![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What three layers exist in the skin?
|
epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous
|
|
|
Can bacteria that invade epidermis spread systemically?
|
nope. there is no blood or lymph in epidermis.
|
|
|
After many days what happens to the bacterial load on the epidermis?
|
bacteria that cannot grow rapidly will be sloughed off with dead skin cells.
|
|
|
What three properties of skin provide prevention against bacterial growth?
|
1) sloughing off
2) low pH 3) dryness |
|
|
Which three organisms routinely infect intact skin?
|
1) Staph. aureus
2) Pseudomonas aeruginosa 3) Propionibacterium acnes |
|
|
Which bacterium infect hair follicles?
|
Staph aureus, Pseudo. aeruginosa
Hair follicle infection is called folliculitis. |
|
|
Which bacterium infect sebaceous glands?
|
Prop. acnes
|
|
|
What happens when Staph. aureus is spread deeper than the hair follicle?
|
Patients with carbuncles and fever most likely have septicemia. This can lead to endocarditis, osteomyelitis. These conditions are rare and is why it's important to not pick or squeeze lesions.
|
|
|
What is the difference between septicemia and bacteremia?
|
Once bacteria enter the blood then people have bacteremia. Symptom causing bacteremia is septicemia.
|
|
|
What physical manifestations are caused by Staph. aureus skin infections?
|
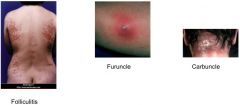
|
|
|
Why does Pseudo. aeruginosa not usually cause folliculitis?
|
it is usually not in great enough number to cause problems, BUTT it loves to grow in hot water.
|
|
|
What is hot tub folliculitis?
|
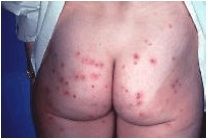
a usually simple infection of the skin caused by Pseudo. aeruginosa growing in hot tubs and people steeping themselves in these uncontrolled hot tubs.
|
|
|
What is acne caused by?
|
Proprionibacterium acnes is normal flora, but increases by some 100,000x before puberty which causes infections of the sebaceous gland -> acne.
|
|
|
How do you treat Proprionibacterium acnes caused skin acne?
|
antibiotics. washing the skin won't help since there is a sebaceous glad infection of the skin. effective tx occurs with topical benzoyl peroxide and antibiotics.
|
|
|
How can you differentiate between Staph and Strep in a lab?
|
Staph = catalase-positive
Strep = catalase-negative |
|
|
What are the the 5 infections caused by epithelial injury in which the stratum corneum is broke?
|
1) Impetigo (lower layers of epidermis)
2) Erysipelas (dermis, lymphatics) 3) Cellulitis (subcutaneous fat) 4) Necrotizing fasciitis (fascial plane) 5) Myonecrosis (muscle) |
|
|
What causative agents result in Impetigo?
|
Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
|
|
|
How does Impetigo present?
|
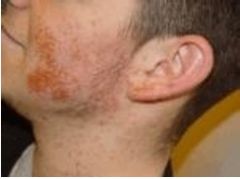
The infection starts as a small red spot (macule). The macule becomes pus-filled and inflamed (pustule) with a red (erythematous) base. A crust
forms after the pustule ruptures. |
|
|
What demographic is usually infected by Impegito?
|
children
|
|
|
Where on the body is Impetigo usually found?
|
face and limbs
|
|
|
How does Erysipelas present physically?
|
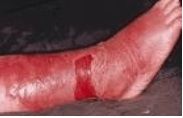
border is sharply demarcated, severe edema, painful inflammation. systemically fever and chills will accompany.
|
|
|
What is the most common causative agent of Erysipelas?
|
Streptococcus pyogenes
|
|
|
What physical symptoms present with cellulitis?
|
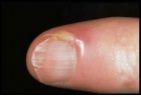
erythema, pain, swelling, warmth, margins are diffuse
|
|
|
What are the most common causative agents for cellulitis?
|
Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus
|
|
|
What are less common causative agents for cellulitis?
|
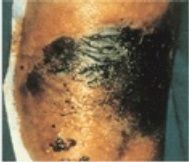
If pt is exposed to contaiminated seawater, Vibrio vulnificus
Clostridium perfringens indicates polymicrobial infection that is anaerobic cellulitis. |
|
|
What are the physical symptoms present with necrotizing fasciitis?
|
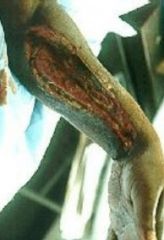
dark red swelling, severe pain, very quickly spreading skin darkness
|
|
|
What are the two most common causative agents for necrotizing fasciitis?
|
Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus
|
|
|
What is a less common causative agent for necrotizing fasciitis?
|
Vibrio vulnificus when exposed to salt-water.
|
|
|
What is the mortality rate of those with necrotizing fasciitis?
|
30 - 50%; with renal failure -> 70%
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of myonecrosis?
|
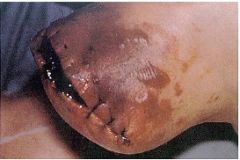
severe pain, tenderness, local swelling, fever, apathy followed by shock and renal failure
|
|
|
What is the mortality rate of myonecrosis?
|
30 - 50%
|
|
|
What is the most common causative agent of Myonecrosis?
|
Clostridium perfringens, endospore forming anaerobe
|
|
|
Where is Clostridia usually found?
|
soil
|
|
|
Gas gangrene is also known as
|
myonecrosis
|
|
|
What is a common contaminant of severe burn wounds?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
What kind of infection is a burn wound infection?
|
opportunistic infection
|
|
|
What is the concern of a Pseudo. aeruginosa with burn wounds?
|
Antibiotic resistant Gram(-) Pseudo. aeruginosa can cause bacteremia because the epidermis is compromised and the bacteria can gain access to the bloodstreadm
|
|
|
What clinical sign should one look for when concerned with bacterial infection of a burn wound victim?
|
1) change in wound color -> red, brown, black
2) change in color of surrounding tissue -> green, violet |
|
|
What less common contaminants of severe burn wounds?
|
Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes
|
|
|
What are the four diseases that infect the skin and lead to systemic infection and their causative agents?
|
1) Clostridium tetani causing tetanus
2) Leoptospira causing leptospirosis 3) Staph. aureus causing staylococcal scalded skin syndrome and toxic shock 4) Strep. pyogenes which causes toxic shock |
|
|
What is the causative agent for tetanus?
|
Gram(+) anaerobe endospore forming Clostridium tetani
|
|
|
What is the route of infection for tetanus?
|
deep penetrating wound that infects wounds with spores. Spores germinate and in 7 - 21 days vegetative cells produce the tetanospasmin toxin
|
|
|
tetanospasmin
|
toxin produced by vegetative form of Clostridium tetani endospores that produce symptoms associated with tetanus disease by blocking the release of glycine and GABA from presynaptic terminals of motor neurons -> uncontrolled muscle contraction
|
|
|
what muscles are most often involved in tetanus?
|
large muscles of the back, jaw
|
|
|
neonatal tetanus
|
tetanus caused by umbilical cord infection
|
|
|
tetanus dx and tx
|
dx based on clinical findings. pathogen isolated to site of infection and takes too long to identify. if wait for lab findings, pt will be dead. give antibiotics, antibodies, and toxoid -> Ab production.
|
|
|
What is the causative agent for leptospirosis?
|
terminal hook-shaped spirochete Leptospira
|
|
|
What is the route of infection for leptospirosis?
|
wild mammals, rodents, dogs, cats, livestock are carriers. by handling meat, contaminated water, or urine containing specimens can cause infection through mucus membranes or any break in the skin
|
|
|
What activities are at most risk for leptospirosis?
|
farm workers, vets, pet shop owners, meat handlers, recreational activities
|
|
|
What are the stages of leptospirosis?
|
1) 7 - 12 day incubation
2) 4 - 7 days of fever, chills, weakness, myalgia when pathogen is in blood and CSF 3) bacteria present in urine, but not blood and CSF 4) usually self limiting |
|
|
How does severe leptospirosis present?
|
jaundice, abdominal pain w/ diarrhea or constipation, renal and pulmonary dysfunction
|
|
|
Icteric disease or Weil's disease
|
severe leptospirosis in 10% of infected pts
|
|
|
What is the most common causative agent of scalded skin syndrome?
|
Staph. aureus in neonates
|
|
|
Ritter disease
|
staphycoccal scalded skin syndrome
|
|
|
What causes symptoms associated with scalded skin syndrome?
|
+ Nikolsky's sign
burned skin look because of Staph. aureus exfoliative toxin (serine protease) which spreads from mouth to rest of the body |
|
|
What is the expected steps of Ritter disease?
|
1) Staph. aureus colonizes skin
2) Staph. aureus releases exfoliative toxin serine protease 3) visible redness starts at corners of mouth and spreads to entire epidermis 4) + Nikolsky's sign 5) epidermis is sloughed off 6) epidermis grows back self limiting 7 - 10 days |
|
|
Nikolsky's sign
|
slight pressure displaces the skin
|
|
|
What is a milder form of scalded skin syndrome?
|
Bullous impetigo, which causes isolated blistering
|
|
|
What are the common symptoms of toxic shock syndrome?
|
rapid onset of high fever, shock, hypotension, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, erythroderma
|
|
|
What increases the risk for Staph. aureus toxic shock syndrome?
|
women who use tampons
|
|
|
What is the most common causative agents of toxic shock syndrome?
|
Staph. aureus (TSST-1) or Strep pyogenes (SPE or pyrogenic exotoxins)
|
|
|
What is the course of infection with Strep. pyogenes toxic shock syndrome?
|
a wound causes a localized infection that spreads to the blood stream and becomes septic
|
|
|
TSST-1 and SPE
|
superantigens associated with toxic shock syndrome
|
|
|
What is toxic shock syndrome secondary to for both Staph. and Strep. toxic shock?
|
Staph. - vaginal infection
Strep. - skin wound |
|
|
What are the differentiating features of Staph. and Strep. toxic shock?
|
Staph. - flu symptoms, generalized erythroderma, bacteremia uncommon
Strep. - no flu symtpoms, no erythroderma, bacteremia common |
|
|
What are the 6 diseases and causative organisms caused by arthropod bites?
|
1) Borrelia burgdorferi causing Lyme disease
2) Francisella tularensis causing tularemia 3) Yersinia pestis causing plague 4) Rickettsia rickettsii causing Rocky Mountain spotted fever 5) Rickettsia akari causing rickettsialpox 6) Rickettsia typhi causing Murine (endemic or flea-borne) typhus |
|
|
What is the causative agent and vector for lyme disease?
|
Borrelia burgdorferi carried by ticks that remain on the skin for ~48 hrs
|
|
|
What is the most common first symptom of lyme disease?
|
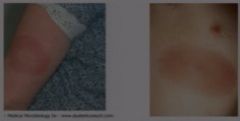
Erythema migrans of round or oval shape. The lesion will spread to form a large red spot sometimes with a clearing and red dot in the middle, sometimes not.
|
|
|
What are the other common presenting symptoms occur with lyme disease?
|
low-grade fever, fatigue, headache, myalgia, athralgia
|
|
|
What is indicative of multiple lesions when there was a single initial lesion appearing on a suspected lyme's disease patient?
|
spread of infection in the blood
|
|
|
What if Lyme's disease is left untreated?
|
the skin lesions will fade and hematogenous dissemination can cause cardiac dysfunction, meningitis, facial palsy and even arthritis months or years later
|
|
|
What is the most common causative agent of Tularemia?
|
Francisella tularensis
|
|
|
How often is Tularemia found in TN?
|
endemic!
|
|
|
What is the most common clinical presentation of tularemia?
|
ulceroglandular form:
an ulcer forms at the site of the bite organism spreads lymphatically causing regional lymphadenopathy pneumonia may develop after hematogenous spread |
|
|
What are the vector paths for tularemia?
|
1) tick bite -> human
2) tick -> cat/rabbit -> human |
|
|
hematogenous spread
|
spreading through the blood
|
|
|
Is there human to human spread of tularemia?
|
nope
|
|
|
Typhoidal tularemia
|
second common form of tularemia
abrupt onset fever, chills, malaise, fatigue with no ulcers or lymphadenopathy |
|
|
What is the common causative agent for the plague?
|
Yersinia pestis
|
|
|
What are the normal vectors for the plague?
|
rats, squirrels, rabbits, cats which are infected, spread infection by fleas
|
|
|
Why is it called bubonic plague?
|
once infected, organisms travel to lymph and cause lymphadenopathy (commonly axillary) which are called buboes.
|
|
|
Pneumonic plague
|
hematogenous spread that gets to lungs, can be spread from person to person and is major cause of epidemics as mortality approaches 100%
|
|
|
Septicemic plague
|
plague that skips the lymph node infection and goes directly to the blood. no buboes are formed.
|
|
|
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever causative agent and vector
|
Rickettsia rickettsii carried by ticks
|
|
|
What fluids can all Rickettsia bugs spread through?
|
Via blood or lymph
|
|
|
What is special about identifying Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever caused by Rickettsia rickettsii as well as Murine typhus caused by Rickettsia typhi in the lab?
|
they are unlikely to culture because it is a strict intracellular pathogen
|
|
|
What is the physical presentation of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
|
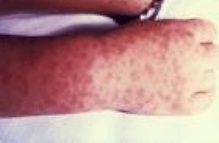
macular rash, mild fever, headache and myalgia.
first is the onset of fever. the rash will start 2 to 6 days after the fever at the wrists and ankles and spread to the rest of the body (including palms and soles). |
|
|
What is a major concern with Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever that is not visible upon physical inspection?
|
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
|
|
|
What epidermal epithelial cells are uniquely involved in Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
|
palm and sole
|
|
|
What is the differentiating features of Rickettsialpox and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
|
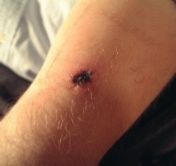
c Rickettsialpox ulcer at the site of initial infection and less severe/self-limiting and no palm or sole involvement
|
|
|
What is the causative agent and vector for Rickettsialpox?
|
Rickettsia akari and ticks.
This is almost identical to Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever... almost. |
|
|
What is the causative agent and vector for Murine Typhus?
|
Rickettsia typhi carried by rats, passed to humans by fleas
|
|
|
How does the Murine Typhus rash spread?
|
from trunk to limbs
|
|
|
What bug is transferred through Cat or Dog bites or scratches because it's part of their normal flora?
|
Pasteurella multocida
|
|
|
What is the drug of choice for all Rickettsia bug diseases?
|
doxyclycline
|
|
|
What is the general antibiotic type that is used for Pasterurella infection per dog and cat attacks?
|
polymicrobial, broad spectrum antibiotic because Pasterella just establishes infection and gives opportunistic bugs that change to settle in.
|
|
|
What infections can dog/cat bites lead to?
|
cellultis
abscesses osteomyelitis septic arthritis |

