![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Key features of microscopic colitis.
|
Chronic diarrhea, mucosa looks normal. need biopsy.
|
|
|
Crohn's Disease vs Ulcerative Colitis:
Inflammatory patterns Granuomas Location of inflammation |
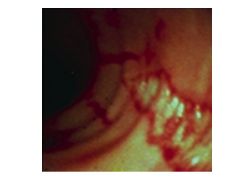
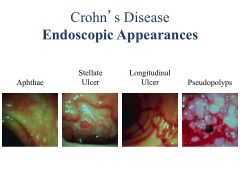
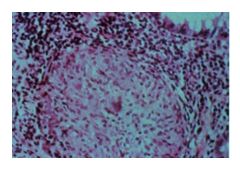
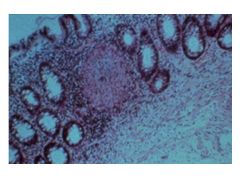
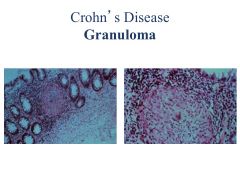
Crohn's: patchy (SKIP LESIONS), transmural; affects any part of GI tract
Noncaseating granuloma Ulcerative: DIFFUSE mucosal; limited to colon; affects rectum but can expand to rest of colon Non-granulomatous |
|
|
Crohn's Disease vs Ulcerative Colitis:
Peak age of presentation Effect of smoking Effect of appendectomy |
Crohn's:
First peak--teens/20's Second peak: 7th-8th decade Smoking is a RISK FACTOR Appy may be a RF Ulcerative colitis: Teens and 20's: first peak 7th-8th decade: second peak Smoking is PROTECTIVE Appy is PROTECTIVE |
|
|
Crohn's Disease vs Ulcerative Colitis:
Monozygotic Concordance Dizygotic Concordance |
Crohn's:
Monozygotic concordance: 44-50% Dizygotic: 8% Ulcerative Colitis: Monozygotic: 5-14% Dizygotic: 0% |
|
|
Nod2:
AKA Function Associated Disease |
Nod2 = CARD15
Protein that recognizes bacterial Ag's and releases NF-kappa B Associated w/Crohn's |
|
|
The gut is normally in a state of ______.
How does this relate to IBD? |
Note: NOD2-->Defensins (natural Abx)
Normally gut is mildly inflamed; most of us able to down-regulate it. Those who can't advance to IBD. |
|
|
This cytokine is linked to both Crohn's and IBD.
Effects of cytokine? |
IL-23 (linked to Crohn's and IBD)
Drives innate and T cell-mediated inflammn |
|
|
These cytokines suppress immune responses.
|
TGF-beta
IL-10 |
|
|
Crohn's Disease vs Ulcerative COlitis:
Presentation Extracolonic Involvement |
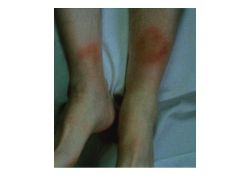
Crohn's: Diarrhea, n/v, wt loss, fever, FISTULA
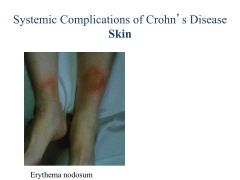
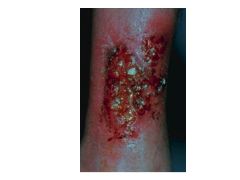
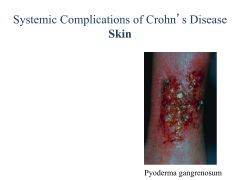
Extratest involvement: erythema nodosum, arthritis, uveitis UC: Rectal bleeding! Tenesmus (push to poop but can't go)/cramping Diarrhea Extracolonic: Arthritis, erythema nodosum, uveitis |
|
|
How does IBD differ from IBS?
|
IBD has anemia, high PLT, high sed rate, low albumin
IBD has weight loss, fever, perianal dz, bloody stools, tenesmus (strain to poop and nothing comes out), fecal WBC, occult blood IBS has none of these things! |
|
|
Acute Infection vs IBD:
Duration of Symptoms Onset of Symptoms PLT HCT Biopsy Results |
Acute Infection:
Syx <2 weeks, abrupt onset, nl PLT, nl HCT, nphils on bx IBD: Syx >4 weeks, insidious onset; PLT >450K; low HCT, bx shows abnml crypt architecture, lymphoid aggregates, basal plasmacytosis |
|
|
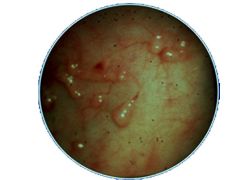
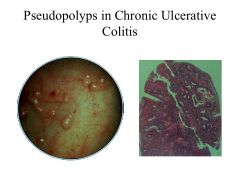
Pseudopolyps are indicative of ________.
|
Chronic ulcerative colitis
|
|
|
Ulcerative colitis:
Current surgical option |
Ileo-anal anastomosis with reservoir (attach ileum to rectum after colectomy)
|
|
|
Fistulas are a complication of _______.
|
Crohn's disease
Can happen anywhere (air in urine = fistula to bladder) |
|
|
What is the most common extraintestinal symptom of IBD?
|
Peripheral arhritis
Note: it is monoarticular, asymmetrical and favors large joints over small joints (no synovial destruction!) |
|
|
What are the systemic complicaitons of small bowel inflammation?
|
Bile-salt wasting or depletion, Gall stones
Bile-salt depletion-->malabsorption, bacterial overgrowth Kidney stones, fistulae, amyloidosis |
|
|
All IBD patients should have testing for ______.
Why? How does this differ for CD and UC? |
All IBD pts should have vit D testins bc osteoporosis occurs in 20-30% of IBD pts.
All CD pts should get bone scan (DEXA); UC if using steroids/RF. Ca2+/Vit D prophylaxis, bisphosphonates too! |
|
|
How is IBD presentation different in children?
|
Fall off growth curve (avoid steroids)
|
|
|
Risk factors for ischemic colitis.
|
Smoking, birth control, age
|
|
|
Sulfasalazine:
MOA Indication |
Pro-Drug: Sulfapyridine + 4-ASA
cleaved by gut bacteria-->reduces inflammation in pts w/UC |
|
|
Sulfasalazine:
Sulfa vs 5-ASA AE's Combined AE's |
Sulfa:
Male infertility Hemolytic anemia Agranulocytosis 5-ASA: Nephritis Both: Alveolitis Pancreatitis |
|
|
Steroids:
Use in UC |
Excellent for induction medication in UC and CD
Do not work for maintenance LOTS OF SIDE EFFECTS |
|
|
This drug has 90% first pass metabolism by the liver.
Why is this a good thing? |
Budesonide
only 10% makes it to systemic circuln; since this is a steroid drug, this will limit its side effects! |
|
|
Azathioprine/6-Mercaptopurine:
MOA AEs |
Inhibits purine synthesis
Inhibits T-helper activity AEs: Hypersens rxns (fever, rash, pancreatitis, hepatitis) BM suppression Opportunistic Infections NO STEROID-LIKE COMPLICATIONS |
|
|
Infliximab:
AEs |
Infusion rxns
TB (!!), fungal infections HBV reactivation |
|
|
IBD patients:
Vaccine recommendations |
Annual influenza
Pneumoccocal vaccine if immunosuppressed (steroids etc) HBV/HAV if not immune HPV in women Varicella |
|
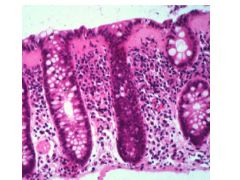
|
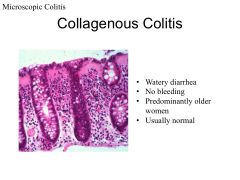
|
|
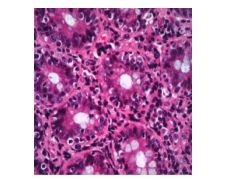
|
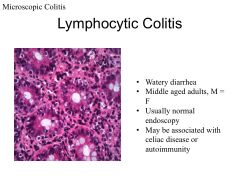
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

