![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
According to the recent systematic reviews:
‣ > _% of implants will successfully osseointegrate ‣ 5 years survival rate: _% ‣ 10 years survival rate: _% (in single crown cases) |
98%
95% 89% |
|
|
|
|
|
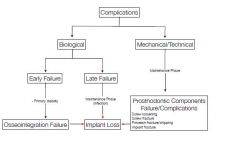
Mechanical complications can be the following types
|
Implant related (implant fracture)
Connection-related (loosening, fractures) Suprastructure-related (framework, veneer, loss of retention) |
|
|
Mechanical/ prosthetic complications
What are 5 yr Success rate of FDP on Implant vs Tooth? |
Implant 61.3%
Tooth 84.3% |
|
|
What is the highest cause of mechanical failure of FDP on tooth?
|
Loss of vitality
|
|
|
What is the highest cause of mechanical failure of FDP on implants ?
|
ceramic chipping or fracture
|
|
|
What is the highest cause of mechanical failure of Single Crown on implant?
|
Loose abutment or screw
|
|
|
List the types of mechanical complications
|
Caries in abutment
Loss of vitality Loss of retention Framework fracture Ceramic chipping or fracture Abutment tooth/ implant Loose abutment or screw |
|
|
What is the aetiology for fracture ceramic chipping or fracture?
|
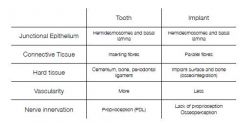
Absence of periodontal ligament
Leading to loss of proprioception Dependence of mechanoreceptors in the surrounding bone (osseoperception) - difficulty in food location, control of force and direction, no reflex Patient factors: bruxism, hx of complications Technical factors: length of suprastructure, cantilever, screw vs cement |
|
|
How to prevent mechanical complications?
|
Patien rsk assessment
occlusal analysis Restoration driven implant placement Allow access to oral hygiene |
|
|
How to manage mechanical complication?
|
occlusal adjustment
Repair |
|
|
What are the Biological complications?
|
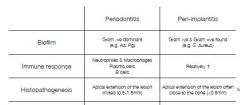
Peri-implant mucositis
Peri implantitis Soft tissue complications: fistula, excessive swelling, hyperplasia, etc |
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
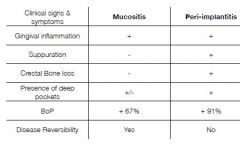
What to look for during the clinical exam to Dx?
|
• Plaque assessment
• Mucosal conditions: Swelling, fistula, redness, etc. • Peri-implant probing depth/ attachment level: PPD≥5mm • Bleeding on Probing (BoP) • Radiographs |
|
|
T/F
Implant mobility is not a common feature and poor indicator |
True
|
|
|
Can a regular probing damage the peri-implant soft tissues?
|
Separations do occur but will restore in 5 to 7 days
|
|
|
What are the methods of management of peri-implant mucositis?
|
• Removal of suprastructure if possible
• Removal of plaque and calculus • OHI • +/- antiseptics (0.2% CHX) |
|
|
What are the methods of management of peri-implantitis?
|
Cumulative Interceptive Supportive Therapy
|
|
|
What is Cumulative Interceptive Supportive Therapy?
|
PPD <3mm: Mech debridement/polishing and scaling
PPD 4-5mm: Antiseptic cleaning (CHX gel 2x a day) PPD >5mm: Systemic or local AB therapy, resective/regenerative surgery |

