![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
If I give you a dim stimulus, it won't take much of an increase in brightness to see a difference, but if I give you a bright stimulus, it will take a much larger increase in brightness to see a difference" These are common terms for what law?
|
Weber's law
|
|
|
|
What is the definition of threshold for a forced choice method?
|
Halfway between 50 and 100%
|
|
|
|
What variable in the Steven's power law changes depending on what is being measured?
|
the exponent b
|
|
|
|
What does signal detection theory try to remove from the determination of threshold?
|
criterion
|
|
|
|
Is signal detection theory used clinically? Why?
|
No, signal detection theory takes forever
|
|
|
|
What are the two ways a person can be right in signal detection theory
|
1. hit
2. correct rejection |
|
|
|
What are the two ways a person can be right in signal detection theory
|
1. miss
2. false alarm |
|
|
|
What d' value is considered to mean that one cannot distinguish between signal and noise?
|
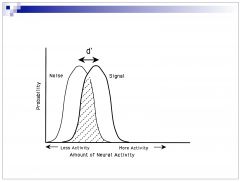
d'=0
|
|
|
|
What d' value is considered threshold?
|

d'=1
|
|
|
|
Name two ways to manipulate a patients criterion?
|
1. change the payoff
2. ? |
|
|
|
Where is hue discrimination best?
|
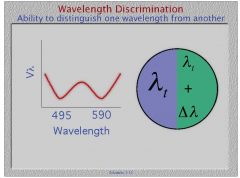
Hue discrimination is best at wavelength blue-green (490nm) and yellow-red (590nm)
|
|
|
|
What is the change in hue associated with the change in luminance?
|
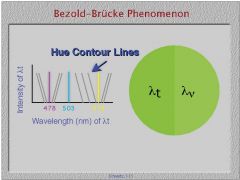
Bezold Brucke Effect
|
|
|
|
In which three specific wavelengths of light is the hue not effected by the luminance?
|
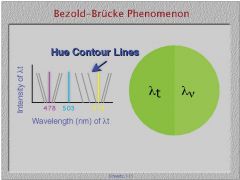
1. 478nm
2. 503nm 3. 578nm |
|
|
|
According to the Bezold Brucke effect stimuli below 500nm appear more _____ as instensity increases, while stimuli above 500nm appear more _____ as intensity increases.
|
According to the Bezold Brucke effect stimuli below 500nm appear more blue as instensity increases, while stimuli above 500nm appear more yellow as intensity increases.
|
|
|
|
If a neutral density filter transmits 10% of the light incident upon it, what is its optical density?
|
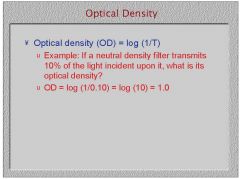
|
|
|
|
What do you the system of color-stimulus notation in which an attempt has been made to have the notation correspond to the sensory experience given?
|
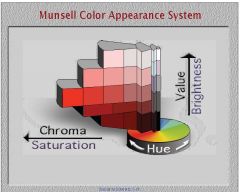
Munsell color system
|
|
|
|
In the Munsell color system 100 different hues are evenely spaced where?
|
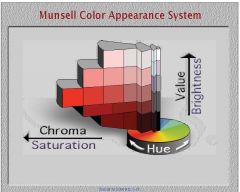
100 different hues are uniformly spaced around the circumference of the circle
|
|
|
|
Which system of color-stimulus notation has attempted to make the notation correspond to the sensory experience given?
|
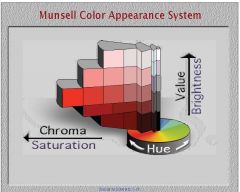
Munsell color system
|
|
|
|
Of the three subjective attributes of the Munsell color system, which subjective attribute refers to the reflectance of the sample and is related to brightness
|
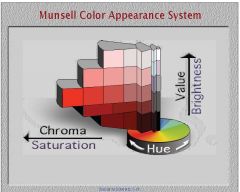
value
|
|
|
|
Would a value of 10 at the top of the Munsell cylinder be darker or lighter?
|
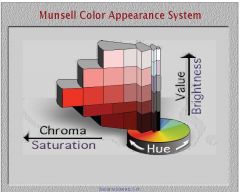
10 is completely dark
0 is completely light |
|
|
|
Where do you find the most pure or highest chroma value on the Munsell cylinder? What would that value be?
|
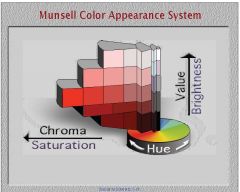
The greater the radius from the center of the cylinder the higher the chroma or more pure. 14 denotes the highest purity further out, while 0 would be the least pure further in.
|
|
|
|
Munsell notation uses a pseudofraction to quantify the three subjective attributes, in what order are these attributes presented?
|
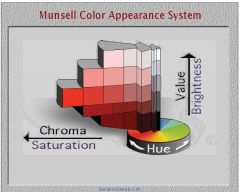
H/V/C
|
|
|
|
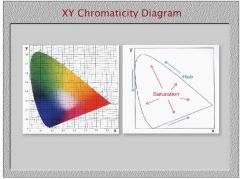
What do you call the monochromatic hues arranged around the perimeter of the CIE diagram?
|
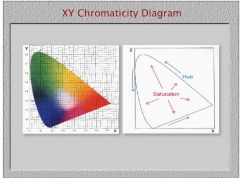
spectral locus
|
|
|
|
If I mix equal amounts of 510nm and 560nm, where should I place the point M, indicating the resultant mixture?
|
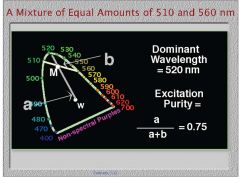
First draw a line between the two wavelengths on the spectral locus, then since they are mixed in a one to one ratio, place M halfway in between
|
|
|
|
What two points do I connect to draw the line indicating the dominant wavelength?
|
The resultant mixture M and the theoretical equal mixture at x=0.33 and y=0.33 W (white).
|
|
|
|
What is the excitation purity of equal mixtures of two wavelengths?
|
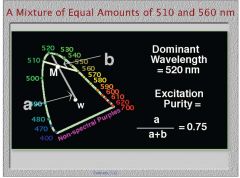
a=the distance between M and the dominant wavelength at the spectral locus, relative to the total distance from W to the spectral locus
b-relative distance between M and W, relative to the total distance from W to the spectral locus |
|
|
|
What do you call two colors on the CIE diagram that combine to form white?
|
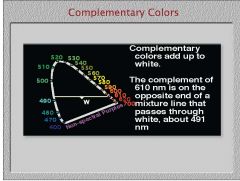
complementary colors
|
|
|
|
What do you call the perceptual areas in the CIE diagram in which all colors will appear the same even if they are physically different?
|

MacAdams Ellipses
|
|
|
|
Which theory of color vision states that color information is coded by a limited number of cone types (perhaps 3), and the relative activities of these cone-types encodes color?
|

Young-Helmholz a.k.a. Trichromatic theory
|
|
|
|
What determines the hue in Opponent color theory?
|

|
|
|
|
What determines saturation in opponent color theory?
|

|
|
|
|
What determines brightness in opponent color theory?
|

|
|
|
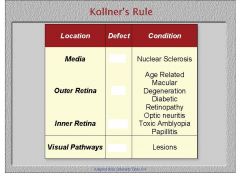
1. Does Kollner's rule apply to congenital color defects?
2. Which are R/G color defects and which are B/Y |
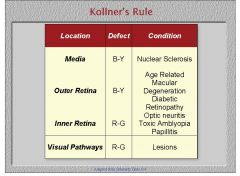
1. Kollner's rule only applies to acquired color defects
|
|
|

Name the potential conditions that would cause the indicated type of color deficiency in this general area.
|
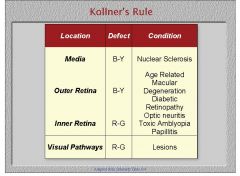
|
|
|
|
What do you call the line formed by connecting the three primaries of the Nagel anomaloscope plotted on the CIE chromaticity diagram?
|
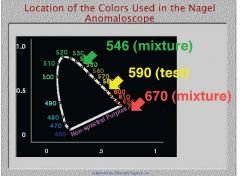
Rayleigh equation
|
These correspond to a color confusion line shared by deuteranopes and protanopes
|
|
|
What is varied in the top field of the Nagel anomaloscope and what is the range?
|

The ratio of 670nm (red) light to 546nm (green) light is varied. 0 is defined as completely 546nm light, while 73 represents exclusively 670nm (red) light
|
|
|
|
What does turning a knob change in the lower field of the Nagel anomaloscope? What is the range?
|

Radiance is varied. Turning the knob to 0 represents very dim yellow, while turning the knob to 87 represents very bright yello.
|
|
|
|
1) When asked to match the top mixture field with the lower test field, at what number does a normal trichromat set the upper mixture field?
2. Where does a normal trichromat set the lower test scale? |

45 on the mixture scale and 17 on the test scale
|
|
|

Where does the normal trichromat set mixture and test fields and how does it appear to him?
|

|
|
|
|
What does a normal trichromat see on the Nagel anomaloscope for a setting at zero?
2. What will he see at 23? What will he see at 52? 3. What will he see at 73? |

1. 0=green
2. as you increase to 45 it gets more yellow 3. as you go from 45 to 73, the yellow gets more red. |
|
|

1. Where will a protanope adjust the test field luminance when matching short green stimuli of the mixture field?
2. Where will he set the test field when matching longer red stimuli of the mixture field? |

1. as bright as 35 since the short stimuli appear bright
2. as dim as 5 since the long stimuli appear dim |
|
|

When asked to match the mixture and test field, where would a deuteranomalous trichromat set the mixture field knob?
|

He'll probably set it lower than 45, maybe around 20 since he needs more 546 nm light to make up for his missing M pigment.
|
|
|
|
When asked to match the mixture and test field, where would a protanomalous trichromat set the mixture field knob?
|

He would set the mixture knob higher than 45, maybe around 60, to increase the amount of 670nm wavelength to make up for his lack of L pigment.
|
|
|

Where does a protanomalous trichromat set the test field stimulus?
|

test field less than 15, becaue the protanomalous trichromat must add extra 670nm to the mixture field, the mixture field appears dimmer, and he must reduce the test field luminance to compensate.
|
|
|
|
What type of color vision tests are desaturated D-15, Farnsworth D-15, and 100 hue test?
|
arrangement tests
|
|
|
|
Is the Desaturated D-15 test more or less sensitve than the regular D-15 test?
|
more sensitve, and especially useful for picking up subtle acquired defects like glaucoma
|
|
|
|
What are the axes of the ROC (receiver operating curve)?
|
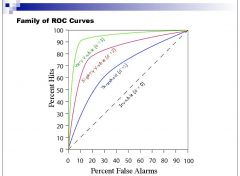
|
|
|
|
How do you define the colorimetric purity?
|
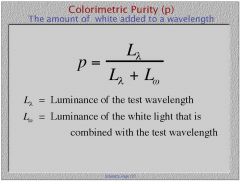
|
|
|
|
What does Grassman's law of additivity state?
|
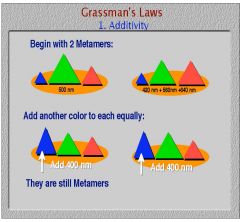
|
|
|
|
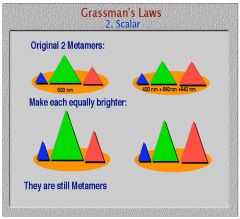
What does Grassman's scalar law state?
|
|
|
|
|
Are Landholt C or Landholt ring recognition or resolution acuity tests?
|

|
|
|
|
Is minimum separable acuity a resolution or recognition acuity test?
|

|
|
|
|
1. How small is the lower limit of human resolution?
2. How small can a letter be and still be visible? |

|
|
|
|
A letter E is 5mm in height and displayed at a distance of 10m. What visual angle does the letter subtend?
|

|
|
|
|
What is the logMar score for 20/20 visual acuity?
|

|
|
|
|
What is the logmar acuity for 20/20-1 Snellen?
|

|
|
|
|
What is the formula for diameter of the airy disc produced by optical diffraction of a point source object?
|

|
|
|
|
What states that two objects will be resolved when their separation is equal to the radius of the airy disc?
|

|
|
|
|
How wide can you make a line before you can detect if it's present or not?
|
minimum separable and resolution acuity are 30 seconds of arc or 1/2 a minute
|
|
|
|
1. What do you call all tasks that require you to localize one part of a target relative to another part of the target?
2. Can you name two examples of this type of acuity? |

|
|

