![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the incidence of birth defects?
|
6/100
|
|
|
what is the peak risk period for developmental defects?
|
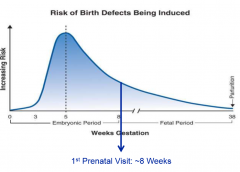
3-8 weeks
|
|
|
briefly define mitosis
|
somatic cell division forming 2 genetically identical daughter cells
|
|
|
briefly define meiosis
|
germ cell division forming male and female gametes
|
|
|
what is the frequency of a meiotic cross over event?
|
dozen per event, 1 per chromosome (roughly)
|
|
|
Roughly estimate the number of oocytes in a newly pubescent woman
|
40-50k
|
|
|
what is the zona pellucida?
|
protein coat surrounding egg
|
|
|
define the cumulus oophorus
|
loose protecting cells surrounding oocyte distantly
|
|
|
define the corona radiata
|
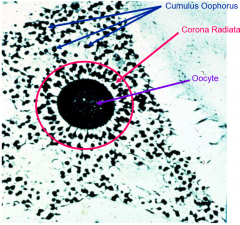
dense protecting cells surrounding oocyte nearby
|
|
|
what is an oocyte?
|
egg in suspended animation
|
|
|
define fimbriae
|
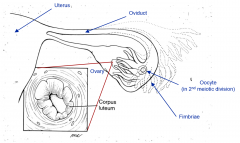
fingerlike appendiges of oviduct used to grab ovary
|
|
|
define acrosome
|
in head of sperm cells, holds enzymes for penetration
|
|
|
define trisomy
|
extra chromosome present
|
|
|
define monosomy
|
a chromosome is missing
|
|
|
what are the most frequent trisomy chromosomes and why?
|
13, 18, 21 (down) (more susceptible? less lethal?)
|
|
|
define translocation and give an example
|
chunk of another chromosome moved to different chromosome, chromosome 21 chunk moved to 14 also causes down syndrome
|
|
|
what percentage of infant death is roughly due to genetic error
|
20-30%
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of down syndrome as well as clinical aspects and prevalence in pregnancies
|
mental retardation, craniofacial abnormalities (slant eyes, flat face, protruding tongue, small ears etc.) prevalence of cardiac defects, thyroid issues, leukemia and premature aging. 1/2000 (under age 25), 1/100 (age 40)
|
|
|
what are the characterstics of angelman syndrome
|
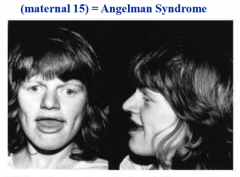
microdeletion on long arm of maternal chromosome 15, mental retardation, cannot speak, craniofacial defects, poor motor development
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of prader-willi syndrome
|
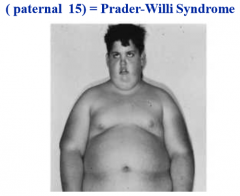
microdeletion on long arm of paternal chromosome 15, mental retardation, craniofacial defects, obesity, hypogonadism
|
|
|
define capacitation
|
conditioning of sperm, removal of glycoprotein coats from plasma membrane over acrosomal region of sperm (~7hrs)
|
|
|
describe phase 1- fertilization
|
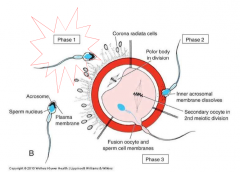
penetration of corona radiata (must be capacitated)
|
|
|
describe phase 2- fertilization
|
penetration of zona pellucida at ZP3 receptor, induces acrosomal region, release acrosin enzyme (need 200-300 sperm releasing acrosin to penetrate, only 1 gets through)
|
|
|
describe phase 3- fertilization
|
sperm and oocyte fuse, calcium wave triggers release of oocyte granules and changes membrane (makes a gap), makes it impermeable. resume meiotic division, activate egg
|
|
|
define the pronucleus
|
female and male formed from egg and sperm, join to become first diploid cell
|
|
|
define blastomere
|
each cell in the 4 cell stage
|
|
|
define the morula
|
8-16 cell stage
|
|
|
describe compaction
|
blastomeres flatten and compact, increase cell to cell contacts, formation of morula
|
|
|
what does the inner cell mass become
|
forms embryo (embryoblast)
|
|
|
what does the outer cell mass become
|
will form trophoblast
|
|
|
when does the blastocyst form
|
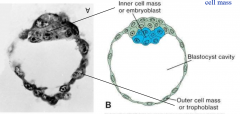
fluid accumulation in morula, forms blastocyst cavity
|
|
|
what is the function L-selectin in fertilization
|
carbohydrate binding protein allows capture of blastocyst to uterine lining
|
|
|
describe an ectopic pregnancy
|
implantation event occurred in the wrong location (probably in oviduct). cannot be carried to term
|
|
|
define epiblast cells and what they do
|
cells split from embryoblast which in turn separate and create the amniotic cavity
|
|
|
what does bilaminar embryo describe
|
epiblast and hypoblast layer on each side
|
|
|
describe Heuser's membrane
|
layer of hypoblast cells which have migrated around the inner cavity of the blastocyste, forms primative yolk sac
|
|
|
what is the chorionic cavity
|
continued spreading and proliferation of hypoblast cells forms another cavity around the yolk sac
|
|
|
describe the definitive yolk sac
|
primary yolk sac is pinched and budded off and removed
|
|
|
define extracoelomic cysts
|
budded off yolk sacs, not important
|
|
|
describe fraternal twins
|
dizygotic, non-identical, 90% of twins, roughly 30/1000 births (premature delivery, low birth weight risks), 2 placentas
|
|
|
describe identical twins
|
monozygotic, identical, 10% of twins, 3/1000 births (premature delivery, low birth weight, twin-twin transfusion risks), 1 placenta (usually)
|

