acid = ALA)
Microcytic anemia, GI and kidney dz, lead lines on gingivae and on epiphyses of long bones on x-ray Basophilic stippling Wrist, foot drop Children-->MR Adults-->HA, memory loss, demyelination Tx: Sucks to be a kid with lead poisoning-->Succimer Adults-->Dimercaprol and EDTA |
|
|
Sideroblastic anemia:
Pathophys Treatment |
Defect in heme synthesis due to X-linked defect in aminolevulinic acid synthase gene
Tx: pyridoxine (B6 tx) Presents with ringed sideroblasts (with iron-laden mitochondria) |
|
|
Transferrin:
Role |
Transports iron in blood
|
|
|
Ferritin:
Role |
Stored form of iron
|
|
|
Iron deficiency anemia vs Anemia of chronic disease:
Serum Fe TIBC Ferritin Fe/TIBC |
Iron def anemia
Fe: low TIBC: high Ferritin: low Fe/TIBC: low low Anemia of chronic dz: Fe: low TIBC: low Ferritin: high (elevated in infections) Fe/TIBC: normal or high |
|
|
Hemochromatosis:
Serum Fe TIBC/Transferrin Ferritin Fe/TIBC |
Serum Fe: high
TIBC/Transferrin: low Ferritin: high Fe/TIBC: high high |
|
|
Pregnancy/OCP:
TIBC/transferrin Fe/TIBC |
TIBC/transferrin high (dec'd transferrin)
Fe/TIBC low |
|
|
Lead poisoning:
Serum Fe TIBC/Transferrin Fe/TIBC |
Lead takes up iron's spot in heme synthesis so:
Serum Fe: high TIBC/Transferrin: low Fe/TIBC: high |
|
|
Folate deficiency:
Findings Causes |
Hyperseg'd nphils
Glossitis Inc'd homocysteine, nl MMA Causes: EtOH (malnutrition), malabsorption, impaired metabolism (MTX, trimethroprim), inc'd requirement (hemolytic anemia, pregnancy) |
|
|
B12 deficiency:
Findings Cause |
Hyperseg'd nphils, glossitis, elevated homocysteine, ELEVATED MMA (methylmalonic acid)
Causes: Insufficient intake (strict vegans) Malabs (Crohn's dz) Pernicious anemia Diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm) NEURO SYX (B12 needed for FA synth--think myelin): Peripheral neuropathy with sensorimotor dysfn Posterior columns (vibration/proprioception) Lateral corticospinal (spasticity) Dementia |
|
|
Normocytic, normochromic anemia:
Intravascular vs Extravascular causes |
Intravascular:
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria Autoimmune hemolytic anemia Mechanical destruction (aortic stenosis, prosthetic valves) Extravascular: Hereditary spherocytosis G6PD def Pyruvate kinase def Sickle Cell HgC defect |
|
|
Nonhemolytic, normocytic anemia:
Causes |
Anemia of chronic dz
Aplastic anemia (destruction of myeloid cells) Kidney dz (low EPO) |
|
|
Anemia of chronic disease:
Pathophys |
Inflammn-->inc'd hepcidin-->dec'd release of Fe from macs
Dec'd iron, dec'd TIBC, dec'd ferritin Can become microcytic, hypochromic in long-standing dz |
|
|
Aplastic anemia:
Findings |
Pancytopenia characterized by severe anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia
Normal cell morphology, but hypocellular bone marrow with fatty infiltration Can be due to: radiation, drugs, alkylating agents, parvovirus, EBV, HIV, HCV, immune mediated; stem cell defect |
|
|
What are the causes of megaloblastic anemia?
|
MAPLE
MTX AZT Phenytoin Liver Dz Ethanol |
|
|
G6PD Deficiency:
Pathophys |
X-linked
Defect in G6PD-->dec'd glutathione-->inc'd RBC susceptibility to oxidant stress |
|
|
What are the complications of Sickle Cell Disease?
|
-Aplastic crisis (due to parvovirus B19 infection)
-Autosplenectomy-->inc'd risk infection w/encapsulated organisms; functional splenic dysfn occurs in early childhood -Salmonella osteomyelitis -Pain crisis (vaso-occlusive) -Renal papillary necrosis (due to low O2 in papilla) and microhematuria (medullary infarcts) Splenic sequestration crisis (infarcts) |
|
|
Cause of anemia:
Microcytic anemia + swallowing difficulty + glossitis |
Plummer-Vinson Syndrome (which is assocd w/Fe def anemia)
|
|
|
Cause of anemia:
Microcytic anemia + > 3.5% HbA2 |
beta-thal minor
|
|
|
Cause of anemia:
Megaloblastic anemia not correctable by B 12 or folate |
Orotic aciduria
|
|
|
Cause of anemia:
Megaloblastic anemia along with peripheral neuropathy |
B12 def
|
|
|
Cause of anemia:
Microcytic anemia + basophilic stippling |
Lead poisoning
|
|
|
Cause of anemia:
Microcytic anemia reversible with B6 |
Sideroblastic anemia
|
|
|
Cause of anemia:
HIV positive patient with macrocytic anemia |
Zidovudine
|
|
|
Cause of anemia:
Normocytic anemia + red urine in the morning |
Paroxymal Nocturnal hemoglobinuria
|
|
|
Cause of anemia:
Normocytic anemia and elevated creatinine |
Chronic kidney dz resulting in low EPO levels
|
|
|
Cold agglutinins:
Pathophys Causes |
Cold ice cream? MMMMMM
Nearly always IgM; antibodies against RBCs interact at low temp (4ºC): IgM-->RBC antigen-->compliment fixation-->MAC lysis Occurs with Mycoplasma pneumoniae, EBV, some malignancies |
|
|
Warm agglutinins:
Pathophys Causes |
Warm weather is GGGreat
Antibodies react against RBC antigens at body temp, nearly always IgG Seen in: Viruses--EBV, HIV SLE Malignancies (CLL, NHL) Congenital Immune Abnlts |
|
|
Direct vs Indirect Coomb's:
General Uses |
Direct Coomb's (DAT):
Prepared Ab's added to pt's washed RBC to detect presence of immunogllobulins already present on RBC (+) in Hemolytic Dz of Newborn, Drug-induced hemolytic anemia, Hemolytic transfusion rxns Indirect Coomb's: Pt's serum incubated w/normal RBC to detect presence of Ab's (+) when ab's present to foreign blood (used to test blood prior to transfusion), screening for maternal Ab's to a fetus' blood |
|
|
Microangiopathic anemia:
Pathophys Findings |
RBCs damaged when passing thorugh obstructed or narrowed vessel lumina
Seen in DIC, SLE, malignant HTN, TTP Schistocytes seen on blood smea due to mechanical destruction of RBCs |
|
|
Macroangiopathic anemia:
Pathophys |
Prosthetic heart valves and aortic stenosis cause hemolytic anemia 2º to mechanical destruction
|
|
|
What is the rate-limiting step of heme?
|
aminolevulinic acid synthase (Glycine + succinyl-CoA-->aminolevulinic acid)
|
|
|
Acute intermittent porphyria:
Presentation Affected enzyme Accumulated substrate |
Painful abdomen with normal CT (due to neuro dysfn)
Port wine urine Polyneuropathy Psych disturbances Precipitated by drugs Acute: think acute abdomen (pain) and acute psychoses Affects Porphobilinogen deaminse (uroporphyrinogen-I-synthase)-->results in porphobilinogen, ALA, uroporphyrin buildup in urine |
|
|
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda:
Presentation Affected enzyme Accumulated substrate |
Blistering cutaneous photosensitivity; most common porphyria
Also associated with hypertrichosis, facial hyperpigmentation, elevated LFTs, HCV, EtOH Enzyme affected: uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase Buildup of uroporphyrin in urine |
|
|
Hemophilia A/B:
Effect on bleed time Presentation |
Both will increase PTT; PT will be normal because hemophilia only affects INTRINSIC PW
Presents with hemarthroses, easy bruising |
|
|
Vitamin K deficiency:
Effect on bleed time Presentation |
Inc'd PT and PTT (general coagulation effect--both extrinsic and intrinsic pw's)
|
|
|
Platelet disorders:
General presentation |
Microhemorrhage-->mucous membrane bleeding, epistaxis, petechiae, purpura, dec'd platelet count
|
|
|
Bernard-Soulier Disease:
Effect on platelet count Effect on bleed time Pathophys |
Dec'd PC
Inc'd BT Dec'd GpIb-->defect in platelet-to-collagen adhesion; can't form platelet plug |
|
|
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia:
Effect on platelet count Effect on bleed time Pathophys |
Normal PC (no thrombocytopenia)
Inc'd BT Dec'd GpIIb/IIIa-->defect in platelet-to-platelet aggregation; defect in PLT plug formation Blood smear shows no platelet clumping |
|
|
Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura:
Effect on platelet count Effect on bleed time Pathophys Treatment |
Dec'd PC
Inc'd BT anti-GpIIb/IIIa Ab's-->peripheral platelet destruction-->dec'd PLT survival Inc'd # megakaryocytes Tx: Steroids |
|
|
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura:
Effect on platelet count Effect on bleed time Pathophys |
Dec'd PC
Inc'd BT Deficiency of ADAMTS13 (vWF metalloprotease)-->dec'd degradation of vWF multimers Large vWF multimers-->inc'd platelet agg and thrombosis Labs: schistocytes, inc'd LDH Neuro and renal syx, fever, low PLT, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia |
|
|
vonWillebrand's disease:
Effect on platelet count Effect on bleed time Effect on PT/PTT Pathophys |
Normal PC, elevated BT, normal PT
Dec'd vWF-->nromal or elevated PTT 9depends on severity; vWF carries/protects factor VIII) Leads to defect in intrinsic PW coag, defect in PLT plug formation (no platelet-to-collagen adhesion) Mild but common |
|
|
DIC:
Effect on platelet count Effect on bleed time Effect on PT/PTT Pathophys Labs |
Dec'd PC
Inc'd BT Inc'd PT/PTT Widespread activation of clotting-->deficiency in clotting factors-->bleed state Causes: STOP Making New Thrombi: Sepsis, Trauma, Ob complications, Pancreatitis, Malignancy, Nephrotic syndrome, Transfusion Labs: schistocytes, inc'd fibrin split products (D-dimers), dec'd fibrinogen, dec'd FV, FVIII |
|
|
What is the rate-limiting step in heme synthesis?
|
ALA synthase (aminolevulate)
|
|
|
What is the cause of ITP?
|
Anti GpIIb/IIIa-ab's-->PLT destruction
|
|
|
What is the defect in Bernard-Soulier disease?
|
Def of GpIb
|
|
|
What is the most common inherited bleeding disorder?
|
vW Dz
|
|
|
What are some of the hereditary syndromes of thrombosis?
|
Factor V Leiden mutation
Prothrombin gene mutation Antithrombin III def Prot C def Prot S def |
|
|
Hematologic tests/findings:
Ham's test |
Used to dx Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
|
|
|
Hematologic tests/findings:
DEB test |
Used to dx Fanconi's anemia
|
|
|
Hematologic tests/findings:
Heinz bodies |
G6PD def
|
|
|
Hematologic tests/findings:
D-dimers |
Fibrin degradation products seen in DIC (or big clot like emboli, DVTs)
|
|
|
Hematologic tests/findings:
Basophilic stippling |
BASt the ox TAIL
Thal Anemia of chronic dz Iron def anemia Lead poisoning |
|
|
Hematologic tests/findings:
Osmotic fragility test |
Used to dx hereditary spherocytosis
|
|
|
Hematologic tests/findings:
(+) ristocetin test |
Used to dx von Willebrand's Dz
|
|
|
Leukemia vs Lymphoma:
General |
Leukemia--lymphoid neoplasms w/widespread involvement of BM. Tumor cells found in peripheral blood
Lymphoma--discrete tumor masses arising from LNs Presentation often blur definitions |
|
|
Hodgkin's Lymphoma:
Key Finding Nodal Involvement (Pattern) Presentation Associated Virus |
Presence of Reed-Sternberg cells = HALLMARK
Lozalized, single group of nodes involved; contiguous spread B symptoms--fever, night sweats, weight loss 50% cases a/w EBV |
|
|
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma:
Nodal Involvement (Pattern) Presentation Associated Virus |
May be associated with HIV, immunosuppression
Multiple, peripheral nodes; extranodal involvement common, NONCONTIGUOUS SPREAD Peak incidence 20-40 |
|
|
Nodular sclerosing lymphoma:
Hodgkin's/Non-Hodgnkin's Prognosis |
Most common HODGKIN'S lymphoma; excellent prognosis bc has high lymphocyte and low R-S cells
|
|
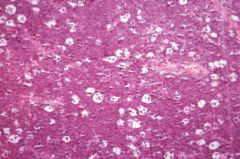
|
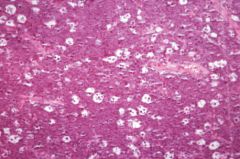
Burkitt's lymphoma--starry sky appearance from macrophage ingestion of tumor cells
|
|
|
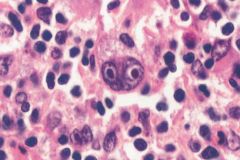
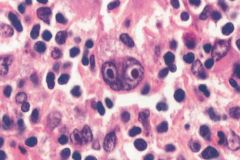
Hodgkin's Disease (Reed-Sternberg cells)--binucleate RS cells displaying prominent inclusion-like nucleoli surrounded by lymphocytes and other reacting inflammatory cells. RS cell is necessary but insufficient pathologic finding for diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease.
|
|
|
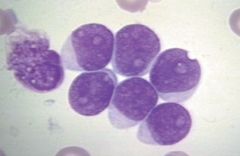
Acute lymphocytic leukemia--affects children less than 10 years of age
|
|
|
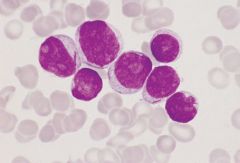
Acute myelocytic leukemia with Auer rods (long arrow); affects adolescents to young adults, but most commonly diagnosed in older adults.
|
|
|
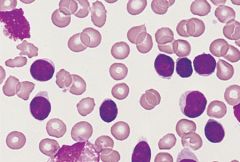
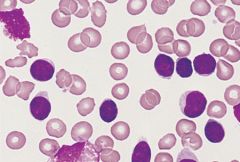
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia--lymphocytes are excessively fragile and are easily destroyed during slide preparation, forming "smudge cells". Affects individuals older than 60 years of age.
|
|
|
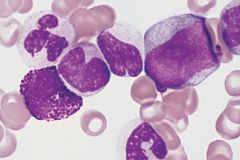
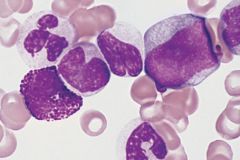
Chronic myeloid leukemia: promyelocytes and myelocytes seen adacent to a vascular structure. Affects individuals from 30 to 60 years of age.
|
|
|
Burkitt's lymphoma;
Genetics Histologic appearance Virus association |
t(8;14) c-myc gene
Starry sky appearance Associated with EBV |
|
|
t(11;14)
|
Mantle cell lymphoma
|
|
|
CD5+ Lymphoma
|
Mantle cell lymphoma
|
|
|
t(14;18)
|
Follicular lymphoma
|
|
|
bcl-2 expression
|
Follicular lymphoma
|
|
|
Acute vs Chronic Leukemia:
General |
Acute:
Rapid onset, rapidly progressive Over 50% myeloblasts (AML) or lymphoblasts (ALL) in BM Numerous blast cells in smear (>20%) Often a/w pancytopenia Chronic leukemia: Insidious onset, gradual progression Mature cells (<5% blasts) Can be either CML or CLL A/w HSM and LAD |
|
|
ALL:
Characteristics |
Bone pain common
Good prognosis in children PAS(+) (periodic acid-schiff stain) |
|
|
AML:
Characteristics |
AUER RODS
CD13/33+ PAS(-) Median age of onset is 50 |
|
|
CLL:
Characteristics |
Adults over 50
B cell markers (CD19/20?) SMUDGE CELLS |
|
|
CML:
Characteristics |
80% progress to AML
Adults 25-60 PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME (t9;22) ALWAYS PRESENT |
|
|
Multiple Myeloma:
Pathophys Presentation |
Monoclonal plasma cell cancer (fried egg appearance) that arises in marrow and produces large amounts of IgG (55%) or IgA
CRAB presentation: hyperCa2+ Renal insuff Anemia Bone lytic lesions/Back pain |
|
|
Why does multiple myeloma exhibit a protein spike?
|
Multiple Myeloma results in overproduction of a single antibody form a plasma cell; so will see an M protein spike when graphing out subunits of Ig's (gamma subunit)
|
|
|
Rouleaux formation:
What is it? a/w? |
Stacked poker chip formation of RBCs
Seen in multiple myeloma |
|
|
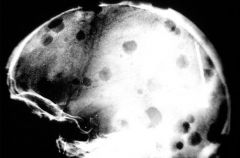
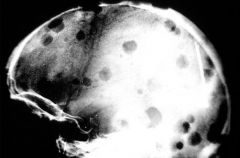
Multiple Myeloma--classic bone lytic lesions
|
|
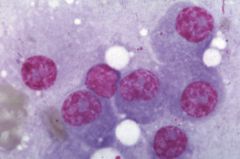
|
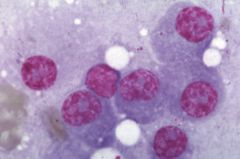
Multiple myeloma--abundance of plasma cells. RBCs will often be seen in rouleaux formation, stacked like poker chips.
|
|
|
Why does multiple myeloma cause hypercalcemia?
|
Make cytokines that build oblasts, stimulate oclasts.
|
|
|
What is a leukemoid reaction?
|
Often confused w/leukemia; inc'd WBC count with left shift (e.g., 80% bands) and inc'd leukocyte alk phos, usually due to infection.
|
|
|
Which chronic myeloproliferative disorder is Philadelphia chromosome positive?
|
CML
|
|
|
Which chronic myeloproliferative disorder is JAK2 mutation positive?
|
Polycythemia vera
Essential thrombocytosis Myelofibrosis (CML is only negative) |
|
|
Polycythemia vera:
What is it? Presentation |
Abnl clone of hematopoietic stem cells increasingly sensitive to growth factors
Erythrocytosis despite low EPO Results in HA, HSM, hyperviscosity |
|
|
Essential thrombocytosis:
What is it? |
Production of PLT despite low thrombopoietin levels
|
|
|
Myelofibrosis:
What is it? |
Fibrotic obliteration of bone marrow
See tear drop cells (bone marrow is crying because it's fibrosed :( ) |
|
|
Teardrop cells
|
Myelofibrosis
|
|
|
What is the role of JAK2?
|
Plays role in hematopoietic GF signaling
|
|
|
Most common leukemia in children
|
"ALL"
|
|
|
Most common leukemia in adults in US
|
"CLL"
|
|
|
Most common lymphoma in US
|
"Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma"
|
|
|
Reed-Sternberg cells
|
"Hodgkin's lymphoma"
|
|
|
AML a/w Down syndrome
|
"M7AML"
|
|
|
Leukemia with more mature cells and less than 5% blasts
|
"Chronic leukemia"
|
|
|
AML that are CD13 and CD33 (+)
|
"M0-M6AML"
|
|
|
Particularly a/w EBV
|
"Burkitt's and Hodgkin's Lymphomas"
|
|
|
Characteristic Auer rods
|
"AML (particularly M2 and M3)"
|
|
|
A/w long term celiac disease
|
"Intestinal T Cell Lymphoma"
|
|
|
Greater than 20% blasts in marrow
|
"Acute leukemia"
|
|
|
Myelodysplastic syndromes have a tendency to progress to ________
|
"AML"
|
|
|
Myeloproliferative disorders may progress to _________
|
AML
|
|
|
AML that is CD 41 and CD 61 (+)
|
"M7AML"
|
|
|
PAS(+) acute leukemia
|
"ALL"
|
|
|
Commonly presents with bone pain
|
ALL
|
|
|
Viscous blood, headache, plethora, splenomegaly, and low erythropoietin
|
"Polycythemia vera"
|
|
|
Leukemia equivalent of Burkett's lymphoma
|
"L3 or B variant ALL"
|
|
|
Lymphoma equivalent of CLL
|
Small lymphocytic lymphoma
|
|
|
Numerous basophils, splenomegaly, and negative for leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP)
|
"CML"
|
|
|
Most common neonatal leukemia
|
M7AML
|
|
|
Always positive for the Philadelphia chromosome (t9;22)
|
CML
|
|
|
Only AML that is CD 13 and CD 33 (-)
|
M7 AML
|
|
|
"Starry-sky pattern" due to phagocytosis of apoptotic tumor cells
|
Burkitt's lymphoma
|
|
|
Always associated with the BCR-ABL genes
|
CML
|
|
|
A/w Sjogren syndrome, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and H. pylori
|
Marginal cell MALToma
|
|
|
Acute leukemia positive for peroxidase
|
AML
|
|
|
Solid sheets of lymphoblasts in marrow
|
ALL
|
|
|
PAS(-) acute leukemia
|
AML
|
|
|
Compare the age distribution of those affected by Hodgkin's lymphoma to those affected by non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
|
HL: bimodal, young and old
NHL: 20-40 (fills gap) |
|
|
What is the most common type of NHL in adults?
In children? |
Adults: Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Children: Lymphoblastic lymphoma |
|
|
What lab findings are indicative of disseminated intravascular coagulation?
|
Elevated PT/INR
Elevated PTT Eleveated BT Dec'd PLT Elevated D-dimer |
|
|
What is the structure of HbH?
What disease results in its production? |
4 beta subunits
alphta-thal |
|
|
What is the structure of Hb Barts?
What disease results in its production? |
4 gamma subunits
hydrops fetalis |
|
|
Hematologic disease:
(+)Ham's test |
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
|
|
|
Hematologic disease:
Heinz bodies |
G5PD def
|
|
|
Hematologic disease:
Basophilic stippling |
Pb poisoning
|
|
|
Hematologic disease:
(+)osmotic fragility test |
Hereditary spherocytosis
|
|
|
Hematologic disease:
(+)DEB test |
Fanconi's anemia
|
|
|
Hematologic disease:
D-dimers |
DIC
|
|
|
Hematologic disease:
Coomb's (+) |
Used to ID autoimmune hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
Hematologic disease:
Coomb's (-) |
Used to ID non-autoimmune hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
Hematologic disease:
( +) ristocetin test |
vW Dz
|
|
|
What are the causes of aplastic anemia?
|
Radiation, Benzene, EBV, Fanconi's anemia, etc.
|
|
|
A patient develops hypercalcemia from the most common primary tumor arising within bones in adults.
What lab findings you expect in this patient? |
Multiple myeloma
Expect: monoclonal Ab spike Punched out lytic bone lesions Bence-Jones proteins in urine Rouleaux formation on blood smear |
|
|
What findings are a/w hereditary spherocytosis?
|
Poz osmotic fragility test
Coombs' neg Pigmented gallstones Splenomegaly Anemia Jaundice |
|
|
What lab findings allow you to distinguish iron deficiency anemia from a microcytic, hypochromic anemia resulting from thalassemia?
|
Fe def:
Dec'd Serum Fe Inc'd TIBC Dec'd Ferritin NO TARGET CELLS Thal: Nl Fe Nl TIBC Nl Ferritin TARGET CELLS PRESENT |
|
|
A child anemic since birth now has been cured with splenectomy.
What is the disease? |
Hereditary spherocytosis
|
|
|
A patient with anemia, hypercalcemia, and bone pain receives a bone marrow biopsy which reveals plasma cells (large, round, off-center nucleus).
What is the diagnosis and what would you expect to see on urinalysis? |
Multiple myeloma
Won't see anything on U/A, need UPEP (electrophoresis for your pee) to see Bence-Jones Proteins |
|
|
What neoplasms are a/w AIDS?
|
Kaposi's
Invasive squamous cell cancer CNS lymphoma NHL |
|
|
A heart failure patient is newly diagnosed with cancer and is being evaluated for chemotherapy.
Which chemotherapeutic agent should be avoided in this pt? |
Doxorubicin or Daunorubicin--cardiotoxicity!
|
|
|
Chromosomal analysis of a leukemia patient reveals the presence of the Philadelphia chromosome t(9;22).
What is the treatment? |
Imatinib
|
|
|
After a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery, the new mom bleeds profusely from her vagina and later from her gums.
What abnormal lab values would you suspect? |
DIC probably to amniotic fluid embolism!
Inc'd BT Inc'd PT, PTT Dec'd PLT Inc'd D-Dimer |
|
|
A 11 year-old child presents with a chronic non healing ulcer on his foot and imaging shows a small calcified spleen.
What drug can improve his symptoms? |
This is sickle cell; tx w/hydroxyurea to create HgF to better carry O2 to tissues
|
|
|
NSAIDs inhibit the production of which substance important in platelet aggregation?
|
Thromboxane
|
|
|
Does HbF have more or less affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate?
|
Less affinity
|
|
|
MOA:
Streptokinase |
Converts plasminogen to plasmin
|
|
|
MOA:
ASA |
Irreversible COX-1 inhibitor
|
|
|
MOA:
Clopidogrel |
blocks ADP receptors
|
|
|
MOA:
Abciximab |
Binds GpIIb/IIIa
|
|
|
MOA:
Tirofiban |
Binds GpIIb/IIIa
|
|
|
MOA:
Ticlopidine |
Blocks ADP receptors
|
|
|
MOA:
Enoxaparin |
Catalyzes Antithrombin III formation and activation
|
|
|
MOA:
Eptifibatide |
Binds GpIIb/IIIa
|

