![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three Types implant systems?
|
Subperiosteal
Transosseious Endosseous |
|
|
Summary of implant fixation
|
Implant installation
Blood clot formation Granulation tissue formation (fibroplasia, angiogenesis) Woven bone formation Bone remodeling (Mature lamellar bone formation) |
|
|
Implant fixation
2 hrs after installation |
Wound chamber filled with blood coagulum (Clot formation)
Primary stability: close contact between the pitches and the bone |
|
|
Implant fixation
Day 4 |
Osteoclasts are observed along the cut bone surface
Granulation tissue formation in the wound chamber |
|
|
Implant fixation
1 week |
Cell-rich woven bone (immature bone) and provisional matrix
formation in the wound chamber: ‘Primary Spongiosa’ Direct contact between the newly formed mineralised trabecular bone and the SLA surface (contact osteogenesis) Osteoblasts (lining the trabeculae) and osteocytes are found |
|
|
Implant fixation
2 weeks |
Large woven bone formation at the ‘apical’ area of the implant
Newly formed bone is continuous with the parent bone and along the SLA chamber surface |
|
|
Implant fixation
4 weeks |
Continuous bone formation and maturation: Increase in mineralised tissue
Intense bone remodelling at a pitch region Newly formed bone extends from the cut bone surface into the chamber |
|
|
Implant fixation
6, |
mixture of woven bone parallel-fibered and lamellar bone
|
|
|
Implant fixation
8 and 12 weeks |
mature bone with marrow space (adipose cells)
|
|
|
Implant fixation
Types of osteogenesis? |
Distance osteogenesis: New bone formation on the surfaces of old
bone in the peri-implant site Contact osteogenesis: Direct new bone formation on the surfaces of the implant itself (SLA surface - osteoconductive characteristic) |
|
|
Define Primary stability
|
mechanical stability of an inserted implant
|
|
|
Micromovement/ Micromotion leads to?
|
‣ Disruption of blood clot formation
‣ Disruption of angiogenesis ‣ Interfere with migration of osteogenic mesenchymal cells ➡ Repair by fibrous tissue NOT OSSEOINTEGRATION |
|
|
Periosteal Differences between teeth and implant
|
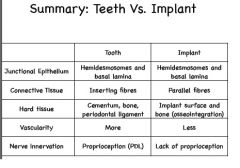
|
|
|
Define BW
|
Soft tissue dimensions that face the teeth - minimum physiological
requirement for the soft tissue support |
|
|
What is BW for teeth and implant?
|
teeth: about 2.04mm
Implant: about 2.93mm |

