![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In unicellular organisms, division of _____________ reproduces the entire organism
|
one cell
|
|
|
Multicellular organisms depend on cell division for:
* Development from a fertilized cell * __________ * __________ |
Multicellular organisms depend on cell division for:
*Development from a fertilized cell *Growth *Repair |
|
|
Multicellular organisms depend on cell division for:
* _________________ * _________________ * Repair |
Multicellular organisms depend on cell division for:
Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair |
|
|
What is the cell cycle?
|
the life of a cell from formation to its own division
|
|
|
___________ is the life of a cell from formation to its own division.
|
Cell cycle
|
|
|
What are the key roles of cell division?
|
Reproduction, Growth, and Repair.
|
|
|
"Bone marrow stem cells grow and divide to give rise to new blood cells" describes which role of cell division?
|
Repair
|
|
|
"Embryonic cells grow and divide to form organism" describes which role of cell division?
|
Growth
|
|
|
"Cells divide to form two daughter cells" describes which role of cell division?
|
Reproduction
|
|
|
True or False: Each cell must receive a complete set of DNA (genes) as chromosomes from original cell.
|
True
|
|
|
True or False: Methods of cell reproduction include Fission, Budding, Mitosis, and Meiosis.
|
True.
|
|
|
What are the methods of cell reproduction?
* Fission * ___________ * Mitosis * ___________ |
What are the methods of cell reproduction?
* Fission * Budding * Mitosis * Meiosis |
|
|
What are the methods of cell reproduction?
* ___________ * ___________ * Mitosis * Meiosis |
What are the methods of cell reproduction?
* Fission * Budding * Mitosis * Meiosis |
|
|
_________ is where outgrowths from a cell detach and become new organisms.
|
Budding
|
|
|
__________ is the method of cell division that produces haploid cells.
|
Meiosis
|
|
|
True or False: Bacteria reproduce through budding, not mitosis.
|
False. Bacteria reproduce through fission.
|
|
|
__________ = complete complement of DNA in a cell
|
Genome
|
|
|
DNA is arranged in structures called ______________
|
Arranged in structures called chromosomes
|
|
|
True or False: Methods of cell reproduction include Fission, Budding, Mitosis, and Meiosis.
|
True.
|
|
|
True or False: Methods of cell reproduction include Fission, Regenesis, Mitosis, and Meiosis.
|
False. Regenesis is not a method of cell reproduction.
|
|
|
What are the methods of cell reproduction?
* Fission * ___________ * Mitosis * ___________ |
What are the methods of cell reproduction?
* Fission * Budding * Mitosis * Meiosis |
|
|
What are the methods of cell reproduction?
* ___________ * ___________ * Mitosis * Meiosis |
What are the methods of cell reproduction?
* Fission * Budding * Mitosis * Meiosis |
|
|
_________ is where outgrowths from a cell detach and become new organisms.
|
Budding
|
|
|
__________ is the method of cell division that produces haploid cells.
|
Meiosis
|
|
|
True or False: Bacteria reproduce through budding, not mitosis.
|
False. Bacteria reproduce through fission.
|
|
|
__________ = complete complement of DNA in a cell
|
Genome
|
|
|
DNA is arranged in structures called ______________
|
Arranged in structures called chromosomes
|
|
|
True or False: Humans have 46 chromosomes
|
True.
|
|
|
True or False: Humans have 46 chromosome pairs
|
False. Humans have 23 PAIRS of chromosomes, totaling 46
|
|
|
True or False: Humans have 23 chromosomes
|
False. False. Humans have 23 PAIRS of chromosomes, totaling 46
|
|
|
True or False: Humans have 23 chromosome pairs.
|
True.
|
|
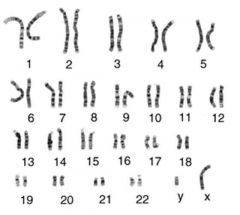
When you see chromosomes arranged and numbered in this manner, what is it called?
|
A karyotype
|
|
|
A ___________ is one of the threadlike "packages" of genes and other DNA in the nucleus of a cell.
|
Chromosome
|
|
|
What is a chromosome?
|
Long, linear DNA molecule with associated proteins (chromatin)
|
|
|
Chromosomes replicate prior to cell division
but remain attached at ___________ |
centromere
|
|
|
What are "sister chromatids"?
|
Two copies of a chromosome attached at a centromere, awaiting cell division.
|
|
|
What causes the chromosomes to become visible prior to cell division?
|
The chromosomes condense, packing themselves tighter than usual.
|
|
|
True or False: Chromosomes look like X's most of the time.
|
False. Chromosomes only look like X's when they are awaiting cell reproduction. The rest of the time they are in prophase, and are composed of single strands of DNA
|
|
|
True or False: A homologous pair of chromosomes contains the same genetic information.
|
False. A homologous pair of chromosomes is composed of genetic information from both mother and father. They each contain information that codes for the same TRAITS (e.g. hair color, eye color, height), although the specific genetic information may be different.
|
|
|
True or False: A homologous pair of chromosomes codes for the same traits.
|
True.
|
|
|
True or False: In a homologous pair of chromosomes, one comes from the mother, and one comes from the father.
|
True.
|
|
|
_____________ composes 90% of the cell cycle.
|
Interphase
|
|
|
True or False: S phase is part of Interphase.
|
True.
|
|
|
True or False: S phase is part of cytokinesis.
|
False. S phase is part of Interphase.
|
|
|
What are the sub-phases of Interphase?
* ________ ___________ * G1 Phase “first ___” * S Phase synthesis * G2 Phase “second gap” |
What are the sub-phases of Interphase?
* G0 Phase “quiescent” * G1 Phase “first Gap” * S Phase synthesis * G2 Phase “second Gap” |
|
|
What are the sub-phases of Interphase?
* G0 Phase “quiescent” * ________ _________ * ________ _________ * G2 Phase “second Gap” |
What are the sub-phases of Interphase?
* G0 Phase “quiescent” * G1 Phase “first Gap” * S Phase synthesis * G2 Phase “second Gap” |
|
|
What are the sub-phases of Interphase?
* ________ _________ * ________ _________ * ________ _________ * ________ _________ |
What are the sub-phases of Interphase?
* G0 Phase “quiescent” * G1 Phase “first Gap” * S Phase synthesis * G2 Phase “second Gap” |
|
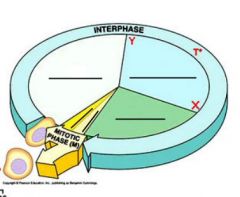
Fill in the blanks
|
G1 (white), S phase (cyan), G2 (green), cytokinesis (dark yellow), mitosis (light yellow)
|
|
|
“____________” - metabolically active, but not actively growing and dividing
|
quiescent
|
|
|
About how long (time) does S phase take?
|
10-12 hours in human cells
|
|
|
About how long (time) does mitosis take from prophase to telophase?
|
1 hour
|
|
|
About how long (time) does it take for a human cell to divide?
|
24 hours
|
|
|
Amongst animal cells, which part of the cell cycle varies the most between species (in terms of length of time to complete)
|
G1- the part between completing mitosis, and replicating DNA for a new division.
|

