![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
There are 3 branches of the Superior Thyroid Artery. Which one does he want us to know and what are the other two?
|
1.**Superior Laryngeal
2. Infrahyoid 3. Glandular Branches |
|
|
There are four branches of the Ascending Pharyngeal but he didn't spend any time on them. What are they?
|
Pam P.:
1. Pharyngeal Branches 2. Anterior Tympanic 3. Meningeal 4. Palatine |
|
|
When someone takes nitroglycerine pills for angina, what vessel does the medication quickly enter for access to the heart?
|
Sublingual
|
|
|
There are six branches of the Facial Artery but he wants us to know three. What are they?
|
1. Ascending Palatine
2. Tonsillar 3. Submental 4. Inferior Labial** 5. Superior Labial** 6. Angular** |
|
|
When does the Facial Artery become the Angular artery?
|
Once it crosses the inferior boarder of the orbit of the eye.
|
|
|
When does the external carotid end?
|
When it reaches the Maxillary and Superficial Temporal branches.
|
|
|
What is the name of the branch that comes off of the Superficial Temporal Artery and parallels the Parotid Duct?
|
The transverse facial.
|
|
|
The Maxillary Artery has three parts...what are they?
|
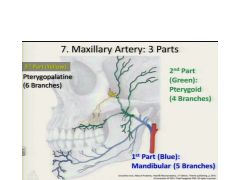
1. Mandibular
2. Pterygoid 3. Pterygopalatine |
|
|
When does the Pterygoid Branch of the Maxillary Artery become the Pterygopalatine?
|
Pterygomaxillary Fissure (named based on the anterior and posterior boundaries)
|
|
|
The Mandibular Branch of the Maxillary Artery has 5 branches but he wants us to know 2. What are they?
|
1. Deep auricular
2. Anterior Tympanic 3. Middle Meningeal ** 4. Accessory Meningeal 5. Inferior Alveolar ** |
|
|
What fossa does the Middle Meningeal pass through?
|
The Foreman Spenosum
|
|
|
The Middle Meningeal can cause problems when pts are hit on the side of the head at this particular spot and cause this particular bleed
|
Getting hit at the pterion can cause an Epidural Hematoma
|
|
|
Describe the course of the Inferior Alveolar.
|
Goes through the Mandibular Foramen on the deep side of the mandible and tunnels through it and forward and exits via the Mental Foramen.
|
|

Indicate where the Pterygoid Branch ends and where the Pterygopalatine Branch begins.
|

When it crosses the Pterygoid plate
|
|
|
There are 4 branches of the Pterygoid Branch but he wants us to know 1. What are they?
|
1. Deep Temporal aa
2. Pterygoid 3. Masseteric 4. Buccal ** |
|
|
There are 6 branches of the Pterygopalatine Branch but he wants us to know 4. What are they?
|
1. Posterior superior alveolar**
2. Infraorbital** 3. Descending palatine** 4. Artery of pterygoid canal 5. Pharyngeal branch 6. Sphenopalatine ** |
|
|
Like the greater and lesser Palatine nn, the greater and lesser palatine arteries split off from what? (See p11 of his lecture)
|
The descending palatine branch of the pterygopalatine branch splits into these two arteries.
|
|
|
The Ophthalmic Artery has 8 branches but he wants us to know 3. What are they?
|
1. Lacrimal
2. Supraorbital ** 3. Posterior Ethmoidal 4. Anterior Ethmoidal** 5. Medial Palpebral 6. Supratrochlear 7. Dorsal Nasal 8. Central Artery of the Retina** |
|
|
This system causes tears to flow. This system causes tears to stop.
|
Parasympathetic = (flow)
Sympathetic = (no flow, via vasoconstriction) |
|

Name
|

1. Ethmoid b
2. Rhomboid b 3. Anterior ethmoidal a 4. Posterior ethmoidal a 5. Sphenopalentine 6. Incisive foramen 7. Kiesselbach's Plexus 8. Facial a 9. Spenopalatine Foramen and Artery and Terminal Branch of Maxillary A |
|
|
You need to finish making NC for this lecture starting at about 32:20.
|
You need to finish making NC starting at about 32:20.
|
|

Name these anastomoses
|

1. Transverse Facial (Superficial Temporal) with Facial and Infraorbital
2. Infraorbital with Dorsal Nasal (Ophthalmic), Angular (Facial), Facial and Transverse Facial (Superficial Temporal) 3. Medial Palpebral (Ophthalmic) & Angular (Facial) 4. Superficial Temporal (Maxillary) & Supraorbital (Opthalmic) |
|

Name these anastomoses of the palate.
|

1. Greater Palatine (Maxillary)
2. Sphenopalatine (Maxillary) |
|

See N70 and know this
|

See N70 and know this
|
|

Name the Cranial Nerves and the Fossa they pass through
FINISH |

CNI - Cribriform Plate
CNII - Sphenoid CNIII - Superior Orbital Fissure CNIV - Superior Orbital Fissure CNV1 - Superior Orbital Fissure CNV2 - Foramen Rotundum CNV3 - Foramen Ovale (a) CNVI - Superior Orbital Fissure CNVII - Internal Acoustic Meatus CNVIII - Internal Acoustic Meatus CNIX - Internal Acoustic Meatus (c) CNX - ?? (c) CNXI - Entry via Occipital Bone/ Exit via Jugular Foramen (b) CNXII - Occipital Bone - Hypoglossal Canal |
|

Name these. Infections can migrate to this area of the cavernous sinus. What would a pt experience? Why?
|

1. CNIII
2. CNIV 3. CNVI 4. CNV1 5. CNV2 A pt would experience double vision because the infection there impinges on the oculomotor neurons, causing unilateral eye movement problems. |
|
|
Describe the overall lymphatic drainage.
|
The Right Upper Quadrant drains into the Right jugular angle. The rest of the body drains into the left jugular angle (thoracic duct?).
|
|
|
What is Waldeyer's ring?
|

It is immunocompetent lymphatic tissues including the tonsils and lymph follicles that surround the passageways from the mouth and nasal cavity to the pharynx.
|
|
|
For the tip of the tongue infection, where would you expect to find a swollen lymph node?
|
In the submandibular region
|
|

Name
|
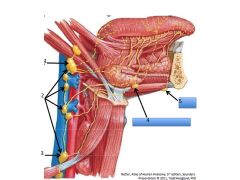
1. Jugulodigastric
2. Deep cervical (internal jugular) 3. Juguloomohyoid 4. Submandibular 5. Submental |
|
|
In terms of lymphatic drainage, how is the tongue divided in regard to the tip, lateral, central and posterior portions?
|

Tip = submental
Lateral = Submandibular Central/Posterior = Superior deep cervical nodes. |

