![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is infarct?
|
caused by local ischemia, there is coagulation necrosis most often because of an embolus or thrombus.
keep in mind that an embolus is just a free-moving thrombus |
|
|
What are the four categories of myocardial ischemia?
|
1. noninfarction subendocardial ischemia (classic angina)
2. Non-Q wave (Non-ST elevation) infarction 3. Noninfarction transmural ischemia 4. ST elevation/Q wave infarction |
|
|
What are the EKG manifestations of
1. noninfarction subendocardial ischemia (classic angina) 2. Non-Q wave (Non-ST elevation) infarction 3. Noninfarction transmural ischemia 4. ST elevation/Q wave infarction |
1. transient ST depressions
2. ST depressions or T wave inversions without Q waves 3. transient ST elevations or paradoxical T wave normalization, sometimes followed by T wave inversions 4. New Q waves preceded by hyperacute T waves/ST elevations and followed by T wave inversions |
|
|
What is the trend of the conduction vector for tissue surrounding ischemic tissue?
|
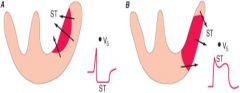
the healthy cardiac tissue projects a conduction vector toward the ischemic tissue
|

