![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
AIM
|
Identify the types of cell sin the body
Identify the structures contained in the cells Understand the functions of the cell structures Understand the terms; Osmosis Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Endocytosis Homeostasis |
|
|
Cel Introduction
|
Trillions of cells in the body
The structural “building blocks” of all plants and animals Cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells Cells form all the structures in the body Cells perform all vital functions of the body There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Somatic cells Cytology - Study of Cells |
|
|
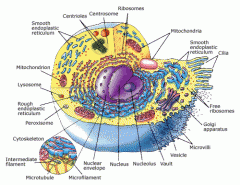
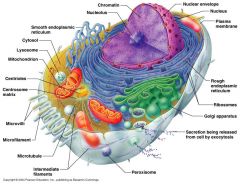
Cell Anatomy
The cell consists of: |
Cytoplasm
Cytosol Organelles Cell membrane |
|
|
Anatomical structures of the cell
|
Organelles
Nonmembranous organelles Membranous organelles |
|
|
Membranous organelles
|
Mitochondria
Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Peroxisomes |
|
|
Nonmembranous organelles
|
Cytoskeleton
Microvilli Centrioles Cilia Flagella Ribosomes |
|
|
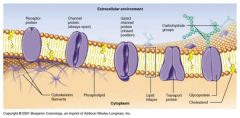
Cell Membrane (Plasmalemma/Phospholipid Bi Layer)
A cell membrane composed of: |
Phospholipids
Glycolipids Protein Cholesterol |
|
|
Diffusion
|
Diffusion is the net passive movement of particles (atoms, ions or molecules) from a region in which they are in higher concentration to regions of lower concentration. It continues until the concentration of substances is uniform throughout.
|
|
|
Osmosis
|
Osmosis is the net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane driven by a difference in solute concentrations on the two sides of the membrane.
A selectively permiable membrane is one that allows unrestricted passage of water, but not solute molecules or ions. Osmosis is the net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane driven by a difference in solute concentrations on the two sides of the membrane. A selectively permiable membrane is one that allows unrestricted passage of water, but not solute molecules or ions. |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion
|
This is the movement of specific molecules down a concentration gradient, passing through the membrane via a specific carrier protein. Each carrier has its own shape and only allows one molecule (or one group of closely related molecules) to pass through.
Selection is by size; shape; charge. |
|
|
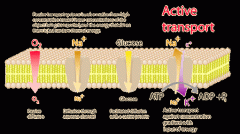
Membrane permeability of the Cell
Active processes |
Uses enzymes and carrier proteins
Ion pumps use energy to transport charged particles such as Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+ An ion pump that moves two ions simultaneously in opposite directions is called an exchange pump. |
|
|
Endocytosis
|
Phagocytosis: “cell eating”
Pinocytosis: “cell drinking” Receptor-mediated endocytosis: Ligands will bind specific molecules to the receptors thereby allowing only specific molecules to enter the cell |
|
|
Homeostasis (from Greek: hómoios, "similar", and, stásis, “standing still”)
|
is the property of a system that regulates its internal environment and tends to maintain a stable, relatively constant condition of properties such as temperature or pH.
|
|
|
PH VALUES
|
Gastric Acid = 1
Lysosomes = 4.5 Granules of chromatin Cells, Skin, Urine = 5.5 Water at 37c = 6.81 Cytosol = 7.2 CSF & Mitochondrial matrix = 7.5 Blood = 7.34 - 7.45 Pancreas 8.1 |
|
|
Transport methods in and out of the cell can be done in what two ways?
|
Passive or active transport
|
|
|
Passive transport has ____ types with it and are ____,_____,_____,_____
|
four, DIffusion, Facilitated Diffusion, Osmosis, and Filtration
|
|
|
All passive transport moves ____ the gradient with ____ energy; area of ____ to _____
|
down, no extra. high to low
|
|
|
Diffusion is the process of moving ____ of the cell from a ____ to ____ concentrate area; constantly in motion
|
out, high to low
|
|
|
Faciliated diffusion is what?
|
Helped diffusion of a substance across the membrane by a carrier protein
|
|
|
Since proteins are not solublem, they can not cross the tail, another carrier of facilitated diffisuion is the ____ or the ____ if it is basing the substance by charge
|
pore, gated channel/ion channel
|
|
|
A gated channel/ion are the ____ cells which have a current across the membrane they are either anim (- charge) or Catim (+charge)
|
excitable cells, the muscles make them move.
|
|
|
Osmosis is what?
|
The movement of water across a semi permeable membrane
|
|
|
In Osmosis what force pulls water across the membrane and where is it most located?
|
The osmotic pressure, the side with greater concentration has more pressure
|
|
|
Osmosis is concerned with _____ NOT volume and goes where?
|
concentration, goes to the area with less watcr; doesn't matter about the number of solutes
|
|
|
What is the difference between a solute and a solvent?
|
A solute is dissolved, solvents do the dissolving
|
|
|
What is filtration?
|
Diffusion where small solutes are pushed across the membrane with force
|
|
|
Why is filtration considered passive if it is being forced?
|
It is not expending any energy
|
|
|
What are the three solutions of the cell membrane?
|
Hypotonic, Isotonic, and Hypertonic
|
|
|
What is the difference between Iso-, Hypo-, and Hyper- tonic solutions?
|
Hypertonic has more solutes so the water leaves the cell because of osmotic pressure, Hypo has less osmotic pressure so water moves into the cell, Iso has equal amounts of solute and no osmotic pressure (moves free)
|
|
|
What are the three types of Active transport?
|
Active transport pumps, Endocytosis and Exocytosis
|
|
|
Active transport pumps require ____ to move ____ the gradient from ____ to ____?
|
ATP, against, low to high
|
|
|
In active transportation why is energy needed?
|
Because the cell is trying to move substances into an area with high concentration
|
|
|
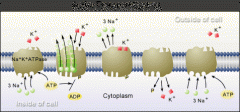
What is one Active Transport Pump?
|
The Sodium Potassium Pump
|
|
|
What are the first step of the Sodium Potassium Pump?
|
3 Sodium go into the channel
|
|
|
What is the second step of the Sodium Potassium Pump?
|
ADP is then added which breaks the two bonds and creates energy, which turns into ADP+Pi and leads to cell respiration ATP
|
|
|
What is the rest of the process after step 2 in the sodium potassium pump?
|
The channel opens, 4 NA^2 leaves which opens the outside, closing the inside and 2 K+ enter and move in which then close the outside and open the inside
|
|
|
With the Sodium Potassium Pump what ALWAYS happens?
|
3 sodium leave and 2 potassium protein come in
|
|
|
What is Endocytosis?
|
The intake of liquid and food when it is too large to move across the membrane
|
|
|
What does Endocytosis need?
|
It is active to it needs ATP
|
|
|
The three types of endocytosis are what?
|
Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, and Receptor mediated endocytosis
|
|
|
What is the difference between Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, and receptor mediated endocytosis?
|
Phago is for solids, Pino is for water/liquids and receptor mediated uses receptor for a substance to bind to the cell surface to enter
|
|
|
Receptor mediated endicytosis' traits are?
|
lock and key fit, binds specifically and brings in specific things
|
|
|
Exocytosis is what?
|
Active transport OUT of the cell. The membrane surrounds a substance and forms a vesicle around it moving it to the cell membrane and then attaching the vesicle and shooting the substance out
|
|
|
What is exocytosis used for?
|
Waste and immunity, granules need to be released to kill bad things
|
|
|
Five steps of Exocytosis are
|
1. Binds, 2. Signals the Golgi, 3. Packages and buds, 4. Moves, 5. Exocytosis
|
|
|
Exocytosis is what for binding?
|
Signal mediated to bind specifically and causes signal transductions which sends signals to the Golgi to package and process so the vessicle can bud and goto a new spot where it will fuse and release contents
|
|
|
For the sodium pump, the sodium goes ____, ____ sodium comes in (trick question!!!)
|
sodium goes out, NO sodium comes in
|
|
|
Phagocytosis is the process where
|
the membrane goes out to engulf.... basically it is brought in by being swallowed
|
|
|
Pinocytosis is brought in how?
|
By a vesicle
|
|
|
Receptor mediated endocytosis must have what
|
Has to be coated with Clathrin
|
|
|
What are the steps of receptor mediated exocytosis?
|
1. Binding occurs 2. Signal to the Golgi 3. The Golgi Packages and buds the vesicle to be directed to a new spot 4. It moves to the cell membrane and fuses 5. Exocytosis occurs emptying the vesicle
|
|
|
The signal mediated process of the receptor mediated exocytosis is when?
|
an extracellular molecule activates a membrane receptor which causes signal transuction, it occurs when they bind
|
|
|
The receptor mediated exocytosis is continuous because it is ______ so it will always be ____ and _____
|
extracellular, made, released
|
|
|
Altogether there are ____ types of active tranport in and out of cells
|
five
|
|
|
What are the five active types of transport?
|
Active transport pump, two types of endocytosis which is phagocytosis, pinocytosis and two types of exocytosis which are receptor mediated and signal mediated
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nil
|

