![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What stain is used in blood staining?
|
Leishman's stain
|
|
|
What rule is used when working with a haemocytometer?
|
North-west
|
|
|
How to measure magnification?
|
Size of structure in picture X real size of structure
|
|
|
Osmosis
|
The movement of water down a concentration gradient through a semi permeable membrane
|
|
|
Why is the bi concaved shape of erythrocytes help it's function?
|
It would have a large area to volume ratio to speed up the gaseous exchange
|
|
|
Lymphocytes help with what?
|
Creating antibodies
|
|
|
What organelles are not found in both palisade mesophyll cell and eukaryotic cells?
|
Cell wall, chloroplasts and permanent vacuole
|
|
|
What is the primary structure?
|
Sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain
|
|
|
What organelle contain a prosthetic group?
|
Haemaglobin
|
|
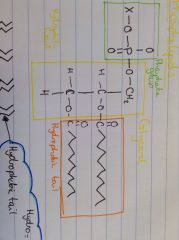
What is this molecule?
|
Phospholipid
|
|
|
How many molecules of oxygen can a haemoglobin contain?
|
4 molecules as there's 4 iron molecule
|
|
|
What is plasma?
|
The liquid part of blood
|
|
|
What is serum?
|
This is where blood-clotting protein and fibrinogen has been removed
|
|
|
What is tissue fluid?
|
Blood which has been passed through the capillaries
|
|
|
What is lymph?
|
Tissue fluid which has drained into lymphatic capillaries
|
|
|
Platelets are fragments of what?
|
Megakaryocytes
|
|
|
What ions are found in blood plasma?
|
Sodium, potassium, calcium and chloride
|
|
|
What are the waste product of blood plasma?
|
Carbon dioxide and urea
|
|
|
What proteins are found in blood plasma?
|
Fibrinogen, antibodies and albumin
|
|
|
What hormones travel in blood plasma?
|
Insulin and oestrogen
|
|
|
What does polar stand for?
|
Something which has different charges
|
|
|
What is serum?
|
This is where blood-clotting protein and fibrinogen has been removed
|
|
|
What are electrolytes?
|
Ions with positive or negative charges
|
|
|
What's the name for positively charged ions?
|
Cations
|
|
|
What is the name of negatively charged ions?
|
Anions
|
|
|
What electrolytes are tested for?
|
Sodium, potassium, chloride and bicarbonate
|
|
|
What do neutrophils do?
|
Engulf microorganisms by phagocytosis
|
|
|
What plasma ions are tested for?
|
Calcium, magnesium and phosphate
|
|
|
What does facilitated stand for?
|
Helped
|
|
|
What is diffusion?
|
The net movement of a substance from a high concentration to a lower concentration.
|
|
|
What is passive diffusion?
|
The movement of a substance down a concentration gradient without energy
|
|
|
What is isotonic?
|
A solution with the same water potential as a cell
|
|
|
What is hypertonic?
|
A solution with a lower water potential than the cell
|
|
|
What is hypotonic?
|
A solution with a higher potential that the cell
|
|
|
What is the protein which helps to transport sodium out and potassium Into the cell?
|
Sodium-potassium pump
|
|
|
What is water potential?
|
The potential energy of water per unit volume
|
|
|
What should be a normal blood glucose level?
|
4-8 millimoles per litre
|
|
|
What do lymphocytes do?
|
B lymphocytes- create antibodies
T lymphocytes- help with cell destruction |
|
|
What should blood glucose level be 90 minutes after eating?
|
Less than 10 millimoles per litre
|
|
|
What is an example of a monosaccharide?
|
Glucose
|
|
|
How many carbons found in a monosaccharide?
|
5 in the ring and a single on the outside
|
|
|
When two glucose are joined what does it produce?
|
Maltose
|
|
|
I'm a disaccharide what bond does a condensation reaction create?
|
Glycosidic link
|
|
|
Disaccharides are made up of what?
|
2 monosaccharides
|
|
|
Example of a polysaccharide?
|
Glycogen
|
|
|
What is this molecule?
|
Glycerol molecule
|
|
|
What's the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids?
|
Unsaturated has a double bond carbon
|
|
|
What is required to break this water bond?
|
Hydrolysis reaction
|
|
|
Cell membranes are made up of?
|
Proteins and phospholipids
|
|
|
Oils which are liquid at room temperature contain what type of fatty acids?
|
Unsaturated fatty acids
|
|
|
Fats which are solid at room temperature contain what fatty acid?
|
Saturated fatty acids
|
|
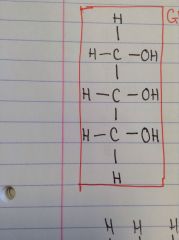
What is this molecule?
|
Glycerol molecule
|
|
|
Leucocytes and tissues of the blood vessel release and enzyme when damaged called?
|
Thromboplastin
|
|
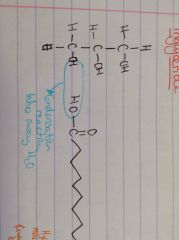
What is required to break this water bond?
|
Hydrolysis reaction
|
|
|
What is this molecule?
|
Phospholipid
|
|
|
What's the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
|
Ribosomes synthesise proteins and distribute around cell
|
|
|
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
|
Synthesis of glycoproteins, polysaccharides, and hormones
|
|
|
Function of the nuclear envelope?
|
Regulates exchange between cytoplasm and nucleus
|
|
|
Whats the definition of eukaryotic cells?
|
Cell with a true nucleus
|
|
|
What is diastole?
|
The relaxation phase of a heart beat
|
|
|
What valve prevents blood entering the aorta?
|
Semi-lunar valve
|
|
|
What is atrial systole?
|
This is where the ventricle contracts and pushes blood into the ventricle
|
|
|
What is ventricle systole?
|
Walls of the ventricle contract and forces the AV valves shut
|

