![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Function |
A function f is a rule that assigns to each element x in a set D exactly one element, called f(x), in a set E. |
f(x) |
|
|
Domain |
The set D of the function |
|
|
|
f(x) |
The value of f at x and is read "f of x" |
|
|
|
Independent variable |
A symbol that represents an arbitrary number in the domain of a function f |
|
|
|
Dependent variable |
A symbol that represents a number in the range of f |
|
|
|
Machine |
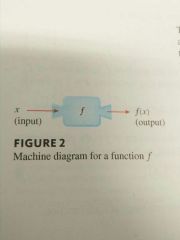
Helpful way to think of functions.
If x is in the domain of the function f, then when x enters the machine, it's accepted as an input and the machine produces an output f(x) according to the rule of the function. Thus the domain is the set of all possible inputs and the range is the set of all possible outputs. |
|
|
|
Arrow diagram |

Another helpful way to look at functions. Each arrow connects an element of D to an element of E. The arrow indicates that f(x) is associated with x, f(a) is associated with a, and so on. |
|
|
|
Graph |
If f is a function with domain D, then its graph is the set of ordered pairs: {(x,f(x)) | x is in D} In other words, the graph of f consists of all points (x,y) in the coordinate plane such that y=f(x) and x is in the domain of f. |
|
|
|
Difference quotient |

The average rate of change of f(x) between x=a and x=a+h. |
|
|
|
The Vertical Line Test |
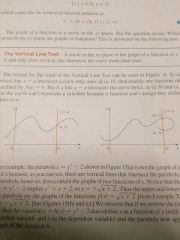
A curve in the xy-plane is the graph of a function of x if and only if no vertical line intersects the curve more than once. |
|
|
|
Piecewise defined functions |

Functions defined by different formulas in different parts of their domains. You would follow the rules to find the coordinates necessary to graph the function. |
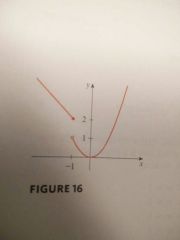
|
|
|
Absolute value |
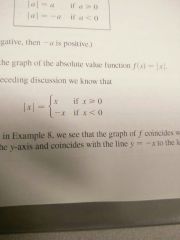
The distance from a to 0. Denoted by |a|. Always positive or 0. |
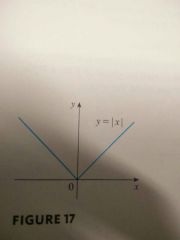
|
|
|
Step functions |

Piecewise defined functions that jump from one value to the next. |
|
|
|
Even function |
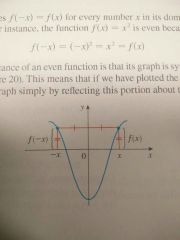
When f(-x)=f(x) for every number x in its domain
In other words, it is a mirror image in respect to the y-axis. Usually parabolas. |
|
|
|
Odd function |
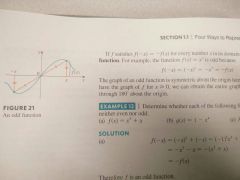
When f(-x)=-f(x) for every number x in its domain
In other words, one half of it is the mirror image of the other half turned 180° about the origin. Symmetric about the origin. |
|
|
|
Periodic function |
When a function has a positive constant T such that f(x+T)=f(x) for all values of x in the domain of f. |
|
|
|
Period |
The smallest value for which T is true in a periodic function. |
|
|
|
Increasing |
A function f is increasing on an interval I if f(x1)<f(x2). Would be denoted by [ or ( and the x-coordinate where the decreasing begins, comma, the x-coordinate where the decreasing stops, and ) or ]. |
|
|
|
Decreasing |
A function f is decreasing on an interval I if f(x1)>f(x2). |
|

