![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is clinically significant about Meckel's Diverticulum?
|
1. most frequent congenital anomaly of the digestive tract
2. < 1/2 contain gastric mucosa but ONLY these ulcerate and bleed 3. meckel's is the culprit for 50% of all GI bleeds in children |
|
|
How is technetium helpful in dx of Meckel's diverticulum?
|
technetium is taken up by gastric mucosa which is abnormal and present in 50% of meckel's. the gastric mucosa containing meckel's are they only ones that ulcerate and bleed. technetium scan is the dx tool of choice.
|
|
|
How is diverticulitis treated?
|
antibiotics that cover both aerobic and gram negative anaerobic like metronidazole + cipro or TMP/SMX
don't give metro to pregnant or alcoholic. don't give cipro to children. |
|
|
What is a fundamental exam for working up large bowel dz?
|
digital rectal. thanks, dr. seaman. 50% of all rectal CAs can be felt with a DRE.
|
|
|
When is angiography used in GI dz?
|
1. chronic/acute mesenteric ischemia
2. severe lower GI bleed (rarely used for upper GI bleed) 3. TIPS for variceal bleeding 4. used therapeutically for embolism or vasopressin |
|
|
Angiography is most successful when the rate of blood loss is what?
|
0.5 or greater
|
|
|
What is diverticulosis?
|
dz of motility that is very common clinically where diverticula occur where the muscle layer is weak. they occur most commonly in the sigmoid colon because of the increased pressure. makes sense, then that acquired is more common than congenital.
|
|
|
What is an important differential to include with diverticulosis?
|
CA. don't assume that a patient's symptoms are diverticular in origin until neoplasm has been ruled out.
|
|
|
What are the 4 types, indicating the most common, of diverticular dz?
board, but not exam here |
1. asymptomatic - most common
2. painful diverticulosis 3. diverticular bleeding 4. diverticulitis |
|
|
What diagnostic tool should be avoided with diverticulosis?
|
colonoscopy requires expansion of the colon with gas insertion. because the tissue could be weak. this could cause a rupture. avoid colonoscopy
|
|
|
What should one suspect with severe attacks with acute peritoneal signs and diverticulitis?
|
suspect abscesses or perforations.
|
|
|
What is the most useful radiological study to dx diverticulitis?
|
CT scan
|
|
|
What is diverticulitis due to?
|
microperforations
|
|
|
How does diverticulitis present clinically?
|
LLQ pain, fever, leukocytosis, can have LLQ rebound tenderness, sigmoid mass on imaging
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of bleeding of the elderly pt > 60?
|
MC = diverticular hemorrhage (will be more profuse "full-on faucet" bleeding, painless)
2nd MC = angiodysplasia (more occult "drippy faucet" bleeding) |
|
|
What sidedness do diverticular hemorrhage bleeds usually take on?
|
R side, even though clinically presentation of pain and tenderness is more commonly L sided.
|
|
|
How is diverticular hemorrhage dx'ed?
|
colonoscopy or technetium tagged RBC scan. angiography if bleeding is severe or continuous.
|
|
|
* What is Ogilvie's syndrome?
|
it's an acute, nontoxic "mega colon" presentation of pseudoobstruction. it shows up as massive dilation of the colon on AXR. there is no mechanical obstruction present.
|
|
|
* When is cecostomy indicated in Ogilvie's syndrome?
|
cecostomy is indicated when the diameter of the colon exceeds 8 cm to avoid ischemic necrosis and perforation
|
|
|
What is the significance of IBS?
|
most common GI dz in clinical practice, more common in females usually < 45 yo
|
|
|
Are there nocturnal or organic symptoms with IBS?
|
yeah, no. i don't think so. definitely not.
|
|
|
What concurrent dzs will present with a complicate IBS?
|
1. 2-4% have concurrent celiac sprue
2. 33% of lactose intolerance will not resolve with lactose restriction because they have concurrent IBS |
|
|
How is IBS treated?
|
Antispasmodic (anticholinergics), but a lot of pts will respond well to placebo.
|
|
|
What is the only treatment for arterial insufficiency?
|
surgical bypass, NOT the same as mesenteric venous thrombosis
|
|
|
What blood condition is mesenteric venous thrombosis related to? This should be obvious.
|
hypercoagulable states, so treated with thrombolytics and long-term anticoagulants
|
|
|
* What is the most common cause of ischemic colitis?
|
usually NOT SPECIFIC CAUSE. can be related to low flow/ HF/hypercoagulability, and usually nonocclusive
|
|
|
* When is ischemic colitis dx'ed with colonoscopy?
|
ONLY if there are no signs of peritonitis.
|
|
|
* What is Heyde syndrome?
|
GI AVM and AS
|
|
|
* What is Osler-Rendu-Weber syndrome?
|
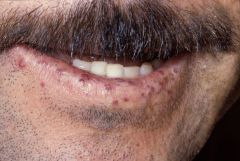
also known as Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), it is a genetic disorder that leads to abnormal blood vessel formation in the skin, mucous membranes, and often in organs. It has a characteristic presentation on the lower lip. see the pic.
|
|
|
Where do SI carcinoid tumors found?
|
argentaffin cells of the crypts of Leiberkuhn in the midgut.
|
|
|
If an inflammatory bowel dz is in the ileum, then is it Crohn's or ulcerative colitis?
|
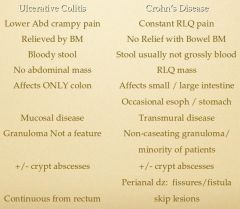
Crohn's, man! U.C. doesn't occur anywhere but in the colon. check out the pic and be able to tell the difference.
|
|
|
* What are the significant labs to differentiate Crohn's from UC?
|
+ ASCA / - pANCA = Crohn's
- ASCA / + pANCA = UC |
|
|
Why should you not tell a pt that they have Crohn's dz without biopsy?
|
Crohn's is a preexisting condition. Don't ever tell a pt
|
|
|
* What is the significance of sulfasalazine and IBD?
|
Sulfasalazine causes reversible infertility in men as a result of abnormal spermatogenesis and decreased motility.
|
|
|
What is celiac dz also known as?
|
non-tropical sprue
|
|
|
What is the HLA associated with celiac dz?
|
HLA-DQ2 is present in 95% of patients
|
|
|
What skin conditions are related to Celiac Dz?
|
psoriasis and dermititis herpetiformis
for boards |
|
|
* What is the test of choice for celiac dz?
|
tTg IgA
|
|
|
What is oculomasticatory myorrhythmia?
|
pendular vergence oscillations of the eyes and synchronous contractions of the masticatory but not palatal muscles that is oathognomonic for whipple's dz
|
|
|
What histologically is significant with Whipple Dz?
|
PAS positive, foamy macrophages
|
|
|
What is a differential for hemorrhage and should not be excluded until dx is positive for hemorrhoids?
|
colorectal CA
|
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of Whipple's?
|
4 cardinal clinical manifestations
1. MC sx = arthralgia for YEARS before dx 2. weight loss 3. diarrhea 4. abdominal pain |
|
|
How does relapse of Whipple's often manifest?
|
CNS symptoms
|
|
|
What factors influence bacterial overgrowth in the gut?
|
1. structural abnormalities
2. non-normal gut motility 3. excessive bacterial load 4. deficient host defense |
|
|
What anatomical structures compose internal and external hemorrhoids?
|
internal - venous swelling from gnlarged internal hemorrhoidal plexus and /\ supporting tissue mass
external - external hemorrhoidal plexus enlargement or thromboses, resulting in bluish mass |
|
|
What is a common symptom of internal hemorrhoids?
|
painless bright red bleeding on the toilet paper and the feeling of vague anal discomfort
|

