![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Skeletal muscle consists of three tissues: Skeletal myocytes, Endothelial, and Connective Tissue Fibroblasts. Cardiac Tissues has three tissue types as well...what are they?
|
1. Cardiac myocytes
2. Endocardium (inner most layer of cells lining the chambers) 3. Cardiac fibroblasts |
|
|
Similar to Sk m, each cardiac myocyte is surrounded by:
|
Basal lamina
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle fibers are large and can have thousands of nuclei located peripherally. What about cardia myocytes?
|
Smaller with nucleus located centrally.
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle is primarily: (Energy production means). This is metabolic strategy is reflected in its cellular matrix, including:
|
It is high aerobic, therefore:
1. Highly fascular 2. Lots of mitochondria 3. Lots of myoglobin 4. Lots of lipid droplets |
|
|
The creatine kinases can be used to diagnose skeletal or cardiac tissue damage. Which one is used to identify each respectively?
|
1. MM-CK = skeletal
2. MB-CK = cardiac |
|
|
What structural feature of cardiac cells allow the cells to beat together?
|
Intercalated discs.
|
|
|
In a cross section of cardiac myocytes, what would you expect to see with respect to vascularization?
|
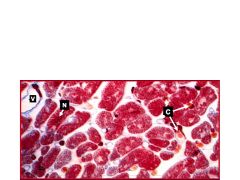
Since it is highly vascularized, you'd expect to see venules and capillaries
|
|
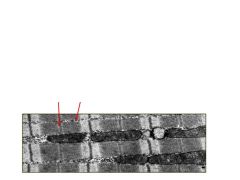
This is a longitudinal section of a cardiac cell. What are the arrows pointing to and what are the two major differences seen here compared to skeletal muscle?
|
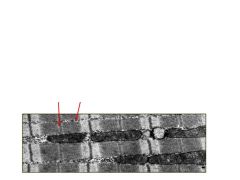
Arrows are pointing to the M line where MB-CK is located (MM-CK in skeletal). And glycogen granuals - Sk doesn't have this - nor does it have as many mitochondira.
|
|
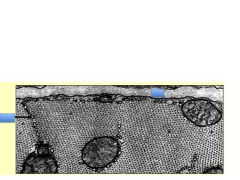
In this cardiac cross section, the blue boxes are covering IDs for what structures?
|
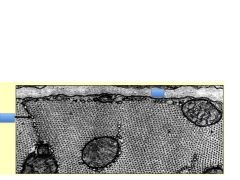
1. Basal lamina
2. Sacroplasmic reticulum |
|
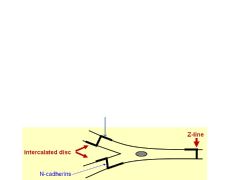
Cardiac muscles has Z-bands with an additional transverse component (arrorw) - what is this for?
|
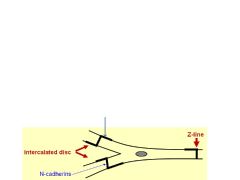
To transmit contractile force, thereby increasing the strength in contractility.
|
|
|
The lateral part of the intercalated discs have Fascia Adherens and Desmosomes. Where are these structures primarily located? Why is this important? What is the major component of the Fascia Adherens?
|
Located between cells. Important for cell-to-cell communication and sync'd beats. Fascia adherens mostly consists of N-cadherins.
|
|
|
The Intercalated Discs of cardiomyocytes also have a lateral part for cell-to cell signaling. What are these structural components?
|
Gap junctions (syn nexus) bade up of connexin molecules and some desmosomes.
|
|
|
What is the critical difference between fascia adherens and zonula adherens?
|
Zonula Adherens complete encirles the cells vs Fascia Adherens that does not.
|
|
|
The atrial myocytes are larger or smaller than ventricular myocytes? Do they have have more or less sarcomeric structure?
|
1. Smaller
2. Less |
|
|
Atrial myocytes contain membrane bound granules near their nuclei that contain:
What does it do? |
A hormone termied Natriuretic Factor that causes the kidney to eliminate water and sodium, vasodilation, etc.
|
|
|
What type of myocytes does the Bundle of His contain?
|
Purkinje myocytes
|
|
|
When developing coronary arteries secrete endothelin, they cause nearby myocytes to differentiate - what is the order of differentiation?
|
Endothelin --> cardiac myocyte --> Purkinje fiber. May form the basis for regenerating cardiac pacemaker tissue.
|
|
|
The endocardium is composed of a single layer of:
|
Endothelial cells
|
|
|
What are the most abundant cell type in the heart (although most numerous, they do not take up the most volume bc they're small)
|
Cardiac fibroblasts.
|
|
|
If you saw a pt exhibiting symptoms of DMD, what would you measure? What about a pt with heart attack?
|
DMD = MM-CK
Heart Attack = MB-CK |
|
|
What are cardiac myocytes innervated by?
|
Branches of the vagus nerve (X) and autonomic nerves.
|
|
|
Of the three troponins, what is released/measured when a heart attack happens?
|
cTnI
|
|
|
Heart attack wound healing begins at day:
Cardiac fibroblasts secrete this: and then this: Ultimately creating a scar by day:: |
1. Day 2-3
2. Fibroblasts secrete collagen--III, then collagen-I to ultimately create scar by day 5 |
|
|
Heart attack wound healing begins at day:
Cardiac fibroblasts secrete this: and then this: Ultimately creating a scar by day:: |
1. Day 2-3
2. Fibroblasts secrete collagen--III, then collagen-I to ultimately create scar by day 5 |
|
|
What are the five steps of heart attack:
|
1. Myocyte death
2. Inflammation 3. Wound healing 4. Angiogenesis 5. Scar formation |
|
|
What are the five steps of heart attack:
|
1. Myocyte death
2. Inflammation 3. Wound healing 4. Angiogenesis 5. Scar formation |
|
|
Can cardiac myocytes divide?
|
No
|
|
|
Can cardiac myocytes divide?
|
No
|
|
|
With respect to the cell cycle, what is an example of how researchers are trying to repair injured heart tissue?
|
By disinhibition of the tumor suppressors that normally keep cardiomyocytes in replicative senescence (Go of the cell cycle). Class eg., Rb, p16
|
|
|
What is the niche of adult cardiac resident stem cells? What two cell marks are used to identify them?
|
They are found outside of the cardiac myocyte and just outside of the blood vessels. They are identified via cell markers: islet-1 and/or c-KIT
|
|
|
A few promising studies show that adult cardiac stem cells can be transplanted and improve heart function. However, Lough doesn't believe that the cells were replaced but that this happened:
|
The paracrine effect - where the transplanted cells secrete factors that enhance cells in the myocardium.
|
|
|
Rather than stem cell harvest, fibroblasts can be converted to stem cells using:
What are these converted cells called? |
1. 4 TF are injected into fibroblasts
2. They become induced pluripotent cells 3. Cardiogenic growth factors are added 4. They become cardiomyocytes 5. Transplantation |
|
|
What are two problems with using iPSCs?
|
1. They take a lot of time to make
2. They often turn into tumors or unwanted cell types. |

