![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where do most fractures of the hip happen?
|
Femoral neck
|
|

Label
|

A. Medial/Lateral Condyles
B. Intercondylar Notch C. Epicondyles D. Adductor Tubercle |
|
|
What is the point of fascia?
|
To increase the efficiency of the muscles - both in power and fatigue.
|
|
|
What causes "snapping"
|
IT band - Iliotibial Band
|
|
|
Where does the IT band originate/insert?
|
Iliac crest to lateral condyle of tibia.
|
|
|
The saphenous opening is inferior to:
|
The inguinla ligament
|
|
|
What passes through the saphenous opening? To join what?
|
Great saphenous passes through to join the femoral vein.
|
|
|
Medially, you've got the iliacus. Laterally, you've got:
|
Gluteus medius.
|
|
|
Anterior Snapping Hip:
1. Muscle involved 2. Painful movement? 3. What structure does the muscle "snap" over? |
1. Iliopsoas
2. Flexion/extension 3. Tubercle |
|
|
What are the three anterior hip muscles?
|
1. Iliopsoas
2. Psoas major 3. Iliacus |
|
|
What is the most powerful flexor of the thigh at the hip? Where does it insert?
|
Iliopsoas - inserts on the lesser trochanter
|
|
|
What is the origin of the Psoas major? What is it innervated by?
|
1. T12 to L5
2. Innervation = ventral rami of L1, L2, L3 |
|
|
What is the iliacus innervated by?
|
The femoral nerve.
|
|
|
What does the Tensor Fascia Lata tighten? What is its insertion and innervation?
|

The iliotibial tract - where it also inserts.
Innervation = superior gluteal nerve |
|
|
What action does the tensor fascia lata have?
|
1. Internally rotates the hip
2. Also stabilizes the hip when you're doing a leg kicking action - important for walking, running |
|

What muscle is this?
|

Obturator externus
|
|
|
The obturator externus is a powerful ? but a weak ? (two movements)
|
Lateral rotator
Adductor |
|
|
What is the innervation for the obturator externus?
|
Obturator nerve
|
|
|
The anterior thigh muscles are innervated by:
In general, what kind of action are they responsible for? |
The femoral nerve
Extensors |
|

What muscle is this?
|

Sartorius
|
|
|
How does the sartorius move the thigh?
|
Flexes, abducts and laterally rotates it
|
|
|
Where does the sartorius originate? Where does it insert?
|
Originates in ASIS: Anterior Superior Iliac Spine.
Inserts at medial tibia. |
|

What muscle is this?
|

Rectus Femoris
|
|
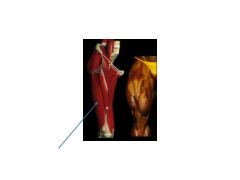
What muscle is this and where does it originate/insert?
|

Vastus Lateralis.
Originates at greater trochanter and lateral lip linea aspera. Inserts at lateral patella retinculum |
|
|
Describe an avulsion injury involving the rectus femoris - comparing children to adults.
|
1. Avulsion is the tearing of the tendon from the ASIS.
2. With a growth plate there, children typically tear the growth plate while adults typically tear the tendon. |
|

What muscle is this? Where dies it originate/insert
|

Vastus Medialis. Originates at intertrochanteric line and linea aspera. Inserts at medial patellar retinaculum
|
|
|
Often when there is a patellar irritation, there is an imbalance between these two muscles:
|
Vastus lateralis and Vastus medialis.
|
|
|
BTW, what is weak in Trendelenburg gait and what nerve is usually affected?
|
Trendelenburg and superior gluteal nerve.
|
|
|
The muscles in the medial thigh are what type of muscles?
|
Adductor muscles
|
|
|
What are the adductor mucles (there are four...the fourth one is a group of two).
|
1. Gracilis
2. Pectineus 3. Adductor Longus 4. Adductor Brevis 5. Adductor Magnus (two parts: Adductor and Hamgstring) |
|
|
What is the most superficial and weakest adductor? Where does it originate and where does it insert?
|

The gracilis. Originates on the inferior ramus of pubis. Inserts at superior part of medial tibia.
|
|

1. What muscle is this?
2. What muscles does it lie between? 3. What vein runs between it and the iliopsoas? 4. What artery lies between it and the adductor longus? |

1. Pectineus
2. Iliopsoas and Adductor longus muscles 3. Medial circumflex artery 4. Deep femoral artery |
|
|
What is the pectineus innervated by?
|
The femoral nerve.
|
|
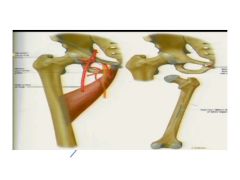
1. What muscle is this?
2. How does it move the leg? 3. Where does it originate? 4. Where does it insert |

1. Adductor longus
2. Adducts and flexes thigh and medial rotator 3. Originates at body of pubis 4. Inserts in middle third of linea aspera |
|

1. What muscle is this?
2. What part is the adductor portion and which the hamstring? 3. What is the adductor innervated by? Hamstring? 4. Where does it originate? 5. Where does adductor insert? 6. Where does hamstring insert? |
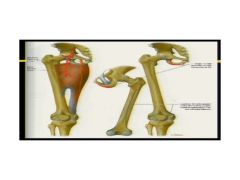
1. Adductor magnus
2. obvious 3. Adductor = obturator n; Hamstring = tibial portion of sciatic n 4. Adductor originates from Inferior ramus of pubs; Hamstring originates from ischial tuberocity (same place?) 5. Adductor inserts on gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera; Hamstring = tibial portion of sciatic nerve |
|

1. What muscle is this?
|

1. Biceps femoris
|
|
|
What are three muscles of the posterior thigh or "hamstring"?
|
1. Semitendinosis
2. Semimembranosis 3. Biceps femoris |
|
|
Where is the most common location for hamstring tear?
|
Musculotendonous junction
|
|

What region is the rectangular arrow pointing to? What three muscles/tendons attach here?
|

Pes anserinus. Sartorius muscle, gracilis tendon, semi-tendinous tendon
|
|
|
What three boundries make up the femoral triangle? What are its contents? (hint, 4 things and its easy if you remember "femoral")
|
SAIL: Sartorius, Adductor longus, Inguinal Ligament,
Contents: Femoral artery, vein, and nerve. Inguinal lymph nodes. |
|
|
Knowing that the femoral nerve, artery and vein exist in the femoral triangle, how would you attempt to draw venous blood?
|
Know the order of these structures going medial to lateral: Vein, Artery, Nerve. So, feel the pulse, and stick medial.
|
|
|
What does the femoral sheath contain?
|
Femoral vessels - IT DOES NOT INCLUDE THE FEMORAL N.
|
|
|
What are the boarders of the Adductor Canal?
|
VAS: Vastus Medialis
Adductor Longs Sartorius |
|
|
What are the contents of the adductor canal?
|
Femoral artery and vein
Saphenous N. |
|
|
What does the Adductor Hiatus function as a junction for? Vessels pass through this and when they do, their names changed. From what to what?
|
It functions as a junction between the adductor canal and the popliteal fossa.
From Femoral Artery/Vein to Popliteal Artery/Vein |
|
|
What are the three major Arteries of the Thigh?
|
Femoral
Profunda Femoris (perforating branches) Circumlex (medial, lateral) |
|
|
What are the two major veins in the thigh?
|
Great saphenous
Small saphenous |

