![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
endosymbiosis
|
organelles originated when a single-called organism engulfed another single called organism
|
|
|
algae
|
-eukaryotic; aquatic; photo-autotrophs; unicellular and multicellular forms
|
|
|
fungi
|
eukaryotic; acquire food via absorption; heterotrophic; cell walls composed of chitin; are now a monophyletic group
|
|
|
Structure of Fungi
|
-cell walls are composed of chitin
-thallus composed of hyphae -mycelium is the vegetative part of a fungus, composed of branched hyphae |
|
|
Two types of hyphae
|
-septate
-coenocytic |
|
|
septate
|
The hyphae are divided into cells by cross-walls called septa
|
|
|
coenocytic
|
The hyphae are not divided by septa, but consist of continuous cytoplasm with hundreds of nuclei
|
|
|
How does fungi reproduce?
|
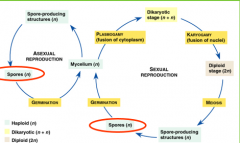
The nuclei in the hyphae of the mycelium are haploid. Fungi reproduce by releasing spores that are produced either sexually or asexually
|
|
|
Fungal divisions
|
zygomycota
Ascomycota basidiomycota |
|
|
zygomycota
|

-mycelium is coenocytic (acetate)
-many disperse aerial spores (asexual reproduction) -forms zygosporangia when food is in short supply (sexually reproduction) -e.g. molds |
|
|
Division zygomycota: If hyphae from 2 different "mating strains" come into contact...
|
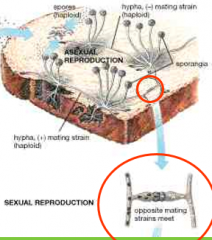
Sexual reproduction will also take place
|
|
|
ascomycota
|

-sac fungi
-produce spores in saclike asci -includes true yeasts; ascomycetes that produce ascocarps (e.g. morels, truffles) |
|
|
Division ascomycota
|
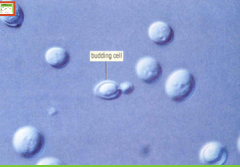
Unlike most ascomycetes, yeast do not form multicellular mycelia, instead they are unicellular
|
|
|
basidiomycota
|

-club fungi
-includes mushrooms (basidiomycetes), smuts and rusts -spores produced in fruiting bodies called basidia |
|
|
Division basidiomycota
|
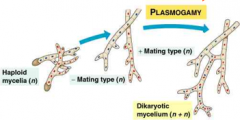
-as in rhizopus, basidiomycetes have different mating strains. What the hypage of 2 difference haploid mating strains meet, the cells fuse called plasmogamy
-the nuclei do not fuse, so the cells of the mycelium that grows after plasmogamy are dikaryotic (they contain paired haploid nuclei) |
|
|
basidiocarp
|
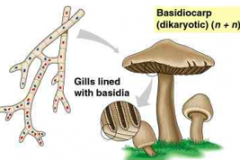
-this dikaryotic mycelium eventually grows above-ground, and forms a mushroom-shaped structure.
|
|
|
gills
|
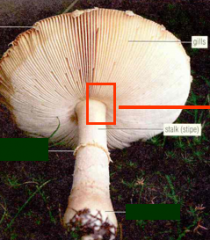
On the undersurface of the mushroom cap are a number of _____ visible to the naked eye
|
|

|
Cross section of a mushroom cap
|
|
|
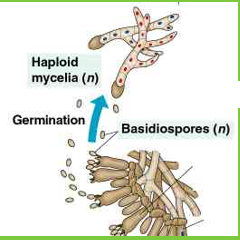
basidiospores
|
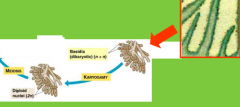
Are formed by the haploid nuclei of the dikaryotic cells lining the gills fuse, forming diploid nuclei. These then undergo meiosis which formed 4 haploid basidiospores
|
|
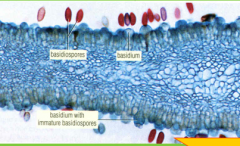
|
basidiospores which can be seen in stained preparation
|
|
|
To complete the life cycle, the haploid basidiospores are shed, and germinate into haploid hyphae. The hyphae grow and again form an underground mycelium
|
|
|
Lichens
|
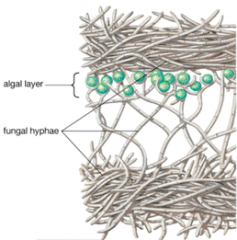
-composite organisms
-symbiotic association between an algae and a fungus -fungus derives sustenance from algae -alga is ostensibly housed by fungus |
|
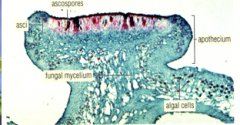
|
Cross section of lichen
|
|
|
foliose
|
"leafy"; most common group of lichen; circular growth & attached at many points
|
|
|
crustose
|
"crusty"; flat unlobed edges; closely attached; hard to remove without damage lichen or substrate
|
|
|
fruticose
|
"shrubby"; common at higher altitudes; often pendulous and attached at a single point; free standing; branching
|
|
|
|
prepared slide of lichen
|
|
agaricus bisporus
|
mushroom sample
|

