![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
immunological diversity
|
number of different in Abs is limitless and is generated by gene rearrangement
|
|
|
immunological specificity
|
each Ab is specific for single Ag/epitope
|
|
|
relative to antigen exposure, when does lymphocyte development/diversity take place?
|
before Ag exposure
|
|
|
variable region is composed of what?
|
variable fragment (V) + diversity fragment (D) + joining fragment (J)
|
|
|
how many different types of recombinatorial D and J fragment types exist?
|
D ~ 12 different types
J ~ 4 different types |
|
|
somatic recombination
|
process by which B and T cell immunoglobulin and TCR (T cell receptors) diversity is achieved
|
|
|
what fragment types compose the Ig heavy chain and TCR beta-chain?
|
V, D, J
|
|
|
what fragment types compose the Ig light chain and TCR alpha-chain?
|
V, J
|
|
|
What are the general steps for recombination of light and heavy chains?
|
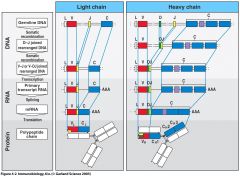
light - V, J made from gene separately
V attaches to J VJ combo is translated into a functional light chain protein heavy - V, D, J are generated D combines with J = DJ DJ combines with V = VDJ protein translation provides function VDJ protein for heavy chain (pic) |
|
|
from gene to functional Ig chain, how is diversity achieved?
|
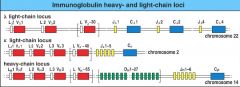
there are only pieces of the gene (loci) that encode for a variable type of V, a variable type of D, and a variable type of J. only one type will end up in the functional Ig chain.
(pic) |
|
|
combinatorial diversity
|
VDJ rearrangement
|
|
|
how are recombination of gene segments in somatic recombination achieved?
|
RSS - recombination signal sequences
1) provide recognition sites for recognition enzymes that cut and rejoin DNA 2) ensure gene segments are joined in the correct order |
|
|
what is the 12-23 rule?
|
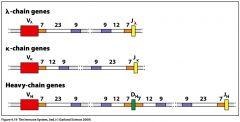
there are portions of the genetic RSS sequence that provide direction on either side of a V, J, or D fragment. The 12-23 rule is that any two adjacent fragments must complement a 23 nucleotide spacer with a 12 nucleotide spacer. So space sequences will be one of two organizations:
1) 7-12-9-9-23-7 2) 7-23-9-9-12-7 this guarantees that there will be 1 V, 1 D, and 1 J (pic) |
|
|
what is VDJ recombinase?
|
a collection of enzymes that in general will recombine V, D, J
ex. 1) RAG-1, RAG-2 2) TdT (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase) |
|
|
What are is the function of recombination activating genes (RAG-1 and RAG-2)?
|
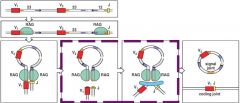
RAGs attach to the RSSs on nearest sides of sequence specific fragments (V and J or V and D or D and J) that come together forming a hairpin loop of unwanted fragments allowing VDJ recombinase to ligate the unwanted segments and join the wanted fragments
(pic) |
|
|
epitope
|
Ag that which an Ab is specific and attaches
|
|
|
how does junctional diversity work?
|
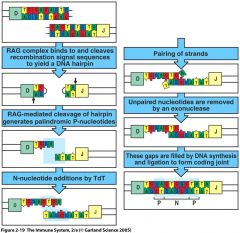
junctional diversity is done by other enzymes that are part of the VDJ recombinase collection.
1) RAG binds to and cleaves 2) RAG generates palindromic P-nucleotides (P nucleotides are not complementary) 3) N-nucleotides are generated by TdT (N nucleotides are complementary) 4) Strands pair, attach 5) extra nucleodies that don't match the palindromic sequence are exised by exonuclease 6) complete DNA sequence is formed to complete the junction between two diversity fragments (pic) |
|
|
second type of combinatorial diversity
|
random combination of heavy and light chains
|
|
|
what is the TCR equivalent to the heavy and light chains?
|
heavy - beta-chain
light - alpha-chain |
|
|
allelic exclusion
|
in a single cell there will only be the expression of one heavy chain and one light chain. to maintain that consistency and specificity, one of the two alleles that represents a gene in a single cell will always be repressed.
|
|
|
somatic hypermutation
|
rapid increase in mutation rates that offers greater specificity after antigen exposure in B lymphocytes. this occurs in heavy and light chain variable regions.
this provides a better second response to an Ag |
|
|
What three diversification events occur before antigen exposure?
|
1) allelic exclusion
2) somatic recombination 3) junctional diversity |
|
|
What diversification events occur after antigen exposure?
|
somatic hypermutation in B cells lymphocytes (Ig) only!
|
|
|
what's the difference between the transmembrane Ig and the secreted Ig?
|
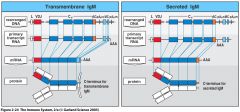
the poly AAA tail is different and the transmembrane type has a transmembrane specific poly AAA tail and respectively for the secreted Ig
|
|
|
what is the purpose of the B cell?
|
to secrete antibodies... it's what it lives to do
|
|
|
antibodies can opsonize a pathogen cell. what does that do?
|
opsonization leads to the activation of complement
|
|
|
isotype switching
|
the process of switching between isotypes of the same Ig such as IgM monomer to IgM pentamer. this happens with IgM and IgG
|
|
|
why is isotype switching necessary?
|
IgM pentamer cannot move from blood to tissue, so it must be switched after it gets to the target antigen
|
|
|
how does isotype switching occur?
|
differential splicing of the same primary RNA transcript. this is a arrangement of germline DNA. very similar to the somatic recombination process.
|
|
|
What is the first produced Ig in an immune response?
|
IgM in its pentomeric form
|
|
|
What should we think of when we think of IgA
|
snot - mucosal secretions
|
|
|
IgE significance
|
allergies and parasites
|
|
|
IgG significance
|
the most prolific Ig in the blood
|
|
|
What are the two reversible actions in diversification of Igs?
|
1) change from membrane bound to secreted forms of Ig
2) switch between IgM expression and IgD expression and coexpression both depend on poly AAA tail cleavage positions |
|
|
IgD significance
|
coexpressed with IgM by differences in poly AAA sites. IgD is just a cell surface marker during development with no other functional significance.
|
|
|
what is the difference concerning gene splicing to produce IgD vs IgM?
|
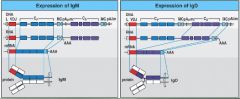
IgD - poly AAA tail is cleaved at the second poly AAA site on the end of the delta gene (longer)
IgM - poly AAA tail is cleaved at the second poly AAA site on the end of the mu gene (shorter) (pic) |

