![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Malaria causes how many deaths per year?
|
> 1 M
|
|
|
Neurological signs with Malaria occur with this species
|
Plasmodium Falciparum
|
|
|
Malaria vector
|
FEMALE ANOPHELES MOSQUITO
|
|
|
Places with endemic Malaria
|
Africa
S. America Mexico S. Europe |
|
|
Malaria Exoerythrocyte form occurs in the _______
|
liver
|
|
|
Malaria:
Transmitted by __1__ mosquito -> mosquito bite releases __2__ into bloodstream -> carried to the liver and infects hepatocytes -> in hepatocytes, sporozoite divides into __3__ --> infect __4__ --> In RBC's Merozoites develop into __5__ -> divide into many __6__ --> burst RBC's |
1. Anopheles
2. Sporozoite 3. Merozoite 4. RBC's 5. Trophozoite 6. Merozoites |
|
|
Gametocyte of Falciparum malaria has this shape
|
Banana
|
|
|
Type of ring that indicates Falciparum
|
double-ring
|
|
|
Explain the pathology of Falciparum in the Brain
|
Falciparum causes "knobs" in infected RBC's and cause them to stick to eachother and capillaries --> vessel occlusion and hemorrhage
|
|
|
This indicates Plasmodium infected erythrocytes
|
Brown pigment (Falciparum metabolizes hemoglobin to form pigment)
|
|
|
Malaria symptoms
|
cyclical fever and chills
Anemia Hepatosplenomegaly |
|
|
Toxoplasmosis:
-seroprevalence in adult pop: 1 -most infections are __2__ -__3__ is the rule |
1. 30-50%
2. asymptomatic = "good" parasite 3. premunition = once infected, always infected |
|
|
Definitive host for Toxoplasmosis
|
Cats: shed millions of Oocysts in their feces after primary infection
-only animals capable of producing OOCYSTS |
|
|
Toxoplasma __1__, present in tissue __2__, are capable of recredescence in IMMUNOCOMPROMISED HOSTS
|
1. Bradyzoites
2. cysts |
|
|
Toxoplasmosis tissue cysts are found in all tissues, but _____ relapse is the most common and most serious
|
CNS
|
|
|
Mainstay of treatment for Toxoplasma in IC'ed population
|
Sulfonamide + Pyrimethamine
|
|
|
IC'ed patients with these symptoms should receive a CT
|
headache
Neurological signs |
|
|
When does Serology of Toxoplasmosis work well
|
only in Immunocompetent
|
|
|
Tissue cysts contain slowy replicating _________
|
bradyzoites
|
|
|
Is there an immune response to toxoplasmosis cysts
|
little, if any
|
|
|
Rupture of Toxoplasmic cysts in IC'ed patients results in continuously replicating _______
|
Tachyzoites
|
|
|
Tachyzoites infect these cells
|
any cell and rapidly reproduce and cause cell lysis
|
|
|
Toxoplasmosis is part of this Syndrome
|
TORCH
|
|
|
Congenital Toxoplasmosis infection is possible only during ______ infection of the mother
|
Acute
|
|
|
Symptoms of Congenital Toxoplasmosis
|
Mental Retardation
Chorioretinitis -> blindness *usually occur later after birth |
|
|
Risk of Toxoplasma transmission is greatest during this trimester
|
3rd trimester, but disease is milder
|
|
|
Infection with Toxoplasma during the 1st trimester often results in....
|
spontaneous abortion
|
|
|
Free living Amebae that can cause corneal ulcers and ophthalmitis in contact lens wearers or in contaminated hot tubs
|
Acanthamoeba
|
|
|
Free living Amebae found in farm ponds and causes frontal meningoencephalitis
|
Naegleria fowleri
|
|
|
Access to the CNS of Naegleria Fowleri causing Encephalitis always occurs via the _______
|
Cribriform plate
|
|
|
Histologic characteristics of Naegleria fowleri
|
Large size and pale nuclei
|
|
|
Leishmania vector
|
Phlebotomus Sand Fly
|
|
|
Species causing Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
|
L. Mexicana
L. Braziliensis |
|
|
Species causing Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis (nasal-oral)
|
L. braziliensis
|
|
|
Species causing Visceral Leishmaniasis
|
L. donovani
|
|
|
Leishmania reservoirs
|
humans
dogs rodents |
|
|
Leishmania replicate in _______
|
macrophages
|
|
|
Explain the Promastigote form of Leishmania
|
flagellated form outside of Macrophages
|
|
|
Explain the Amistigote form of Leishmania
|
nonflagellated form within Macrophages
|
|
|
Agent of Chagas' disease
|
Trypanosoma Cruzi
|
|
|
Age range for Chagas' disease
|
20-40 yoa
|
|
|
Pathology of Chagas' disease
|
Cardiomegaly
-arrhythmias Megaesophagus Megacolon |
|
|
Vector for Chagas' disease
|
Triatoma Reduviid bud
|
|
|
Primary Lesion of Chagas' disease
|
Swelling around the eye (orbital edema) = Romana's sign
|
|
|
This is pathognomonic of Chaga's Myocarditis
|
apical thinning
|
|
|
Agent of African Trypanosomiasis
|
Trypanosoma brucei
|
|
|
Vector of T. brucei
|
Tsetse fly
|
|
|
Unique feature of Trypanosoma brucei
|
can have antigenic variation of surface coat to escape host antibodies
|
|
|
Where does T. brucei replicate
|
bloodstream
|
|
|
Synonym for African Trypanosomiasis
|
African sleeping sickness
|
|
|
3 clinical stages of African sleeping sickness
|
1. Chancre = scar at bite site
2. Hemolymphatic 3. Meningoencephalitis |
|
|
What do Trypanosomes look like within bloodstream?
|
Seahorses
|
|
|
T. brucei causes somnolence via cerebral lesion resulting from ________ caused by microbe invading ________
|
Vasculitis
Endothelial cells of cerebral small vessels |
|
|
Plasma cells in a brain histology of African Trypanosomiasis often exhibit ________
|
Russel bodies = collections of protein (Ab) in the cytoplasm
|
|
|
Sign during Hemolymphatic stage of African Trypanosomiasis
|

Winterbottom's sign = lymphadenopathy along the back of the neck
|
|
|
Exo-erythrocyte form of Malaria (plasmodium) in a HEPATOCYTE --> jaundice
|

What is this showing?
|
|
|
Plasmodium Falciparum
-can cause neurological signs in Malaria |

What protozoa is this guy?
|
|
|
Plasmodium falciparum = cause "knobs" in RBC's causing them to clump in vessels
Cerebral Malaria |

What Protozoa?
What site? What is happening? |
|
|
Plasmodium Falciparum = brown dots due to hemoglobin metabolization
|
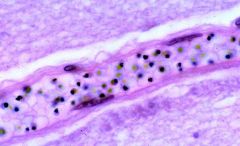
Protozoa in this pic?
|
|
|
Toxoplasma gondii
Cats |

Protozoa?
How transmitted? |
|
|
Toxoplasma gondii
|

Protozoa?
|
|
|
Toxoplasma cysts containing Bradyzoites
If ruptures = Tachyzoites usually only ruptures in IC'ed |

What is this?
|
|
|
Toxoplasma gondii
Tachyzoites that have ruptured from a cyst |

Protozoa?
What are these called? |
|
|
Toxoplasma gondii
Congenital infection -3rd trimester |

Protozoa that caused this?
|
|
|
Toxoplasma gondii
|

Protozoa that causes Congenital Chorioretinitis and Mental Retardation?
|
|
|
Acanthamoeba = free-living
|

Protozoa that affects contact wearers causing corneal ulcers?
|
|
|
Naegleri fowleri
from Farm ponds |

Protozoa that causes Frontal Meningoencephalitis?
Where is it found? |
|
|
Naegleria fowleri
Free-living amebae are Large and have Pale nuclei |

Protozoa?
How can you tell? |
|
|
Leishmania
|

Protozoa?
|
|
|
Leishmania
|

Protozoa?
|
|
|
Trypanosoma Cruzi = Chagas
Romana sign = swelling of one eye |

Protozoa?
What is the boy positive for? |
|
|
Trypanosoma cruzi = Chagas
-Cardiomegaly -Mega-esophagus -Megacolon |

Parasite responsible for these pathologies?
|
|
|
Trypanosoma Cruzi = chagas
-monocyte response -chronic myocarditis |

Parasite?
|
|
|
Trypanosoma brucei = African sleeping sickness
3 stages -Chancre -Hemolymphatic -Meningoencephalitic |

Protozoa?
|

