![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Macrocytic vs Megaloblastic Anemias
|
Macrocytic: Big RBCs
Megaloblastic: Impaired DNA production in setting of normal RNA production in production of RBCs |
|
|
Effect of B12 deficiency on DNA metabolism.
|
No B12--> folic acid gets stuck as MTHF (?) and isn't available for DNA metabolism (megaloblastic anemia!)
|
|
|
Vitamin B12:
Source Must be bound to ______ |
Animal origin
Must be bound to intrinsic factor released by stomach |
|
|
Transcobalamin I vs Transcobalamin II:
Cell Transfer Function Manifestation of HereditaryDeficiency |
Transcobalamin I:
Poor B12 transfer to cells Binds and stores B12 Deficiency-->dec'd serum B12, no anemia Transcobalamin II: Rapid transfer of B12 to cells Transports B12 Deficiency-->megaloblastic anemia |
|
|
Pernicious Anemia:
Genetic Features Pathophys Symptoms |
Occurs in family members, identical twins; inc'd incidence of auto-ab's in unaffected relatives (rheumatoid arthritis)
Pathophys: auto-ab's to gastric parietal cell cytoplasm, anti-intrinsic factor ab's Syx: (there aren't many!) Syx of anemia Paresthesias (pins and needles) |
|
|
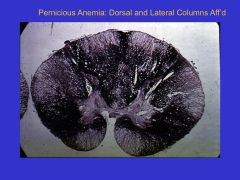
Neurologic Manifestations in Pernicious Anemia:
Location of Lesions Mild vs Moderate vs Severe Syx |
Located in dorsal columns (demyelination)
Mild: Paresthesia (none or slight impairment of touch/temp sensation) Mod: Weakness, undsteady gait, clumsiness; dec'd vibration and position sense; positive Rhomberg Severe: Severe weakness, spasticity; hyperreflexia, clonus, babinski; affects DORSAL AND LATERAL columns |
|
|
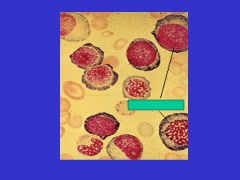
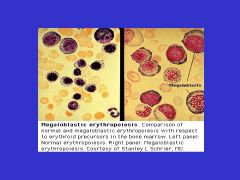
Ineffective Erythropoiesis:
What is it? |
Inc'd erythroid precursors when compared with released reticulocytes
Inc'd plasma iron turnover Dec'd life span of circulating RBCs |
|
|
What is achlorhydria and how can it be used to detect B12 deficiency anemia?
|
Gastric pH >3.5
pH does not drop after administration of histamine in patients with B12 def |
|
|
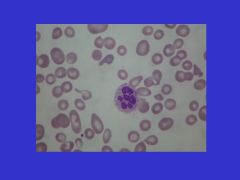
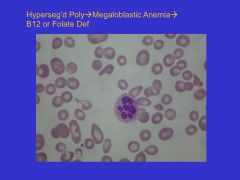
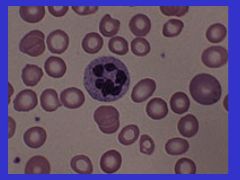
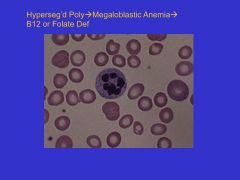
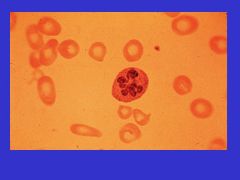
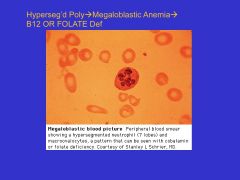
Hypersegmented _____ are indicative of _____.
|
Hypersegmented polys are indicative of megaloblastic anemia (B12 def)
|
|
|
B12 is absorbed in the _______.
|
Terminal ileum
|
|
|
What does each part (I, II, III) of the Schilling test determine?
|
Part I: Is B12 absorbed normally? Will pee out radiolabeled B12. Seen in vegans.
Part II: Can abnl absorption be corrected by intrinsic factor? If pee out B12 (because gave hot B12 and intrinsic factor), then lacking IF. Part III: Is abnl absorption result of intestinal bacterial overgrowth? Could be due to gastrectomy! |
|
|
What symptom of pernicious anemia does NOT resolve in response to B12 supplementation?
|
Achlorhydria
|
|
|
What disease of the ileum affects B12 absorption?
|
Crohn's Dz
|
|
|
When is oral B12 indicated?
|
In those with B12 dietary deficiency (vegans)
|
|
|
Cyanocobalamin:
Methods of administration Uses |
Used for treating non-dietary B12 deficiencies
Administered parenterally or SQ |
|
|
How does folic acid differ from B12?
Absorption Transport Stores |
Folic Acid: absorbed in jejunum, doesn't require protein transporter; stores last 6 weeks
|
|
|
Causes of folate deficiency:
General Medications Syndromes |
Dietary deficiency
Inc'd requirements (pregnancy, infancy, hemolysis) EtOH*** Methotrexate (antifol), Dilatin (anticonvulsant) Malabsorption syndromes (gluten intol) |
|
|
What clinical features does folate deficiency share with B12 deficiency?
What feature is not shared? |
Shared:
Due to Anemia: pallor, tach, wide pulse pressure, angina, CHF, dypnea NO NEUROLOGIC DYSFN |
|
|
Folate replacement therapy:
General examples In response to methotrexate |
General:
Oral folic acid Aqueous folic acid soln (IV, SQ, IM) FOLINIC ACID in response to methotrexate |
|
|
When is prophylaxis for folate deficiency indicated?
|
Before and during pregnancy (reduces NT defects)
Hemolytic states Pts receiving total parenteral nutrition |
|
|
What will be elevated with folate deficiencies?
|
Elevated serum homocysteine
|
|
|
What will be elevated with B12 deficiencies?
|
Elevated serum homocysteine and MMA (methylmalonic acid)
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

