![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What three diseases commonly cause GI infections and are caused by the normal flora?
|
1. Diverticulitis
2. Appendicitis 3. Peritonitis |
|
|
Characterize diverticulitis
|
diverticula (pouches) formed in the colon in which an overgrowth of normal flora can occur. overgrowth causes inflammation which results in diverticulitis
can lead to abscess formation or peritonitis common symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, constipation or diarrhea |
|
|
Characterize appendicitis
|
blockage of the appendix opening allowing overgrowth which can lead to appendix perforation -> bacteria in peritoneal cavity -> abdominal abscesses & peritonitis
|
|
|
Common demographic for diverticulitis?
|
geriatrics
|
|
|
What is the antibiotic of choice for normal flora caused infections of the GI tract?
|
metronidazole
|
|
|
Characterize peritonitis
|
inflammation of the peritoneum symptomatically showing abdominal pain and fever
|
|
|
What is the difference between primary peritonitis and secondary peritonitis?
|
1. chronic liver disease which causes bacterial shedding from liver caused by E. coli and Strep.
2. from GI tract infection caused by polymicrobial infection E. coli, Bacteroides, other obligate anaerobes |
|
|
What five diseases start in the GI tract but result in systemic infection?
|
1. typhoid (enteric) fever
2. botulism 3. listeriosis 4. Vibrio vulnificus septicemia 5. Streptococcal endocarditis |
|
|
What is the causative agent of typhoid fever?
|
Salmonella typhi
paratyphoid fever is caused by Salmonella paratyphi |
|
|
What are the common symptoms of typhoid fever?
|
fever, chills, headache, myalgias, anorexia, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, rose spot rashes
can be asymptomatic and contagious |
|
|
How is typhoid fever spread?
|
contaminated food, water, shellfish
|
|
|
What is the spread of infection steps of typhoid fever in the human body?
|
1. Salmonella are ingested
2. Engulfed by macrophage and replicate within macrophage 3. Macrophage travel through lymphatics and primary/secondary lymph tissue is seeded 4. Bacteria enter blood stream 5. Gallbladder is infected and bacteria is released in stool to continue cycle |
|
|
Characterize Typhoid fever rose spots
|
One-third of patients exhibit a characteristic rash known as rose spots. The spots are extremely
sparse 1-4 cm lesions on the trunk. They generally resolve within two to five days. |
|
|
How is Salmonella typhoid fever diagnosed?
|
isolate from blood, bone marrow, or stool
|
|
|
What is Tx of typhoid fever?
|
antibiotics and monthly stool cultures for three months after resolution to test for complete resolve
|
|
|
What cells produce the botulism toxin?
|
vegetative cells produce toxin, NOT spores
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of botulism?
|
flaccid paralysis because toxin blocks acetylcholine
Adults: dry mouth, double vision, difficulty swallowing/speaking, weakness in extremities Infants: constipation, poor suckling, poor head control |
|
|
What is the causative agent of botulism?
|
Clostridium botulism
|
|
|
What is wound botulism?
|
infection via wound (not ingestion) which causes all the same symptoms as Adult botulism
|
|
|
What food can cause infant botulism?
|
HONEY
|
|
|
Tx of botulism?
|
begin supportive therapy immediately (respiratory support, Ig anti-toxin)
NO antibiotic |
|
|
Dx of botulism?
|
clinical findings and history
contact CDC for identification |
|
|
What is the causative agent of Listeriosis which can lead to gastroenteritis, meningitis, and bacteremia?
|
Listeria monocytogenes
|
|
|
What foods are found to have Listeria monocytogenes?
|
unpasteurized milk, soft cheese, fresh vegetables, hot dogs, deli meats, cabbage
|
|
|
What demographic is particularly at risk of Listeriosis?
|
1. pregnant women: bacteremia, premature labor, abortion, stillbirth, neonate and transplacental transmission
2. immunocompromised: meningitis, bacteremia 3. neonates: premature birth, septicemia, abscesses, granulomas, meningitis, septicemia |
|
|
Tx of Listeriosis
|
antibiotic
|
|
|
Dx of Listeriosis?
|
CSF - higher sensitivity
blood |
|
|
What causative agent causes the most moralities because of ingestion and is found in as much as 1M bacteria per gram of shellfish in warm months?
|
Vibrio vulnificus gastroenteritis
|
|
|
What demographic are at high risk of Vibrio vulnificus gastroenteritis?
|
cirrhosis of liver
|
|
|
What are symptoms of Vibrio vulnificus gastroenteritis?
|
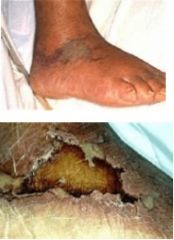
high fever, chills, myalgia, severe pain in legs, multiple hemorrhagic bullae, extensive bruising, watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting
|
|
|
Dx of Vibrio vulnificus?
|
feces culture
bulla aspirate culture blood culture |
|
|
Tx of Vibrio vulnificus?
|
NO antibiotic for gastroenteritis
Antibiotics for septicemia |
|
|
What group of streptococci causes Streptococcal endocarditis?
|
viridans group which causes subacute infective endocarditis. they are part of normal flora of oral cavity
|
|
|
How does Strep viridans group lead to endocarditis?
|
dental work, dental abscesses, poor dental hygiene, brushing teeth causes sepsis and deposit on the surface on heart valve by attachment virulence factor
|
|
|
Symptoms of Streptococcal endocarditis?
|
fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss, heart murmurs
|
|
|
Dx Streptococcal endocarditis?
|
Draw 3 - 5 blood samples over 24 hour period to see bacterial load vs. time before starting antibiotic therapy
|
|
|
Tx Streptococcal endocarditis?
|
antibiotics IV over 4 week period
|
|
|
What demographic needs special Tx for Streptococcal endocarditis?
|
abnormal heart valves or prosthetic valves should take prophylactic antibiotics before undergoing dental procedures or surgery of respiratory or GI tracts
|

