![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is superficial mycoses?
|
Mycoses of the outermost layers of skin and hair. Usually cosmetic.
|
|
|
What is cutaneous mycoses?
|
Keratinized surface infections: skin, hair, nails. Cutaneous infections and perpetuated by keratinase produced by fungus that breaks down keratin.
|
|
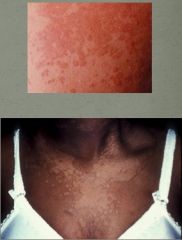
What superficial mycoses presents as irregularly pigmented macules that are well demarcated occuring on any part of the body?
|
Tinea Versicolor
|
|
|
What is the causative agent of Tinea Versicolor? And is it contagious?
|
Liphilic yeast Malassezia furfur. YES. Direct or indirect.
|
|
|
How to dx Tinea Versicolor?
|
Microscropy or Culture with oil agar, also lesions fouresce under a Wood lamp a yellowish color, where as eythasma fluoresces pink.
|
|
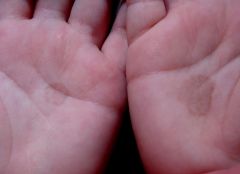
What cutaneous fungus presents with solitary irregular pigmented brown or black macules on the soles or palms?
|
Tinea Nigra
|
|
|
What is the causative agent for Tinea Nigra?
|
Hortaea wernickii
|
|
|
What is the best lab method to identify H. wenickii?
|
KOH mount, followed by culture. Mount shows two cell oval yeast w/ short hyphae.
|
|
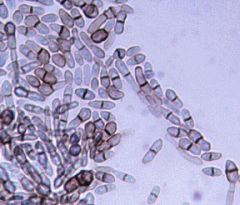
What fungal etiology is shown?
|
two cell oval yeast and short hyphae of H. wernickii, which causes Tinea Nigra.
|
|
|
What is the differential for H. wevneckii and Tinea Nigra?
|
Malignant melanoma.
|
|
|
What is the difference between white and black piedra?
|
White - caused by Trichosporon around the groin and axilla. Black - caued by Piedraia hortae and occurs on the scalp.
|
|
|
How is the White Piedra causing Trichosporon visualized with microscropy and culture?
|
Microscopy - hyphae, arthroconidia, budding yeast. Culture - arthroconidia, blastoconidia.
|
|
|
How is the Black Piedra causing P. hortae visualized with microscopy and culture?
|
Microscopy - Brached, pigmented hyphae. Culture - Ascus, ascospores.
|
|
|
Treatment for all superficial mycoses?
|
Topical antifungal cream, hair removal for piedra.
|
|
|
Where do cutaneous mycoses reside?
|
Exclusively in keratin containing tissue: hair, nails, skin.
|
|
|
What are dermatophytes?
|
Fungus that invades keratin containing tissue, also known as keritinophilic fungi.
|
|
|
What special enzyme do dermatophytes secrete?
|
Keratinase, recall they are called keritinophilic, to digest keratin.
|
|
|
How are dermatophytes catagorized?
|
By route of transmission:
1) Anthrophilic - person to person transfer 2) Geophilic - earth to person 3) Zoophilic - animal to person |
|
|
What microscopic structural characteristics do dermatophytes possess?
|
macroconidia or microconidia
|
|
|
Describe the Epidermophyton - E. flocossum dermatophyte.
|
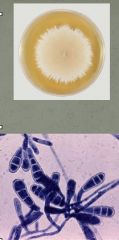
infects in skin and nails
culture forms yellow-white cotton appearance Macroconidia can be visualized as a big paddle with segments. No Microconidia |
|
|
Describe the Microsporum dermatophyte species.
|
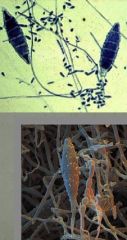
infects skin and nails
wood lamp fluoresces bright green visualized macrocodia like symmetrical spindles with segments |
|
|
Describe the Trichophyton dermatophyte species.
|

infect skin, hair, nails
Microconidia with various shapes, macroconidia rare |
|
|
What tissue is infected by Trichophyton and Microsporum?
|
skin, hair, nails
|
|
|
What climate are T. ruburm, T. mentagrophytes and M. canis most frequently found in?
|
tropical and tmperate
|
|
|
What hair follicle abnormality does T. schoenleinii uniquely cause?
|
favus (air bubbles)
|
|
|
What condition does Epidermophyton cause?
|
rarely tinea unguium and never tinea capitis or barbae
|
|
|
Where are M. Canis and T. equinum from and what type of dermatophyte are they?
|
dogs and horses, zoophilic, and they tend to infect beards and hair
|
|
|
What etiology is geophilic Tinea capitis in children?
|
M. fulvum
|
|
|
Where does Tinea Capitis usually occur?
|
scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes
|
|
|
What are the three patterns of fungal invasion of hair?
|
ectothrix (outside), endothrix (inside), favic (root)
|
|
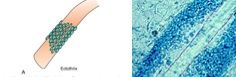
What type of fungal invasion is shown?
|
Ectothrix
|
|

What type of fungal invasion is shown?
|
Endothrix
|
|
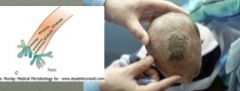
What type of fungal invasion is shown?
|
Favic
|
|
|
What fungal condition manifests as inflammatory circular lesions, burning sensation, that can occur anywhere excluding scalp, groin, palms and soles?
|
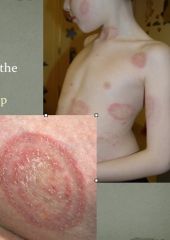
Tinea Corporis (ring-worm)
|
|
|
What fungal condition is limited to the bearded areas of the face and neck, is almost exclusive to men, and causes inflammatory, deep plaques?
|
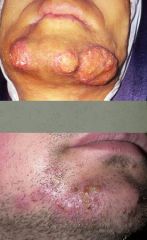
Tinea Barbae
|
|
|
What fungal condition results in well demarcated groin and adjacent skin rash that is acutely moist and chronically dry with papular annules? It can occur in both men and women.
|
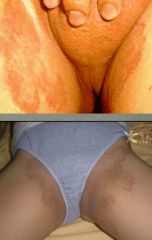
Tinea Cruris
|
|
|
This is the most common dermatophyte and it causes prurtic, scaly soles, painful interdigitary fissures, and rare ulcers or vessicles on the feet?
|
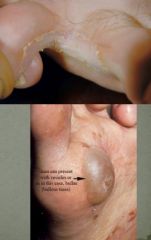
Tinea Pedis
|
|
|
What does tinea mean?
|
A discolored ring.... ringworm (general term for cutaneous mycoses)
|
|
|
What mycoses manifests as a fungal infection of the nails?
|
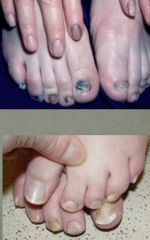
Tinea Unguium or Onychomycosis
|
|
|
What is the treatment for dermatophytes?
|
Topical antifungal or oral therapy.
|
|
|
What is the treatment for cutaneous mycosis?
|
Same thing as dermatophytes: Topical antifungal or oral therapy.
|

