![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
biconcave disks that are 7-8microns with a lifespan averaging 120 days are...
|
RBCs
|
|
|
What condition would result if barometric pressure was decreased? (Low O2)
|
Hypoxia
|
|
|
what is the result of lowered O2? (hypoxia)
|
creation of erythropoietin.
|
|
|
What is the function of erythropoietin?
|
tells bone marrow to make RBCs.
|
|
|
Most numerous element in blood is?
|
RBCs
|
|
|
These are a defense mechanism found in the blood, essential for immune response, phagocytosis.
|
White blood cells aka leukocytes.
|
|
|
What are thrombocytes and what are they needed for?
|
Blood platelets, they are fragments of a larger cell and are needed for Blood Coagulation.
|
|
|
What is hemostasis?
|
To stop bleeding.
|
|
|
what causes vasoconstriction(mechanically)?
|
contraction of smooth muscle in wall of vessel. local event
|
|
|
aggregation of platelets in small vessel can form...
|
a platelet plug
|
|
|
Give general info on the three stages of blood coagulation
|
Stage I - Formation of prothrombin Activator complex.
Stage 2 - Conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. Stage 3 - Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin strands. |
|
|
What protein leads to formation of Prothrombin Activator Complex (PAC)?
|
THromboplastin
|
|
|
Trauma to tissue (intrisic or extrinsic pathway of blood coaguation)?
|
Extrinsic
|
|
|
blood in glass (intrisic or extrinsic pathway of blood coaguation)?
|
intrinsic
|
|
|
what is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic pathways?
|
intrinsic happens inside the blood while extrinsic occurs from events that begin in tissues outside of the blood.
|
|
|
What turns fibrinogen into fibrin?
|
Thrombin
|
|
|
What is needed to turn fibrin monomer into fibrin polymer
|
Calcium is essential for polymerization. Fibrin stabilizing factor.
|
|
|
What turns prothrombin(present in blood) into thrombin?
|
Prothrombin Activator complex (PAC)
|
|
|
What is serum?
|
Fluid pushed out of clot after coagulation, does not contain clotting factors.
|
|
|
What anticoagulant effects mast cells?
|
Heparin
|
|
|
A calcium chelator such as EGTA can be used as...
|
An anticoagulant since Ca2+ is a necessary component of blood clotting.
|
|
|
What vitamin is responsible for some clotting factors?
|
Vitamin K
|
|
|
What causes a stroke?
|
Blood clot within the brain.
|
|
|
What causes heart attack?
|
Blood clot in heart vessel.
|
|
|
How to remove a blood clot?
|
Fibrinolysis by serine protease.
|
|
|
Fibrinolysis can be done by this serine protease, ____(1) which is released by _______(2).
|
1-plasmin
2-plasminogen |
|
|
Tissue plasminogen activator and streptokinase (Beta-hemolytic streptococci) has what role in relation to blood.
|
turning plasminogen(globulin) into plasmin (fibrin).
|
|
|
AP in the heart is called....
|
Cardiac impulse
|
|
|
Cardiac impulse is what kind of event? (systolic/diastolic)
|
systolic
|
|
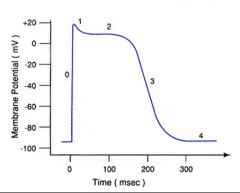
Explain phases and details for this representation of transmembrane potential in a typical cardiac cell.
|

0-rapid depolarization; opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels.
1-notch-"fast" Na+ channels close shortly after opening. 2-Plateau phase-depolarization maintained by increasing Ca++ Conductance and keeping K+ conductance low. 3-Repolarization phase;Increase in K+ conductance. 4-Resting potential. |
|
|
Refractory period
|
does not respond to same stimuli, must be increased.
|
|
|
Absolute Refractory period
|
no response regardless of stimulus
|
|
|
Refractory period is exceptionally long, what does this mean for Absolute Refractory period?
|
ARPeriod is about 70-85% of AP.
|
|
|
What structure in cardiac muscle makes electrical activity from one cell to it's neighbor possible?
|
Gap junctions.
|
|
|
Relaxation (diastole/systole)?
|
diastole
|
|
|
contraction (diastole/systole)?
|
systole
|
|

give name of every red dot
|

Chapter 11 Fig. 1
|
|
|
Give the first four steps of cardiac impulse, beginning at initial AP.
|
SA node -> AV node -> Bundle of His ->Purkinje Fibers
|
|
|
What node depolarizes spontaneously? And what is spontaneous depolarization?
|
SA node. Spontaneous depolarization means without external electrical stimulation from the nervous system.
|
|
|
How many times in a minute does SA node mormally depolarize?
|
70 times
|
|
|
What is an ectopic pacemaker
|
If cardiac impulse originates @ place other than SA node, aka abnormal pacemaker.
|
|
|
What would cause a compensatory pause.
|
Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC). Extra details on PVC; extrasystole originated from an ectopic focus located in ventricles, makes QRS broad and unusual. premature atrial contraction have an early P wave with modified shape.
|
|
|
Where can Beta-1 receptors be found and what effect to they have?
|
Heart contains B1-receptors which riase HR and contractility. (sympathetic)
|
|
|
Where can Beta-2 receptors be located and what effect do they have?
|
Lungs, cause bronchodilation. (sympathetic)
|
|
|
Abnormal bronchoconstriction is a problem known as...
|
Asthma
|
|
|
What is best drug type that cuases vasodilation of bronchioles?
|
Beta-2 Agonist ( adrenergic)
|
|
|
Why would epinephrine be a bad choice for causing vasodilation clinically?
|
Effects more than just Beta-2 Agonist, would have many side effects.
|
|
|
Give name of synthetic Beta agonist and antagonist.
|
Agonist: Isoproterenal
Antagonist: Propanalol |

