![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does molecular weight affect gel electrophoresis?
|
Heavier molecules will stay near wells (cathode (-) end), whereas lower weight molecules will move toward anode (+) end.
|
|
|
Southern blot:
Utility |
DNA probe allows for identification (via comparison) of a DNA segment
(SNoW DRoP) |
|
|
Northern blot:
Utility |
RNA probe allows identification (via comparison) of an RNA segment
(SNoW DRoP) |
|
|
Western blot:
Utility |
Antibody allows identification of a protein
(SNoW DRoP) |
|
|
ELISA:
Utility |
Tests antigen-antibody reactivity
Determines whether a particular antibody, e.g., anti-HIV, is present in patient's blood sample. Both sensitivity and specificity of ELISA approach 100% but both false-positives and false-negatives do occur. |
|
|
FISH:
Utility |
Fluorescent DNA or RNA probe binds specific gene of interest; used for specific localization of genes and direct visualization of anomalies (microdeletions)
|
|
|
Codominance:
Define Example |
Neither of 2 alleles is dominant
Ex: blood group--A, B, AB |
|
|
Variable expression:
Define Example |
Nature and severity of phenotype vary among individuals
|
|
|
Incomplete penetrance:
Define |
Not all individuals with mutant genotype show mutant phenotype (may skip generations)
|
|
|
Pleiotropy:
Define Example |
1 gene has >1 effect on individual's phenotype
Ex: PKU causes MR, hair/skin changes, etc. |
|
|
Imprinting:
Define Example |
Differences in phenotype depend on whether mutation is of maternal or paternal origin
Ex: Prader-Willi and Angelman's Syndromes |
|
|
Anticipation:
Define Example |
Severity of dz worsens or age of onset of dz is earlier in succeeding generations
Ex: HD |
|
|
Loss of heterozygosity:
Define Example |
If pt inherits or develops mutation in tumor suppressor gene, complementary allele must be deleted/mutated before cancer develops.
Not true of oncogenes Ex: retinoblastoma |
|
|
Dominant negative mutation:
Define Example |
Exerts a dominant effect.
Heterozygote produces nonfnal altered protein that also prevents normal gene product from functioning. Ex: mutation of Tx factor in its allosteric site. Non functioning mutant can still bind DNA preventing wild-type Tx factor from binding |
|
|
Linkage disequilibrium:
Define |
Tendency for certain alleles at 2 linked loci to occur together more often than expected by chance. Measured in populn, not in a family; often varies in diff populns
|
|
|
Mosaicism:
Define Example |
Occurs when cells in body have different genetic makeup
Can be germ-line mosaic, which may produce dz not carried by parent's somatic cells Ex: Lyonization--random X inactvtn in females |
|
|
Locus heterogeneity:
Define Example |
Mutations at different loci produce same phenotype
Ex: Marfan's syndrome, MEN 2B, homocystinuria; all cause marfanois habitus Albinism |
|
|
Heteroplasmy:
Define |
Presence of both normal and mutated mtDNA resulting in variable expression in mitochondrial inherited dz
|
|
|
Uniparental disomy:
Define |
Offspring receive 2 copies of chromosome from 1 parent and no copies from other parent
|
|
|
Prader-Willi Syndrome:
Pathophys Presentation |
Chromosomal deletion form paternal allele
Affects both daughters and sons Presents: hyperphagia, short stature, tantrums, hypogonadism (childhood osteoporosis) Confirmed with FISH |
|
|
Angelman's Syndrome:
Pathophys Presentation |
Deletion of normally active Maternal allele
Presents w/MR, seizures, ataxia, inappropriate laughter (happy puppet) |
|
|
Hardy-Weinberg equations:
Disease prevalence Allele prevalence |
Disease prevalence: p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
Where p^2 = homozygous for p allele (same for q^2) Where pq = heterozygous Allele prevalence: p + q = 1 (100% of populn has either p or q alleles) |
|
|
What is the frequency of the BB phenotype and the Bb phenotype if the frequency of allele B is 70%
|
If B = 70% then b = 30%
bc: B + b = 1 p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1 p = BB = 0.7 Thus p^2 = 0.49 = 49% For Bb: 2pq = 2(0.70)(0.30) = 0.42 |
|
|
List 3 mitochondrial inheritance defects.
|
Mitohcondrial myopathies
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy Leigh's syndrome |
|
|
Ragged-red muscle fibers on biopsy
|
Mitochondrial myopathy (mitochondrial inheritance defect)
|
|
|
Subacute sclerosing encephalopathy
|
Leigh syndrome (mitochondrial inheritance defect)
|
|

|
AD dz showing Anticipation
|
|
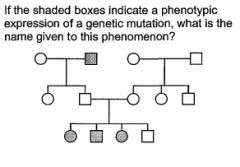
|
Autosomal Dominant dz w/incomplete penetrance
|
|
|
What enzyme is deficient in Niemann-Pick Disease?
|
No man picks his nose with his sphinger.
Sphingomyelinase |
|
|
This genetic condition increases risk of berry aneurysms.
|
AD Polycystic Kidney Dz
Marfan's |
|
|
Which AD disease:
Floppy mitral valve Dissecting aortic aneurysm Berry aneurysm |
Marfan's
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
Mitral valve prolapse Liver disease Berry aneurysm |
AD Polycystic Kidney Dz
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
neural tumors Pigmented iris hamartomas |
NF Type I
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
Strong association with colon cancer |
FAP
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
MI before age 20 |
Familial hyperchol
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
Hemangioblastomas of retina/cerebellum/medulla |
vonHippel Lindau
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
Increased MCHC Hemolytic anemia |
Hereditary spherocytosis
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
Bilateral acoustic neuromas |
NF 2
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
Facial lesions Seizure Cancer risk |
Tuberous sclerosis
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
Caudate atrophy Dementia |
HD
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
Cystic medial necrosis of aorta |
Marfan's
|
|
|
Which AD disease:
Defect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 |
Achondroplasia
|
|
|
Cystic fibrosis:
Pathophys Presentation Diagnosis Treatment |
Defect in CFTR gene
DEfective Cl- channel-->secretion of abnl thick mucus that plugs lungs, pancreas, liver-->recurrent pulm infections (pseudomonas, Staph aureus) Chronic bronchitis Bronchiectasis Panc insufficiency (Malabsorption and steatorrhea) Meconium ileus in newborns Also results in infertility in males due to b/l absence of vas deferencs Fat soluble vit def. (A, D, E, K) Failure to thrive Dx: [Cl-] in sweat >60mEq/L Tx: N-acetylcysteine to loosen mucous plugs |
|
|
Which lyososomal storage disease is a/w renal failure?
|
Fabry's Dz (tx is dialysis)
|
|
|
What are the only two X-LINKED RECESSIVE lysosomal storage diseases?
What is the mode of inheritance of the others? |
Fabry's and Hunter's are X-linked recessive (X marks the spot for a treasure Hunter).
Almost all others are autosomal recessive. |
|
|
What is the most common lysosomal storage disease?
|
Gaucher's Dz
|
|
|
Which lysosomal storage disease are a/w an early death --usually before age 3?
Mode of inheritance? |
Tay Sachs
Niemann-Pick Krabbe's Dz AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE |
|
|
Which lysosomal storage disease is a demyelinating disease?
|
Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (AR)
|
|
|
How might corneal clouding and mental retardation help distinguish between the mucopolysaccharidoses?
|
Hurler's: + corneal clouding, + MR
Hunter's - corneal clouding, +MR Scheie's: + corneal clouding, -MR I-cell: + corneal clouding, ±MR |
|
|
Which lysosomal disease deficiency:
alpha-L-iduronidase |
Hurler's
Scheie's (basically a milder form of Hurler's) |
|
|
Which lysosomal disease deficiency:
Iduronate sulfatase |
Hunter's
|
|
|
Which lysosomal disease deficiency:
Arylsulfatase A |
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
|
|
|
Which lysosomal disease deficiency:
alpha-galactosidase A |
Fabry's
|
|
|
Which lysosomal disease deficiency:
Galactocerebsidase |
Krabbe's
|
|
|
Which lysosomal disease deficiency:
beta-glucocerebrosidase |
Gaucher's (MOST COMMON)
|
|
|
Which lysosomal disease deficiency:
Hexosaminidase |
Tay-Sachs (Sachs-->Sax-->HEXoSAMinidase)
|
|
|
Which lysosomal disease deficiency:
Sphingomyelinase |
Niemann-Pick
|
|
|
Which lysosomal disease:
Accumulation of GM2 ganglioside |
Tay-Sachs
|
|
|
Which lysosomal disease:
Accumulation of dermatin sulfate |
Hurler's
Hunter's Scheie's |
|
|
Which lysosomal disease:
Common among Ashkenazi Jews |
Tay Sachs
Niemann-Pick Some form of Gaucher's |
|
|
Which lysosomal disease:
Crinkled paper cytoplasm |
Gaucher's
|
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis for a cherry red spot on retina?
|
Niemann-Pick
Tay-Sachs Central retinal artery occlusion |
|
|
Which diseases are X-linked?
|
Fabry's Tale: Duke the Muscular Hunter Brutally Lysed the Albino Gopher without aWAre it was a Fragile Hemophiliac!
Fabry's Duchenne MD Hunter Syndrome Bruton's agammaglobulinemia Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome Ocular albinism G6PD def Wiskott-Aldrich Fragile X Hemophilia |
|
|
Duchenne's MD:
Pathophys Diagnosis |
X-linked frame shift mutation-->Dystrophin gene deletion
Accelerated muscle breakdown. Weakness begins in pelvic girdle mm and progresses superiorly Pseudohypertrophy! Dx: Inc'd CPK, muscle biopsy |
|
|
Becker's MD:
Pathophys Diagnosis |
Mutated dystrophin gene; less severe than Duchenne's. Onset in adolescence or early adulthood
Dx: Elevated CPK, muscle bx |
|
|
Fragile X Syndrome:
Pathophys (specific gene mutation) Presentation |
Familial MR gene 1 mutation (FMR1 gene codes for FMRP--cytoplasmic protein found in brain, testes; goes to axons and dendrites where it's involved in mRNA translation)
Fragile X = eXtra-large testes, jaw, ears |
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Glycogen Storage Disease |
AR
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Fragile X |
X-linked recessive
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Polycystic Kidney Disease--Adults vs Infants |
AD--adults
AR--infants |
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
PKU |
AR
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Hereditary spherocytosis |
AD
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Duchenne's MD |
X-linked recessive
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
FAP |
AD
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Lesch-Nyhan |
X-linked recessive
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Bruton's agammaglobulinemia |
X-linked recessive
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Huntington's Disease |
AD
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Thalassemia |
AR
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Sickle Cell |
AR
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Wiscott-Aldrich |
X-linked recessive
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Von Recklinghausen's |
AKA NF-1; AD
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Von Hippel Lindau |
AD
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Hemophilia |
X-linked Recessive
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Mucopolysaccharidosis |
AR
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Familial hypercholesterolemia |
AD
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Sphingolipidosis |
AR
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Marfan's |
AD
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Cystic fibrosis |
AR
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
Hemochromatosis |
AR
|
|
|
Mode of inheritance:
G6PD deficiency |
X-linked recessive
|
|
|
Down Syndrome:
Genetic Pathophys Associated Diseases Quad screen results Ultrasound results |
95% due to meiotic nondisjunciton of homologous chromosomes-->Trisomy 21
4% due to Robertsonian translocation Duodenal atresia, septum primum type ASD, inc'd risk ALL< AD Quad screen: low AFP, high beta-hCG, low E3, high inhibin A U/S: Inc'd nuchal translucency |
|
|
What is Robertsonian translocation?
|
Nonreciprocal chromosomal translocation--occurs when long arms of 2 acrocentric chromosomes (chromosomes with centromeres near their ends_ fust at centromere and 2 short arms are lost.
Balanced translocation normally don't cause abnl phenotype. Unbalanced translocation-->miscarriage, stillbirth, chromosomal imbalance (Down's, Patau's) |
|
|
Edward's vs Patau's Syndrome:
Chromosomes affected Presentation |
Edward's = 18; severe MR, rocker bottom feet, micrognathia, low-set ears, clenched hands, prominent occiput, congenital heart Dz. Death within 1 year (Election age = 18)
Patau's syndrome = 13 (puberty at 13): Severe MR, rocker bottom feet, cleft lip/Palate, holoProsencephaly, Polydactyly, congenital heart dz. Deathw ithin 1 year of birth. |
|
|
Cri-du-chat syndrome:
Pathophys Presentation |
Congenital microdeletion of short arm of chromosome 5 (46XX, 46XY, 5p-)
Findings: microcephaly, MR, HIGH PITCHED CRYING/MEWING ~kidney |
|
|
Williams Syndrome:
Pathophys Presentation |
COngenitcal microdeletion of long arm of chrom 7--deleted region includes elastin gene
Elf facies; MR, hypercalcemia (inc'd sens to vit D), well-dev'd verbal skills, extreme friendliness with strangers |
|
|
What is the probability that a female heterozygous for an X-linked disease will pass it on to her son?
|
If woman has a son, chance is 50%
If don't know sex of child, 25% |
|
|
What is the probability that a female heterozygous for an X-linked recessive disease that mates with a normal male will
have a carrier daughter? |
If daughter-->50%
If prob daughter that is carrier-->25% |
|
|
What is the probability that a female carrier of an X-linked disease will have a child with that disease
assuming she mates with a normal male? |
Prob of having son with defect-->25%
|
|
|
If aa symbolizes an X-linked recessive disease, what is the likelihood that parents Aa and Aa will have a phenotypically
normal child? |
Use punnet square: XA, XA; Y by XA; Xa
Get: XA, XA XA, Y XA, Xa Xa, Y 25% chance having normal child |
|
|
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disorder. Two parents that are heterozygous for cystic fibrosis have
a normal, nonaffected child. What is the probability that the child is homozygous normal? |
Child is normal, obviously can't be homozygous recessive, so chances of being homozygous normal is 1/3 or 33%
|
|
|
Upon examination of a pedigree, you note that both males and females are affected with a disease in every
generation. What type of genetic disease is this? |
AD
|
|
|
What is the frequency of the Aa genotype and the AA genotype if the frequency of allele A is 0.9%?
|
Frequency of heterozygote (Aa) = 0.095 or 10%
Frequency of homozygote dominant (AA) = 0.90 or 90% |
|
|
If 49% of a particular population is homozygous for a curly hair gene that is dominant to a straight hair gene,
what percentage of the population has curly hair? |
P^2 = .49
P = 0.7 Q = 0.3 frequency of straight hair = 0.3 2*0.7*0.3 = 0.42 + 0.49 = 91% populn |
|
|
Which genetic disease:
A/w floppy mitral valve, dissecting aortic aneurysm, berry aneurysm |
Marfan's
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
A/w mitral valve prolapse, liver disease, berry aneurysms |
ADPKD
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
Hemangioblastomas of retina/cerebellum/medulla |
VHL
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
Increased MCHC, hemolytic anemia |
Hered Spherocytosis
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
Cafe-au lait spots, soft tissue growths |
NF 1
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
Macroorchidism and autism |
Fragile X
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
Endocardial cushion defects are common |
Down's
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
Recurrent pulmonary infections, steatorrhea |
CF
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
Multiple fractures, easily confused with child abuse |
OI
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
A/w Alzheimer's after age 35 |
Down's
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
Prone to bilateral acoustic Schwannomas |
NF 2
|
|
|
Which genetic disease:
Excess fibro-fatty tissue deposits amongst muscle |
Duchenne's MD
|
|
|
What test is used to diagnose cystic fibrosis? Which gene is defective?
|
Chloride Sweat Test
Defective CFTR gene |
|
|
What is the difference between Southern Blot, Northern Blot, and Western Blot?
|
Southern:
Sample: DNA, probe: DNA Northern: Sample: RNA, probe: DNA Western: Sample: protein, probe: Ab |
|
|
Which lysosomal storage disease:
Accumulation of GM2 ganglioside |
Tay-Sachs
|
|
|
Which lysosomal storage disease:
A/w renal failure |
Fabrey's
|
|
|
Which lysosomal storage disease:
Accumulation of dermatin sulfate |
Mucopolysaccharidoses:
Hurler's Hunter's Scheie's |
|
|
Which lysosomal storage disease:
Deficiency in hexosaminidase |
Tay-Sach's
|
|
|
Two pts have the same mutation on chromosome 15 but have different phenotypic expressions. One pt
received the mutation from the father while the other received the mutation from the mother. What is this an example of? |
Imprinting
|
|
|
Frequency of CFTR mutation X in pts with cystic fibrosis is 0.1. Cystic fibrosis can be caused by either
mutation X or mutation Yin the CFTR gene. What percentage of cystic fibrosis pts are homozygotes for mutation Y? |
Frequency of allele Y must be 0.9
0.9^2 =81% are homozygous for mutation Y |

