![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an example of a positive transcription control?
|
Positive control means a protein binds to the DNA which increases transcription. (example: Catabolic activator protein)
|
|
|
regulatory proteins= DNA binding proteins
|
true
|
|
|
Bacteria have a variety of pathways that allow them to use different materials. Genes that code for a particular pathway are clustered together.
|
True
|
|
|
True or False: RNA polymerase sits on the promoter
|
True
|
|
|
For repression/inducing, you only need to know the first few steps
|
Instruction to myself
|
|
|
cyclic AMP is an internal sensor for the cell that tells how much glucose is available
|
true
|
|
|
E. coli and its viruses are called ______________ because of their frequent use by researchers in studies that reveal broad biological principles
|
model systems
|
|
|
Viruses are very small infectious particles consisting of _____________ enclosed in a _____________ and, in some cases, a ______________
|
nucleic acid, protein coat, membranous envelope
|
|
|
True or False: Viral genomes may consist of Double- or single-stranded DNA or RNA
|
True.
|
|
|
______________ have the most complex capsids found among viruses
|
Bacteriaphages
|
|
|
True or False: Phages have an elongated capsid head that encloses their DNA
|
True.
|
|
|
True or False: Phages lack a capsid head to enclose their DNA
|
False.
|
|
|
True or False: A protein tailpiece attaches the phage to the host and injects the phage DNA inside
|
True.
|
|
|
A protein _________ attaches the phage to the host and injects the phage DNA inside
|
tailpiece
|
|
|
A ________ tailpiece attaches the phage to the host and injects the phage DNA inside
|
protein
|
|
|
Contributors to the genetic diversity of bacteria:
* _______________ * _______________ * _______________ |
* Rapid reproduction
* mutation * genetic recombination |
|
|
Contributors to the genetic diversity of bacteria:
* _______________ * mutation * _______________ |
* Rapid reproduction
* mutation * genetic recombination |
|
|
True or False: The bacterial chromosome is usually a circular DNA molecule with few associated proteins
|
True
|
|
|
The bacterial chromosome is usually a ________ DNA molecule with few associated proteins
|
circular
|
|
|
True or False: The bacterial chromosome is usually a linear DNA molecule with few associated proteins
|
False. The bacterial chromosome is usually a circular DNA molecule with few associated proteins
|
|
|
In bacteria one can easily identify new mutations by growing bacteria in medium that does not have ______________.
|
amino acid
|
|
|
True or False: In bacteria one can easily identify new mutations by growing bacteria in medium that does not have amino acid.
|
True
|
|
|
True or False: In bacteria one can easily identify new mutations by growing bacteria in medium that does not have carbon.
|
False: In bacteria one can easily identify new mutations by growing bacteria in medium that does not have amino acid.
|
|
|
Mutant bacteria that require added amino acids are called ____________. Their wild type counterparts are called ____________.
|
auxotrophs; prototrophs
|
|
|
True or False: Mutant bacteria that require added amino acids are called auxotrophs. Their wild type counterparts are called prototrophs
|
True
|
|
|
True or False: Mutant bacteria that require added amino acids are called prototrophs. Their wild type counterparts are called auxotrophs.
|
False: Mutant bacteria that require added amino acids are called auxotrophs. Their wild type counterparts are called prototrophs
|
|
|
Three processes bring bacterial DNA from different individuals together:
* ______________ * ______________ * ______________ |
Three processes bring bacterial DNA from different individuals together:
Transformation Transduction Conjugation |
|
|
Three processes bring bacterial DNA from different individuals together:
* ______________ * ______________ * Conjugation |
Three processes bring bacterial DNA from different individuals together:
Transformation Transduction Conjugation |
|
|
What is Transformation?
|
Transformation is the alteration of a bacterial cell’s genotype and phenotype by the uptake of naked, foreign DNA from the surrounding environment
|
|
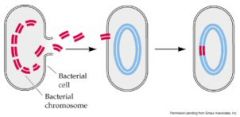
What is shown here?
|
Transformation
|
|
|
What is transduction?
|
In the process known as transduction, phages carry bacterial genes from one host cell to another
|
|
|
“Maleness,” the ability to form a sex pilus and donate DNA, results from an _____________ as part of the chromosome or as a plasmid
|
F (for fertility) factor
|
|
|
True or False: “Maleness,” the ability to form a sex pilus and donate DNA, results from an F factor as part of the chromosome or as a plasmid
|
True
|
|
|
True or False: “Maleness,” the ability to form a sex pilus and donate DNA, results from an M factor as part of the chromosome or as a plasmid
|
False. “Maleness,” the ability to form a sex pilus and donate DNA, results from an F factor as part of the chromosome or as a plasmid
|
|
|
True or False: Plasmids, including the F plasmid, are small, circular, self-replicating DNA molecules
|
True
|
|
|
True or False: Plasmids, including the F plasmid, are small, linear, self-replicating DNA molecules
|
False: Plasmids, including the F plasmid, are small, circular, self-replicating DNA molecules
|
|
|
A cell with a built-in F factor is called an _________ cell
|
Hfr
|
|
|
The F factor of an Hfr cell brings some ________________ along when transferred to an F– cell
|
chromosomal DNA
|
|
|
True or False: R plasmids confer resistance to various antibiotics
|
True.
|
|
|
True or False: F plasmids confer resistance to various antibiotics
|
False: R plasmids confer resistance to various antibiotics
|
|
|
True or False: R plasmids confer resistance to T2 bacteriaphages.
|
False: R plasmids confer resistance to various antibiotics
|
|
|
_______________, often called “jumping genes,” contribute to genetic shuffling in bacteria
|
Transposable elements
|
|
|
Transposable elements, often called “_____________,” contribute to genetic shuffling in bacteria
|
jumping genes
|
|
|
True or False: The simplest transposable elements, called insertion sequences, exist only in bacteria
|
True
|
|
|
The simplest transposable elements, called ______________, exist only in bacteria
|
insertion sequences
|
|
|
The simplest transposable elements, called insertion sequences, exist only in ___________
|
bacteria
|
|
|
True or False: The simplest transposable elements, called conjugated sequences, exist only in bacteria
|
False: The simplest transposable elements, called insertion sequences, exist only in bacteria
|
|
|
True or False: An insertion sequence has a single gene for transposase, an enzyme catalyzing movement of the insertion sequence from one site to another within the genome
|
True.
|
|
|
An _______________ has a single gene for transposase, an enzyme catalyzing movement of the insertion sequence from one site to another within the genome
|
insertion sequence
|
|
|
An insertion sequence has [how many genes] for transposase, an enzyme catalyzing movement of the insertion sequence from one site to another within the genome
|
1
|
|
|
An insertion sequence has a single gene for ______________, an enzyme catalyzing movement of the insertion sequence from one site to another within the genome
|
transposase
|
|
|
Transposable elements called ______________ are longer and more complex than insertion sequences
|
transposons
|
|
|
True or False: Transposable elements called transposons are longer and more complex than insertion sequences
|
True
|
|
|
True or False: Transposable elements called transposons are simpler and more rare than insertion sequences
|
False: Transposable elements called transposons are longer and more complex than insertion sequences
|
|
|
In addition to DNA required for transposition, ____________ have extra genes that “go along for the ride,” such as genes for antibiotic resistance
|
transposons
|
|
|
What are Transposons?
|
Transposable elements called transposons are longer and more complex than insertion sequences
|
|
|
True or False: Genes are expressed (transcribed and translated) when their products are needed
|
True
|
|
|
Genes are expressed (transcribed and translated) when _______________
|
their products are needed
|
|
|
True or False: Genes are expressed (transcribed and translated) during DNA synthesis.
|
False: Genes are expressed (transcribed and translated) when their products are needed
|
|
|
Metabolic control occurs on two levels:
* _________________ * _________________ |
Metabolic control occurs on two levels:
Adjusting activity of metabolic enzymes Regulating genes that encode metabolic enzymes |
|
|
Operons are composed of:
* ______________ * ______________ * ______________ |
Operons are composed of:
An operator, an “on-off” switch A promoter Genes for metabolic enzymes |
|
|
An operon can be switched ____ by a protein called a repressor
|
off
|
|
|
An operon can be switched off by a protein called a __________
|
repressor
|
|
|
A _____________ is a small molecule that cooperates with a repressor to switch an operon off
|
corepressor
|
|
|
A corepressor is a small molecule that cooperates with a repressor to switch an operon ____
|
off
|
|
|
A corepressor is a small molecule that cooperates with a ___________ to switch an operon off
|
repressor
|
|
|
When the repressor binds to the operator, transcription is __________
|
prevented
|
|
|
Repressible and Inducible Operons: Two Types of ____________ Gene Regulation
|
negative
|
|
|
A repressible operon is one that is usually ___
|
on
|
|
|
The trp operon is a ________ operon
|
repressible
|
|
|
An ___________ operon is one that is usually off
|
inducible
|
|
|
An inducible operon is one that is usually ____; a molecule called an inducer inactivates the repressor and turns on transcription
|
off
|
|
|
An inducible operon is one that is usually off; a molecule called an __________ inactivates the repressor and turns on transcription
|
inducer
|
|
|
_______ & ________ figured out the first operon in E.coli: lac operon. They got the Nobel prize for their work
|
Jacob and Monod
|
|
|
The primary source of food for bacteria is __________
|
glucose
|
|
|
Inducible enzymes usually function in ______________
|
catabolic pathways
|
|
|
Repressible enzymes usually function in _____________
|
anabolic pathways
|
|
|
_____________ enzymes usually function in anabolic pathways
|
Repressible
|
|
|
Regulation of the trp and lac operons involves ________ control of genes because operons are switched off by the active form of the repressor
|
negative
|
|
|
Regulation of the trp and lac operons involves ________ control of genes
|
negative
|
|
|
Tryptophan is a _________
|
corepressor
|
|
|
Some operons are also subject to positive control through a stimulatory activator protein, such as _________________
|
catabolite activator protein
|
|
|
catabolite activator protein is an example of a [positive or negative] control.
|
Positive
|
|
|
When glucose (a preferred food source of E. coli ) is scarce, the lac operon is _________ by the binding of CAP
|
activated
|
|
|
When glucose levels increase, CAP detaches from the lac operon, turning it ____
|
off
|
|
|
Process in which genes normally off get turned on is known as _____________
|
induction
|
|
|
Lactose present, glucose scarce (cAMP level ____): abundant __________ synthesized
|
high; lac mRNA
|

