![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the medical term for bunyons?
|
Hallux Valgus
|
|
|
Hammer toe is caused by:
|
An extension of the metatarsophalangeal joint.
|
|
|
What causes bunions?
|
It's a varus deviation of the 5th toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint - protrusion of the joint causes greater contact with the insides of shoes, leading to irritation and discomfort.
|
|
|
What causes/is Morton's Neuroma?
|
Light shoes squeeze the bonds of the feet and cause compression of a branch of the plantar nerve. The condition is often a perineural fibrosis rather than a true tissue mass.
|
|
|
Review N500 re Femoral Artery branches.
1. What does the popliteal artery into after it branches off of the femoral artery? 2. How do they course and what does it supply? |
1. Anterior tibial artery and the Posterior Tibial Artery.
2. Anterior: Courses through the interosseous membrane to supply the anterior tissues of the lower leg. Posterior: Continues more distally in the posterior side of the leg. |
|
|
What does the Posterior Tibial Artery branch into?
|
Fibular (peroneal) artery and the posterior tibial artery.
|
|
|
What is unusual about the Fibular artery?
|
It's in the posterior compartment but it supplies the lateral compartment
|
|
|
At the knee, femoral artery become the:
|
popliteal artery
|
|
|
What are the two pulses typically checked on the foot?
(N522) |
Dorsalis Pedis Pulse
Posterior Tibial Pulse |
|
|
Clinical Q: Where is an embolism if there's a dorsalis pedis pulse but no posterior tibial pulse? (N500, N518, N520)
|
Somewhere between the Popliteal/Anterior Tibial artery branch point and the Posterior Tibial Artery
|
|
|
The Dorsal Venous Arch can drain in two directions, laterally and medially. Where does lateral drain into and what does medial drain into?
|
Lateral = Small saphenous vein and then ultimately into the DEEP popliteal vein. (N471, 3)
Medial = Great saphenous vein. |
|
|
What happens if someone gets a clot in the Anterior or Posterior Tibial Vein or Popliteal Vein?
|
Deep Vein Thrombosis
|
|
|
What happens if someone gets a clot in the superficial veins in the leg?
|
Superficial Thrombophlebitis
|
|

Label/circle the different compartments.
|
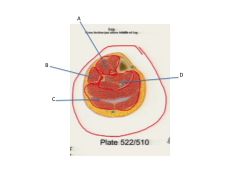
A. Anterior Compartment
B. Lateral Compartment C. Posterior Compartment D. Deep Section of the Posterior Compartment |
|
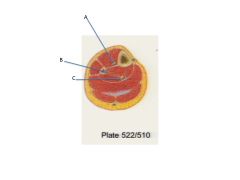
Label
**What muscles does B supply? Why is this unusual? |
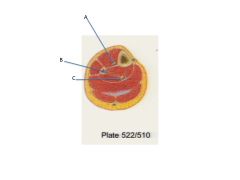
A. Anterior tibial artery and veins and deep fibular nerve
B. Fibular vessels C. Posterior tibial arterya nd veins and tibial nerve **Supply muscles in the lateral chamber. This is unusual because these vessels are in the posterior chamber! |
|
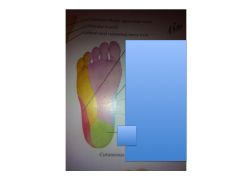
What is each area innervated by? (N510 and N529)
|
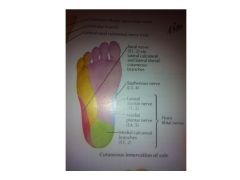
Red = Sural
*Yellow = Lateral *Green = Medial Calcaneal *Blue = Saphenous Pink = Medial Plantar * = All tibial n. Notice how these three make up the center of the foot and the two "S" areas innervate the lateral parts - Sural and Saphenous. Note also how the Tibial nerves make sense...lateral, medial, and calcaneal) |
|
|
Where are three areas where you find lymph nodes in the leg?
|
1. Deep Inguinal
2. Superficial Inguinal 3. Popliteal Lymph Nodes (behind knee) |
|
|
Anterior Compartment muscles of the leg include (3):
|
1. Tibialis anterior m
2. Extensor hallucis longus m 3. Extensor digitorum longus |
|
|
What is Jones' Fracture?
|
Fracture at the base of the 5th metatarsal - often due to tear-off of the Fibularis brevis tendon.
Fracture of the diaphysis of the 5th metatarsal. |
|
|
On extensor side of the foot (top), describe where the veins that reach toes come from.
|
Anterior Tibial Artery to Arcuate Arch to Tarsal Arteries to Phalangeal arteriers
|
|
|
On plantar side of the foot, describe where the veins that reach the toes come from. (N519, 523)
|
Dorsalis pedis artery (remember, posterior medial aspect of foot) to plantar artery supply/branch into the medial plantar artery and lateral plantar arch that supplies the plantar metatarsal and the the digital arteries.
|
|
|
What muscles does the Common fibular (peroneal) n supply?
|
Deep peroneal (fibular) nerve supplies:
1. Anterior compartment muscles. 2. Leg muscles 3. Extensor digitorum brevis muscles |
|
|
The Tibial n becomes the medial and lateral plantar nerves and the medial plantar n supplies these (4) muscles (N529):
|
1. Abductor hallisus
2. Flexor hallisus brevis 3. Flexor digitorum brevis 4. Most medial lumbricals |
|
|
What does the Lateral Planter n supply?
|
With the Medial planter n, the lateral planter supplies a of the remaining intrinsic foot muscles.
|
|
|
What is the only flexor foot muscles?
|
Extensor digitorum brevis
|
|
|
What are the Plantar Layers?
|
1. Skin
2. Plantar Aponeurosis (fasciatis occurs here) 3. Abductor hallicis 4. Flexor digitorum brevis 5. Abductor digiti minim |
|
|
Describe the origin/insertion, vessel, and nerves of the Abductor Hallucis
|
1. Originates at calcaneous, inserts at the proximal phalynx of the great toe.
2. Motor n = medial plantar n, helping to flex the big toe |
|
|
Describe the origin/insertion of the flexor digitorum brevis.
|
It splits or spreads toes.
In originates at the calcaneous and inserts into the middle phalanx of digits 4-5. |
|
|
Describe the origin and innervation of the Abductor digiti minimi
|
Originates from calcaneous
N = lateral plantar n Allows you to abduct small toe and helps with flexion a bit too |
|
|
Describe the 2nd layer of the foot msucles:
|
1. Quadratus Plantae muscle
2. Lumbricals |
|
|
Describe where the Quadratus Plantae Muscle
|
1. Originates from the calcaneous
2. Inserts into the posterior margin of the flexor digitorum longus before it splits 3. It adjusts the pull of the flexor digitorum 4. |
|
|
Look at N522. Notice that the tend for the flexor digitorum longus runs medially. If this muscle that's attached and directly posterior to the tendon didn't exist, the toes would be pulled medially. This muscle aligns the flexion more anterior-posteriorily.
|
Quadratus Plantae m
|
|
|
1. What digits does the Lumbricles attach to?
2. Where do they originate? 3. Where do they insert? 4. (Don't memorize) How are they innervated? |
1. Digits 2-5
2. Originate from the tends of the flexor digitorum longus 3. Insert on the expansions of the extensor digitorum longus on the medial side 4. Motor nerve supply toes 2 medial plantar n; 3-5 lateral plantar n. (don't memorize) |
|
|
Describe the 3rd layer of foot muscles.
|
1. Flexor hallucis brevis
2. Adductor hallucis muscle 3. Flexor digiti minimi brevis |
|
|
N523
1. Does the flexor hallucis brevis muscle do? 2. Where does it originate 3. Where does it insert? 4. How is it innervated? |
1. Helps flex the big toe
2. Originates from the cuboid and the lateral cuniform bones 3. Splits/Inserts at the sesmoid bones 4. Medial plantar n |
|
|
1. Where does the Adductor hallucis originate?
2. Where does it insert? 3. What does it do? |
1. Originates from the 2-4 metatarsals
2. Inserts at proximal phalynx of great toe. 3. It pulls the big toe back, adducting it. |
|
|
NN523)
1. Describe where the flexor digiti minimi brevis originates. 2. Where it inserts 3. What it's innervated by 4. What it allows you to do. |
1. Originates at the 5th metatarsal
2. Inserts on the proximal phalynx of the 5th toe 3. Innervated by lateral plantar 4. Allows you to flex little toe |
|
|
How does the axis of abduction/adduction differ in the foot vs hand?
|
In Hand it's around 3rd digit.
In foot, it's around 2nd |
|
|
What are the muscles of the 4th layer? How do they move the toes?
|
1.Plantar Interosseus (Remember PAD - Plantar Interosseus mm Are ADductors)
2. Dorsal Interosseus (Dorsal interosseus mm are ABductors) |

