![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
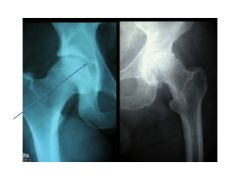
What is the space occupied here? What disease is the right?
|
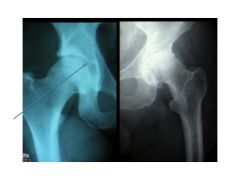
Hyaline cartilage. Osteoarthritis
|
|
|
What is the best way to image an SI joint fracture?
|
CT scan
|
|
|
What are the four ligaments of the hip joint? ("need to commit to memory"
|
ilio, ischial, pubo-femoral, ligamentum teres
|
|
|
The hip joint is made up of three bones:
|
Ilium, ischium, pubic bone
|
|
|
When are the ligaments of the hip most relaxed and most vulnerable? When is this a serious problem?
|
When their are flexed. Car accidents often cause dislocation bc of this where the hip is disclocated posteriorly.
|
|
|
When the hip is dislocated, it can damage the blood supply. Most often, this artery is damaged:
|
Medial circumflex femoral artery. PTs get avascular necrosis.
|
|
|
What muscle/nerve is affected in the Trendelenburg Gait? If someone has this injury and needs a cane, which side would that person hold the cane.
|
Gluteus medius/superior gluteus nerve. Hold cane on the opposite side of the painful hip.
|
|
|
What are the three compartments of the knee?
|
Medial, lateral femoral-tibial, and patello-femoral
|
|
|
What are the four main ligaments in the knee?
|
Medial/Fibular collateral; Anterior/Posterior Cruciate ligaments
|
|
|
What muscle is responsible for locking the knee? How does it rotate the knee?
|
Popliteus. It rotates the femur laterally relative to the tibia for flexion
|
|
|
When looking at an MRI, it's easy to distinguish between the medial and lateral compartment based on the convect/concavity. Which is which?
|
Convex = Lateral (latex)
Concave = Medial |
|
|
Define a 1st, 2nd and 3rd degree sprain.
Describe a sprain vs strain |
1st: Stretch
2nd: Partial tare 3rd: Complete tare Sprain = ligament Strain = muscles/tendons *straining your muscles |
|
|
When the posterior cruciate ligament is torn, the tibia is displaced:
When the anterior cruciate ligament is torn, the tibia is dispaced: |
Posteriorly
Anteriorly |
|
|
Anterior Drawer test vs Lachman test evaluates the ACL. Describe the difference. Which one's "better" and why?
|
Drawer: Evaluate flexes hip 45 degrees and the knee 90 degrees, sits on foot, and pulls knee anteriorly. The Lachman test holds the knee bent at 20-30 degrees and pull it back and forth. This places the hamstring and quads in balance to avoid the secondary effects of these muscles trying to hold joint in place.
|
|
|
The proximal tib-fib joint is a ? joint.
The distal tib-fib joint is a ? joint. |
Proximal = synovial joint (moveable)
Distal = Syndesmoses (fibrous) joint (non-moveable) |
|
|
What type of joint is the ankle joint?
|
Hinge joint
|
|
|
What are the three joints of the ankle?
|
1. Articular capsule
2. Medial (deltoid) ligament 3. Lateral ligament |
|
|
What are the most commonly sprain ligaments in the ankle?
|
1. Ant talo-fib
2. Calc-fib 3. Post talo-fib |
|
|
What ligament is sprained when a high ankle sprain happens?
|
Inferior tib-fib ligament
|
|
|
Why are deltoid sprains not often seen? What is more likely?
|
Bc it's extremely strong. More likely, you'll see an avulsion where the bone is broken off with the ligament attached. (especially the superficial deltoid attached to tibia)
|

