![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
saprobes
|
organisms that exist in dead or decaying material
|
|
|
symbionts
|
symbiotic mutual beneficial life
|
|
|
commensals
|
may or may not benefit, but does not harm. the fugus can chill until the host is immunocompromised, then it can be pathogenic
|
|
|
parasites
|
parasite benefits, host is hurt
|
|
|
Why is mycoses nomenclature confusing?
|
there are two forms of fungus: the asexual anamorphic spore producing flavor and the sexual telomorphic spore producing flavor
|
|
|
What is the fungal cell structure?
|
Fungus are eukaryotes, so they have membrane-bound organelles and cytoskeleton, plasmalemma, cell wall, sometimes a capsule.
|
|
|
What is the only relevant encapsulated fungus?
|
Cryptococcus neoformans - encapsulated yeast
|
|
|
What is the structure and function of the plasmalemma?
|
they function as a cell membrane to protect the cytoplasmic contents and regulates the intake and secretion of solutes. The bilayered structure is made of phospholipids and sterols.
|
|
|
What is significant about the cell wall of a fungus?
|
It is antigenic, so it activates an immune response and is made of 90% polysaccharides and 10% proteins.
|
|
|
What is the most important component of the cell wall of fungus?
|
chitin = N-acetyl glucosamine
|
|
|
What is dimorphism in fungus?
|
fungus that can operate as mold or yeast depending on environmental conditions.
|
|
|
What are the significant characteristics of yeast?
|
unicellular, reproduce by nuclear fission or budding, structurally display buds and pseudohyphae (hyphae shaped buds)
|
|
|
What are the significant characteristics of mould?
|
multicellular, have true hyphae, mycelium, and spores. hyphae will form mycelium
|
|
|
How are hyphae catagorized?
|
The presence of septa and the shape.
|
|
|
What are the three shapes of hyphae?
|
Racquet - spiral, nodular - rootlike, pectinate - chandler
|
|
|
What's the difference between septate and nonseptate?
|
septate are segregated into single nucleated cells by crosswalls. they have septum. nonseptate or coenocytic are actually multinucleated hyphae.
|
|
|
What are mycelium?
|
they are precursed by hyphae, but are longer projections. they can either be vegetative (grows beneath the surface) or aerial (projects above the surface)
|
|
|
What are the role of spores in a fungal life cycle?
|
They are the form of fungus that undergoes sexual or asexual reproduction. They are haploid and unicellular.
|
|
|
What is the process of asexual fungal reproduction?
|
Mycelium gives rise to spore-producing structures. Spores are released and germination takes place which eventually produces mycelium.
|
|
|
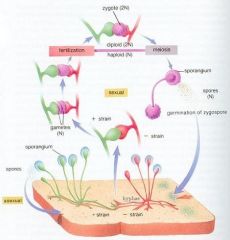
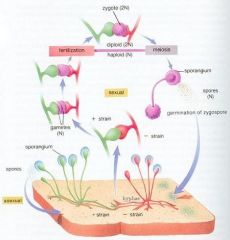
What is the process of sexual fungal reproduction?
|
Mycelium is formed and plasmogramy takes place (the fusion of cytoplasm between two mates). The fusion produces a geterokaryotic stage which leads to karyogamy (fusion of nuclei). Thish produces a zygote. The zygote undergoes meiosis for form new haploid fungus. These form spore-producing structures which produce spores and germinate into mycelium.
|
|
|
What are the three types of fungal sexual spores?
|
zygospores, ascospores, basidiospores
|
|
|
What is a zygospore?
|
A fungal sexual spore caused by the fusion of two hyphae.
1) A (+) and (-) hyphae mate 2) a (n) gametangia or zygosporangium is formed 3) a (2n) zygote is formed 4) a (2n) zygospore is formed 5) meiosis will occur to go back to an (n) state of a normal fungus. |
|
|
What is an ascospore?
|
An ascus is a cell that is the site of meiosis. An ascospore is a spore born in an ascus (sac). There are 8 ascospores in an ascus. Ascospores in an ascus look like peas in a pod.
|
|
|
What is a basidiospore?
|
Basidium is a cell where karyogamy and meiosis take place. Basidiospores are sexual fungal spores born on the outside of a basidium.
|
|
|
What are the two asexual fungal spore?
|
sporangiospores and conidia
|
|
|
What are sporangiospores?
|
Asexual fungal spores produced within sporangium which stains as a pink stalk with a sporangium containing red sporangiospores. Stalk and bulb.
|
|
|
What are conidiaspores?
|
A conidiophore is a specialized hyphal branch. Conidiaspores are born at the end of this stalk. Conidiophore stalk with bulbous vesicle and finger-like conidiaspore projections.
|
|
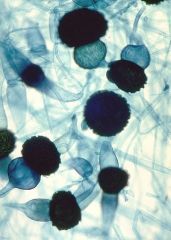
What class of fungus are these?
|
Zygomycetes - forms zygospores, sporangium
|
|

What fungal class is this?
|
Ascomycetes - ascospores, conidiophores, can see septate hyphae
|
|

What is the fungal class?
|
Basidomycetes - mostly mushrooms, which are important because of toxicity. Most recognized human pathogen is Cryptococcus neoformans.
|
|
|
What class of fungus is called the imperfect fungi, has never been witnessed reproducing sexually, and has been moved to Ascomycetes for the most part?
|
Deuteromycetes
|
|
|
What four techniques are used to visualize mycoses?
|
microscopy, culture, serology, molecular techniques
|
|
|
What four stain types are used to identify mycoses microscopically.
|
Gram, KOH, calcofluor, India Ink.
|
|
|
What two cultures are used to identify mycoses microscopically?
|
Sabouraud dextrose agar, mycobiotic agar.
|
|
|
|

