![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What different types of small bowel obstruction exist?
|
partial or complete, non-strangulated or strangulated
|
|
|
What is penumoperitoneum?
|
"free air" usually due to bowel perforation such as in perforated peptic ulcers, bowel obstruction, divertiulitis, or appendicitis with perforation
|
|
|
What is the term for free air in the abdomen on KUB xray?
|
double bowel wall sign
|
|
|
What is a Bochdalek hernia?
|
posteriorly located congenital diaphragmatic hernia; 80% occur on the left side
|
|
|
What is a Morgagni hernia?
|
anteriorly located congenital diaphragmatic hernia; 90% occur on the right
|
|
|
What are the top two MC sites of GI tract lymphoma?
|
#1 stomach
#2 small bowel |
|
|
What is the significance of the sigmoid volvulus?
|
MC type of colonic volvulus. more common in elderly and can lead to bowel ischemia if not reduced promptly.
|
|
|
What is the best imaging tool for gallstones?
|
US
|
|
|
What does a procelain gallbaldder increase the risk of?
|
gallbladder CA
|
|
|
What is an Apple core lesion?
|
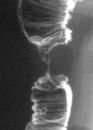
The radiologic hallmarks of the classic colonic “apple core” lesion are a relatively short, sharply defined region of annular, constricting colonic narrowing with overhanging margins; ulcerated mucosa; and an eccentric and irregular lumen. Can be seen in the esophagus as well.
|

