![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The epidemiology of periodontal diseases is much more difficult to study compared to for example dental caries due to a number of reasons:
List them |
Both the gingiva and the periodontal ligament/alveolar bone complex are involved, each with its own characteristic disease process
Although gingivitis occurs throughout life, periodontitis has its greatest incidence later in life Periodontal diseases do not lend themselves well to objective measurement Until 1982 data from different studies were difficult to compare due to the use of different indices |
|
|
CPI Data can be expressed as either.. what?
|
Percentage of people with highest score (prevalence)
Mean number of sextants with different scores (severity) |
|
|
Who keeps the global oral health data bank for periodontal diseases?
|
University of Niigata Japan
|
|
|
Gingivitis and calculus deposits are more prevalent and severe in low-income nations. Why?
|
The reason for this lies in that personal oral hygiene and professional oral care can control gingivitis and calculus deposits.
|
|
|
There is much less global differences occurring in the prevalence of severe periodontitis among developed and developing nations. Why?
|
presence of plaque or calculus isn’t a prerequisite for the development of periodontitis and is closer linked to the compromised host model of periodontitis.
|
|
|
Describe the trend of prevalence of gingivitis with age.
|
At the population level gingivitis is found in early childhood, is more prevalent and severe in adolescence, and then tends to level off after that.
|
|
|
Gingivitis would be lower in developed and higher in developing countries. Why?
|
Due to improved oral hygiene practices in developed countries
|
|
|
Describe the trend of periodontitis with age
|
Periodontal disease prevalence and severity tend to be higher in older age groups as compared to younger age groups.
|
|
|
Gingivitis is CPI score of what? What about periodontitis?
|
1 and 2 for gingivitis
3 and 4 for peronditis |
|
|
What does CPI score of X mean?
|
It was not able to be recorded
|
|
|
Using highest education qualification is an indication of what?
|
SES
|
|
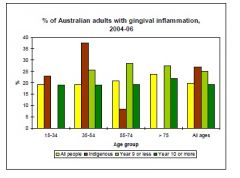
Why is there large difference between "year 9 or less" and "year 10 or more"?
|
This is gingivitis which is dependent on SES. Level of education is an indication of SES hence lower the SES the more gingivitis prevalence
|
|
|
what are the risk factors in perio diseases?
|
tobacco use
nutrition and diet alcohol oral hygiene, plaque and micro-organism local factors (overhanging margins) diseases and other conditions (diabetes HIV Down syndrome) |
|
|
what is the difference between condition and disease?
|
Disease involves micro-organisms
Conditions don't |
|
|
What is dental fluorosis caused by?
|
Intake of systemic fluoride during tooth development
|
|
|
There is universally accepted index to measure fluorosis which is Dean's Index and is recommended by WHO (T/F)
|
False
There is no universally accepted index but DI is recommended by WHO |
|
|
Sources of fluoride have decreased (T/F)
|
False, sources of F have increased
|
|
|
Is prevalence of fluorosis on the rise globally? Is it significant?
|
It is on the rise but only in mild form
|
|
|
In Ethiopian Rift Valley, there is an endemic of fluorosis. Why is that?
|
The naturally occurring amount of fluoride is unusually high.
|
|
|
In Western Australia, there was a decrease in fluorosis between 1989/90 and 2000. Why is this?
|
Changed the pattern of toothpaste and supplement use. Stopped using fluoride tablets
|
|
|
What are the determinants of fluorosis?
|
amount linked to concentration of fluoride in the source and the time at which fluoride consumption is initiated
|
|
|
When is it crucial to avoid fluoride consumption to avoid fluorosis?
|
first 6 years
|
|
|
Is dental fluorosis a public health problem? Why?
|
Two criteria for a public health problem are: (1) it must be widespread causing serious morbidity or mortality and (2) it must be recognised by a governing body or a politician.
Almost all fluorosis is in very mild form hence it is not a public health problem |
|
|
What is the driver behind the increase in fluorosis prevalence in floridated and non-fluoridated communities?
|
Fluoride exposure from sources other than drinking water: eg. tablets, high F conc bottled water
|
|
|
What is the maximum level of fluoride in drinking water? (ppm)
|
0.8ppm
|
|
|
What is the maximum conc of fluoride to provide fluoride supplements?
|
0.3ppm
|
|
|
The prevalence of oral cancer is higher in which gender? Why?
|
men. lifestyle
(not applying sunscreen) |
|
|
Is mortality due to oral cancer related to SES?
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the best way to address oral cancers in early detection?
|
reduce consumption of alcohol and tobacco
|
|
|
Globally, has morbidity due to oral cancer decreased?
What about mortality? Why? |
morbidity: steady
mortality: decrease. earlier diagnosis and better treatment methods |
|
|
Where is the most prone site for oral caner in Australia? Why?
|
The Lip because of the sun
|
|
|
What are the risk factors involved in oral cancer?
|
Sex (male)
Age (older) Ethnicity (the minority) Tobacco Alcohol Sunlight Chronic inflammatory and infectious disease (lichen planus) |
|
|
What are available indices to measure fluorosis?
|
Dean's Index
TF TSIF |
|
|
What benefits does TF have over DI?
|
TF is more sensitive
Can distinguish between children having only a few teeth with pitting and those having all their teeth pitted |
|
|
What is different about TSIF from other indexes?
|
It combines the elements of DI and TF.
Places more emphasis on cosmetic appearance of fluorosis |
|
|
Periodontitis results from greater susceptibility at older ages. T/F?
|
False
It does not result from greater susceptibility at older ages but from a cumulative progression of disease over time. |
|
|
Women or men have poorer periodontal health?
|
men
|

