![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What 5 things must always be considered when you read an EKG and in this order?
|
1. Rate
2. Rhythm & Intervals 3. Axis 4. Hypertrophy 5. Infarct & Ischemia |
|
|
What specific measurements are important to EKG analysis?
|
P interval
P wave size QRS width (interval) QT interval QRS wave size (voltage) abnormal Q waves T waves U waves ST segments |
|
|
What/where are the important leads related to axis?
|
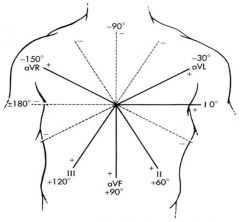
+aVL = -30
+II = +60 +aVF = +90 +III = +120 +aVR = -150 LAD = -30 to -90 RAD = +110 to +180 ERAD = -90 to -180 Normal = -30 to +110 |
|
|
What does the P wave, PR interval, QRS complex, T wave represent?
|
P wave - completion of atrial excitation
PR interval - impulse delay at AV junction QRS complex - ventricular electrical excitation T wave - ventricular repolarization |
|
|
What is the position and name of all of the 12 leads of an EKG?
|
Limb
I = +L, -R II = -R, +F III = +F, -L aVL = -R/F, +L aVR = -F/L, +R aVL = -L/R, +F Precordial V1 = R 4th interspace V2 = L 4th interspace V3 = midway between V2-V4 V4 = L 5th interspace, midclavicular line V5 = L V4 latitudinal line, anterior axillary line V6 = L V4 latitudinal line, midaxillary line |
|
|
Why would one add R leads such as V4R to the standard 12 lead EKG?
|
w acute inferior MI one can detect R ventricular involvement
|
|
|
What are the paper standards for EKG measurements?
|
25 mm/sec horizontal
1mV/10mm vertical 1mm = small box = 0.04 sec 5mm = large box = 0.2 sec |
|
|
What is a normal PR interval in adults?
|
0.12 to 0.2 seconds or 3-5 small boxes
|
|
|
What is a normal QRS interval in adults?
|
less than 0.12 seconds or less than 3 small boxes
|
|
|
What does the QT interval represent, what is the normal duration, and what is the relative rule of the QT interval?
|
QT interval represents ventricular depolarization and repolarization
normal duration is between 0.33 and 0.42 sec QT interval that exceeds one half of the RR interval is prolonged provided the HR is 80 bpm or less |
|
|
What is the corrected QT interval and what is it significant?
|
QTc = QT/sqrt(RR), normal is shorter than 0.47 sec
should be checked before prescribing drugs that prolong the QT interval |
|
|
What is the clinical dx criteria and some associated symptoms of long QT syndrome (LQTS)?
|
QTc > 0.44 sec
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy => sudden cardiac death deafness |
|
|
What is the normal QRS interval?
|
beginning of Q wave to end of S wave should be < 0.12 sec or < 3 small boxes
if longer, then check for BBB |
|
|
Why is it important to have a family hx and note whether a relative has an unexplained death before 50?
|
LQTS will cause 10 year 70% mortality, it is congenital, and it can be reduced to 4% with tx.... among other things.
|

