![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
define the autonomic nervous system |
nervous system that innervates the smooth (largely) involuntary muscles of the body mostly out of conscious control |
|
|
where are the 'cell bodies of origin' for sympathetic nerves in the head/neck region |
nerves must climb up to the 3 cervical ganglia superior-- pupils, salivary glands, heart middle-- heart inferior-- heart |
|
|
describe the greater splanchnic nerve |
Celiac ganglion T5-T9 foregut |
|
|
describe the lesser splanchnic nerve |
Superior mesenteric ganglion
T10-T11 midgut |
|
|
describe the lumbar (least) splanchnic nerve |
Inferior mesenteric ganglion T12 hindgut |
|
|
what are two examples of other splanchnic nerves and how do they differ from the thoracic splanchnic nerves |
cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves-- they're post synaptic pelvic splanchnic nerves-- they're from the parasympathetic nervous system |
|
|
define the stellate ganglion and its clinical relevance |
sometimes the inferior cervical ganglion fuses with the first thoracic pain management |
|
|
describe the cause of the phenomenon 'referred pain' |
somatic and autonomic sensory nerves often share the same dorsal root ganglia, converge on similar nerves in spinal cord pain is learnt, don't typically feel viscera when one structure sends a signal the brain can misinterpret it as pain from somewhere else sharing space with those nerves (ie) heart=left arm pain, kidney= skin pain |
|
|
describe viscero-somatic interactions |
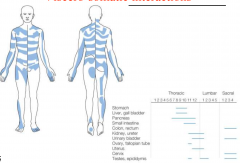
referred pain, 'dermatomes' for autonomic nervous system |
|
|
what are the 4 major cranial nerves for parasympathetic innervation |
III- occulomotor VII- facial IX- glossopharyngeal X- vagus |
|
|
describe the vagus nerve function |
'mixed nerve' somatic: pharynx (swallowing) and larynx (speech) autonomic, parasympathetic: heart, lungs and abdominal organs many in nodose ganglion |
|
|
what is the difference between short and long reflex arcs |
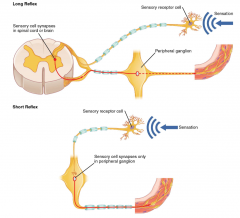
short reflex arcs bypass the spinal cord sensory meets motor straight in ganglion |
|
|
describe the transmitter system of the somatic nervous system |
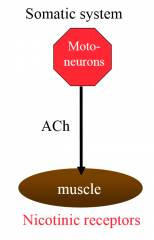
motor neurons use acetylcholine, muscle has nicotinic receptors |
|
|
describe the transmitter system in the parasympathetic autonomic nervous system
|
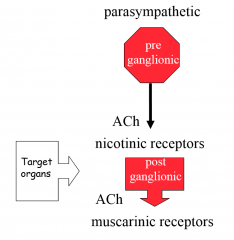
preganglionic axons use acetylcholine, nicotinic receptors on ganglia
postganglionic axons use acetylcholine, muscarinic receptors on target tissue |
|
|
describe the transmitter system in the sympathetic autonomic nervous system |
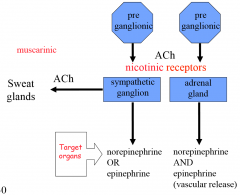
preganglionic axons use acetylcholine, nicotinic receptors on sympathetic ganglion: use ACh-- muscarinic receptors on sweat glands use norepinephrine OR epinephrine on target organs adrenal gland: use norepinephrine AND epinephrine (vascular release) |

