![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
J point |
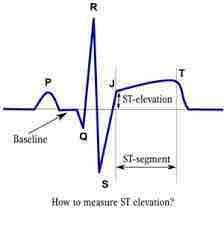
Junction between end of QRS complex and onset of ST segment |
|
|
Intervals we measure on ECG |
PRinterval: fromSA node → AV node/bundle of His QRS interval: depolarization allthroughout ventricles QT interval: repolarization (include QRSdepolarization) b/c there is a more discrete place to start measuring |
|
|
QRS axis |
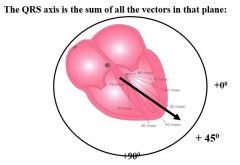
|
|
|
ECG axis |
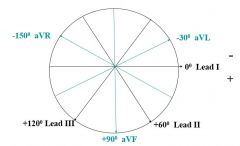
|
|
|
If you have marked hypertrophy of the R ventricle, what happens to the axis of the heart? |
Right axis deviation (>+105 degrees) |
|
|
If you have marked hypertrophy of the L ventricle, what happens to the axis of the heart? |
Left axis deviation (>-30 degrees) |
|
|
What is axis deviation a clue to? (2) |
Ventricular hypertrophy Interruptions in normal depolarization - abnormal pathways of depolarization |
|
|
Normal QRS axis is ______ |
between -30 and +105 |
|
|
How to identify QRS axis |
1) Chart the direction of any two leads at their correct points on the axis 2) Examine QRS complexes for upward deflections (same direction as lead) or downward deflections (opposite direction from lead) and plot potential lead directions on axis 3) Find overlapping quadrant - you know the axis has to be in this quadrant 4) For more precision, find an isoelectric lead and plot this lead's position on the axis 5) You know that the axis has to be perpendicular to the isoelectric lead and in the quadrant identified in step 3 |
|
|
Right atrial enlargement |
Tall P wave in lead I, II, III, or aVF (>/= 3 mm) |
|
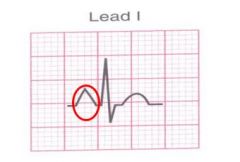
|
Right atrial enlargement |
|
|
Sign of left atrial enlargement on ECG? |
P mitrale in lead II Negative (or late negative) deflection in V1 (must be 1 box deep and 1 box wide to qualify) |
|
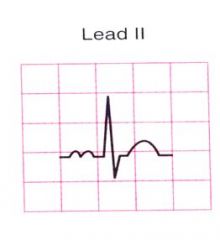
|
P mitrale - left atrial enlargement |
|
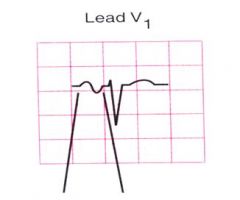
|
Left atrial enlargement - late negative deflection in V1 |
|
|
Criteria for ventricular hypertrophy are based on... |
size of QRS |
|
|
What lead to examine for RVH? |
Size of QRS complex in V1 |
|
|
Criteria for R ventricle hypertrophy? What do you often see as well? |
RVH = > 7 mm in V1 Also may see right axis deviation and right atrial enlargement (however absence of RAE does not preclude RVH) |
|
|
Left ventricular hypertrophy criteria |
1) Voltage criteria: R in V5 or V6 > 26 mm, or R in aVL >/= 11 mm, or S in V1 + R in V5 or V6 =/> 35 mm 2) Left atrial enlargement: atrium contracting meets increased resistance with stiff ventricle 3) Abnormal repolarization: ST-T wave changes: "strain pattern" - inversion of lateral T wave and ST segment is depressed compared to baseline |
|
|
Potential causes of low voltage? |
Obesity, emphysema, infiltrative cardiomyopathy, pericardial effusion |

