![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
GROUNDING problem |
A grounding problem occurs when the motherboard or adapter is not properly installed and a trace (metal line on the motherboard or adapter) touches the computer frame, causing the adapter to possibly stop other components to stop working. |
|
|
|
ESD (electrostatic discharge) |
Is a difference of potential between two items that causes static electricity. Static electricity can damage equipment without knowledge. (Humans need a static discharge of 3000 volts to feel but components can be damaged with as little as 30 |
|
|
|
Antistatic wrist band |
Prevents ESD. Circles wrist and at the other end, an alligator clip that attaches to the computer. (Grounding post or metal part such as power supply) An antistatic wrist strap allows the person and computer to be at the same voltage potential. |
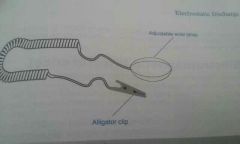
|
|
|
# antistatic wrist band |
Don't wear an ESD antistatic wrist strap when working inside a CRT monitor because of the high voltages there |
|
|
|
EMI (electromagnetic interfere) EMR(electromagnetic radiation) |
Noise caused by electrical devices. Many devices can cause EMI, such as pencil sharpener,printers, air conditioner, fluorescent light, computer,motor,vacuum cleaner, electrical devices around computer case, including CRT monitor and speakers cause more problems for a computer |
|
|
|
RFI (radio frequency interfere) |
RFI is simply those noises that occur in the radio frequency range. Anytime after computer has an intermittent problem, check the surrounding devices for the source of the problem. |
|
|
|
# tools |

|

|
|
|
# do not use magnetized screwdrivers |
Avoid using them when working on a computer. It can cause permanent loss of data on hard drives or floppy disks. Magnetism can also induce currents into components and damage them. |
|
|
|
PIN 1 |
Pin 1 on a cable connects to pin 1 on a connector. In the event that the pin 1 is not easily identified, both ends of the cable should be labeled with either a 1 or a 2 on one side or a higher number, such as 24,25,49,50, and so on, on the other end. Pins 1& 2 are always on the same end of a cable. If you find a higher number, pin 1 is on the opposite end. Also, the cable connector usually has an arrow etched into its molding showing the pin 1 connection |

|
|
|
# pin 1 |
Numbers on adapters are easier to distinguish. When the number 2 is etched beside the adapter connector, connect the cables pin 1 to the side. Remember pin 1 and 2 are always on the same side, whether on the connector or on a cable. |
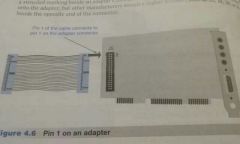
|
|
|
# solder joints |
Silver blobs on the back of the motherboard or adapter. Solder joints connect electronic components to the motherboard or adapter. They're normally round except joint pin 1 which is square. |
|
|
|
I/O shield |
A part that allows for optimum air flow and grounding for motherboard ports. The I/O shield helps ensure the motherboard is installed correctly and property aligned with the case (Allows cooling) |

|
|
|
Standoffs |
Some computer cases have cases or plastic or metal (commonly brass) that allow the motherboard to be screwed into the case without the motherboard solder joints touching and grounding to the computer case, causing the motherboard to not work. |
|
|
|
(Plastic) standoffs |
Some standoffs are plastic and they slide into slots on the computer case. Do not remove these kinds of standoffs but just leave them attached and slide the motherboard out of the slots. |
|
|
|
(Metal) standoffs |
The most common type, that screws into the case; this standoff has a threaded side that the motherboard sits on and a screw that attaches the motherboard to the stand off |
|
|
|
Scribe (tool) |
A plastic scribe is the best tool to use for levering some laptop and mobile devices that require it. |
|
|
|
Preventive maintenance |
Includes certain procedures performed to prolong the life of a computer. Must be cleaned at least once a year. Typical preventive measures include vacuuming (do first befire blowing dust with compressed air)computer/printer and cleaning the optical drive laser, keyboard key, printers, and display screen. |
|
|
|
# |
A useful CD/DVD/BD cleaning kit can include a lens cleaner that removes dust,dirt,fingerprints, and oils from the disk; and scratch repair kit used to resurface, clean, and Polish CDs DVDs and BDs. |
|
|
|
AC (alternating current) |
One of two types of electricity. The electricity provided by a wall outlet is AC. Devices such as radios, toasters, TVs use AC power. With AC electrons flow in alternately in both directions. |
|
|
|
DC (direct current) |
Type of electricity used by computer components. DC power is used for a computer's internal components and anything powered by batteries. DC electrons flow in one direction only |
|
|
|
Voltage |
Voltage is a measure of pressure pushing electrons through a circuit, is measured in volts. |
|
|
|
Volts |
A power supply's output is measured in volts. Power supplies typically put out +3.3V (volts) +5V, +12V and -12V |
|
|
|
Standby power (SB) |
Another designation is +5VSB. This is for the computers standby power. This power us always provided, even when the computer is powered off. This supplied voltage is why you must unplug a computer when working inside of it |
|
|
|
Capacitor |
A component that holds charge even after the computer is turned off. Capacitors inside a monitor can hold a charge for several hours after the monitor is turned off. |
|
|
|
Current - amps |
Current is measured in AMPS (amperes), which is the number of electrons going through a circuit each second. (Waterpipe analogy) every device needs a certain amount of currents to operate. A power supply is rated for the amount of total current. (In amps) it can supply at each voltage level. A power supply can be could be rated at 20 amps for the 5 volt level and 8 amps for the 12 volt level. |
|
|
|
# Waterpipe analogy |
Voltage is the amount of pressure to force the water through the pipe, (makes more come out and makes mire current flow)and current is the amount of water flowing |
|
|
|
Power - watts |
Power us measured in watts, which is a measurement of how much work is being done. It is determined by multiplying volts by amps. Power supplies are described as providing a max number of watts. This is the sum of all outputs: for example 5 volts x 20 amps (100 watts) plus 12V 8 amps (96 watts) equals 196 watts. |
|
|
|
Resistance -ohms |
Resistance measured in ohms, which is the amount of opposition to current in an electric circuit. The resistance range on a meter can be used to check continuity or check Wether a fuse is good. (Ohms is usually illustrated with the omega symbol) |
|
|
|
Continuity check |
A continuity check is used to determine whether a wire has a break in it. A conductor (wire) in a cable or a good fuse will have a very low resistance to electricity (close to zero ohms) a broken wire or bad fuse will have very high resistance (millions of ohms sometimes shown as infinite ohms or OL) |
|
|
|
# power supply overview |
The power supply is essential as it convert AC voltage to DC voltage and distributes it to the components, no computer would work without it. The AC voltage accepts either 100 to 120 volts or 200 to 240 volts. Some duel voltage power supplies accept either |
|
|
|
# Power supply overview 2 |
There are two badic types of power supplies: switching and linear. *A computer uses a switching power supply. It provides efficient power to all the computers internal components (and possibly to external ones like USB devices) it also determines heat, come in small devices, and is cheaper than linear power supplies. *A switching power supply requires a load (something attached to it) in order to operate property. |
|
|
|
# form factors |
The form of the components or hardware or connectors that go together |
|
|
|
24 pin (ATX power supply connector) |
Main ATX power connector to the motherboard Voltages-+3.3, +5, +12, -12 |
|
|
|
20 pin (ATX power supply connector) |
Main power connector to the motherboard Voltages- +3.3, +5,-5, +12, -12 |
|
|
|
15 pin (ATX power supply connector) |
SATA connector Voltages- +3,+5,+12 |

|
|
|
8 pin (ATX power supply connector) |
12V for CPU used with any ATX12V v1 Powe supply Voltage-+12 |
|
|
|
Pin 8 (ATX power supply connector) |
PCIe video, connects to a PCIe video adapter. Note that some connectors are 6+2 pin meaning they accept either the 6- or 8-pin cable Voltages- +12 |
|
|
|
6 pin (ATX power supply connector) |
PCIe video; connects to PCIe video adapter Voltage - +12 |

|
|
|
6 pin (ATX power supply connector) |
Sometimes labeled as AUX; connects to the motherboard if it has a connector Voltages- +3.3, + 5 |
|
|
|
4 pin molex (ATX power supply connector) |
Connects to peripheral devices such as hard drives and and CD/DVD drives Voltages- +5, +12 |
|
|
|
4 pin berg (ATX power supply connector) |
Connects to peripheral devices such as the floppy drive Voltages- +5, +12 |
|
|
|
4 pin (ATX power supply connector) |
Sometimes labeled as AUX or 12V; connects to the motherboard for CPU voltage- +12 |

|
|
|
3 pin (ATX power supply connector) |
Used to monitor fan speed volt speed N/A |
|
|
|
Power good signal (Labeled PWK_OK) p |
Goes to the motherboard and prevents a computer from attempting to operate on improper voltages and damaging itself. |
|
|
|
# Purposes of power supply |
*convert AC to DC * provide DC voltage to motherboard and components, peripheral devices *provide cooling and facilitate air flow through case |
|
|
|
# ATX power supply |
An ATX power supply does not connect to the front panel switch as the old AT- style power supplies did. With the ATX power supply, a connection from the front panel switch to the motherboard supply provides a 5 volt signal that allows the motherboard to tell the power supply to turn on. The ATX style power supply blows air inside the case instead of the back. Known as reverse flow cooling. (Keeps inside clean) |

|
|
|
Power supply tester |
Can be used to check DC power levels on the different power supply connector |
|
|
|
# battery types |
*NiCad (nickel cadmium) originally used in laptops. Now replaced. *NiMH (nickel metal hydride) replaced NiCad * li-ion (lithium ion) batteries. Replaced the previous two. |
|
|
|
Li-ion (lithium ion) batteries |
Are very light and can hold a charge longer than any other type. They're also more expensive. Mobile phones,smartphones, tablets, portable media and digital cameras use li-ion batteries.these batteries lose their charge over time even if they're not used. Make sure that a laptop with an li-ion battery is not plugged into an AC outlet all the time |
|
|
|
#all power supplies are not created equal |
You must replace a power supply with one that provides equal or greater amount of power. A general rule of thumb is that if two power supplies are equal in wattage, the heavier one is the better because it uses a bigger transformer, bigger heat sinks, and more quality components. |
|
|
|
ACPI (advanced configuration and power interface) |
Gives the BIOS and operating system control over various devices' power and modes of operation With ACPI, the user can control how the power switch operates and when power to specify devices, such as the hard drive and monitor, is lowered. |

|
|
|
Wake on LAN |
The wake on LAN feature allows a network administrator to control the power to a work remotely and directs the computer to come out of sleep.
Software apps can also use the Wake on LAN feature to perform updates, upgrades, and maintenance tasks. Allows the computer to wake when a LAN signal is received |
|
|
|
Wake on ring |
Allows a computer to come out of sleep mode when the telephone line has an incoming call. This let's the computer receive phone calls, faxes, and emails when the user is not present |
|
|
|
Delay prior to thermal (common BIOS power settings) |
Defines the number of minutes the system waits to shut down the system once an overheating situation occurs |
|
|
|
CPU warning temperatures (common BIOS power settings) |
Specifies the CPU temperature at which a warning message is displayed on the screen |
|
|
|
ACPI function (common BIOS power settings) |
Enables or disables ACPI in the event of a problem |
|
|
|
Soft off (common BIOS power settings) |
Specifies the length of time a user must press the power to turn off the computer |
|
|
|
Deep S4/S5 (common BIOS power settings) |
Uses less power and only wakes from S4/S5 states with the power button or RTC (real time clock) alarm, such as waking the computer to complete a task |
|
|
|
Resume by alarm (common BIOS power settings) |
Allows a date and time to be set when an adapter or external device supports wake on ring |
|
|
|
CPU THEM throttling (common BIOS power settings) |
Allows a reduction in CPU speed when the system reaches a specific temperature |
|
|
|
Power on function (common BIOS power settings) |
Specifies which key (or key combo) will activate the systems power |
|
|
|
Hot key power on (common BIOS power settings) |
Defines whar keystrokes will Reactivate system power |
|
|
|
Doze mode (common BIOS power settings) |
When the system is in a reduced activity state, the CPU clock is throttled (slowed down). All other devices operate at full speed |
|
|
|
After power failure (common BIOS power settings) |
Sets power mode after a power loss |
|
|
|
Duel rail power supply |
A duel rail power supply has two +12V output lines. A triple rail power supply simply has three +12V output lines for devices. |

|
|
|
Auto switching |
An auto switching power device monitors the incoming voltage from the wall outlet and automatically switches itself accordingly. Auto switching power supplies accept from 100 to 240VAC at 50 to 60Hz. |
|
|
|
AC circuit tester |
A device used to verify that an AC wall outlet is wired property. Small device containing a power plug and several indicator lights |

|
|
|
Undervoltage |
When the voltage falls below 110 volts AC. Devices for the voltage is too low, a computer cannot provide enough power to all the components. The power supply draws too much current, causing it to overheat, weakening or damaging the components. |
|
|
|
Spike (Overvoltage subtype) |
A spike lasts 1 to 2 nanoseconds. A nanosecond is one billionth of a second. A spike is harder to guard against than a surge because it has such short duration and high intensity |
|
|
|
Surge (Overvoltage subtype) |
A surge lasts 3 or more nanoseconds than a spike. Also called transient voltage. Causes of surges include lightning, poorly regulated electricity, faulty wiring,, and devices that turn on periodically, such as elevators, air conditioning, and refrigerators |
|
|
|
Brownout (Undervoltage) |
In a brownout, power circuits become overloaded. Occasionally, an electric company intentionally causes a brownout to reduce the power drawn by customers during peak periods |
|
|
|
Sag (Overvoltage subtype) A sag occurs when the voltage from the wall outlet drops momentarily. |
Blackout (Overvoltage subtype) A Blackout is a total loss of power. |
|
|
|
Surge protector |
A surge protector, aka a surge strip or surge suppressor, is commonly a multi outlet strip that offers but in protection against overvoltage. Surge protectors don't protect gains tax undervoltage, they protect against overvoltage. |

|
|
|
MOV (metal oxide varistor) |
Most surge protectors have an electronic component called MOV, which protects the computer or device that plugs into one of the outlets on the surge strip. When a surge occurs, MOV prevents the extra voltage from passing to the outlets. If a large surge occurs, the MOV will take the hit and be destroyed. It's Located in between the AC coming in and the outlet into which devices are plugged. |
|
|
|
Clamping voltage (Surge protector features) |
The level at which surge protector start protecting the computer. The lowest the value, the better the protection |
|
|
|
Clamping speed (Surge protector features) |
How much time elapses before protection begins. The lower the value, the better the protection. Surge protectors cannot normally protect against power spikes because of their rated clamping speed. |
|
|
|
Energy absorption/dissipation |
The greater the number of joules (unit of energy) that can be dissipated, the more effective and durable the surge protector is. This feature is sometimes called energy absorption. A surge protector of rating of 630 joules is more effective than a rating of 210 joules |
|
|
|
TVS (transient voltage suppressing) rating (Surge protector features) |
This is also known as response time. The lower the rating the better. For example, a 330TVS rated surge protector is better than a 400 TVS rated one |
|
|
|
UL rating (Surge protector features) |
UL(underwriters laboratories) developed the UL 1449 VPR (voltage protection rating) standard to measure the max amount of a voltage surge protector will let through to attached devices. The UL 497A standard is for phone line protection, the UL 1283 standard is for EMI/RFI |
|
|
|
# MOV |
MOV sometimes have a status lamp to indicate if it's destroyed or not |
|
|
|
Power/line conditioner |
An alternative for computer protection. More expensive than surge protectors, but they protect a computer from over voltages, undervoltages, and adverse noise conditions over electrical lines. It monitors AC elec. If voltage is too low, it boosts voltage to the proper range. If it's too high, the line conditioner clamps down the voltage and sends the proper amount to the computer l. |

|
|
|
UPS (uninterruptable power supply) |
Provides power to a computer or other devices for a limited amount of time when there is a power outage. A UPS provides enough time to save work and safely shut down the computer. Some operating systems do not operate properly if power abruptly cuts off and the computer is not brought to a logical stopping place. A network server, the main computer for a network is a great candidate for a UPS |
|
|
|
UPS (2) |
Provides power conditioning for the devices attached to it. AC power is used to charge the battery inside UPS. The battery inside UPS supplies power to an inverter. The inverter makes AC for the computer. When AC power from the outlets fail, the battery inside the UPS continues to supply power. |
|
|
|
# installing UPS |
*Connect UPS to outlet as it needs to charge first after you buy it. *power off UPS *attach power cords, such as PC, to the UPS. Ensure the UPS is rated for the connected device *power up the UPS |
|
|
|
SPS (standby power supply) |
A device similar to UPS. An SPS contains a battery like the UPS, but the battery provides power to the computer only when it loses AC power. It does not provide constant power, like the UPS. It's not as effective as a UPS because the SPS must detect a power out condition first and then switch over to the battery to supply power to the computer. As a result, SPS switching time is important. Any time under 5 milliseconds is fine for most systems. |
|
|
|
Phone line isolator Modem isolator |
Provides protection against line surges. No pc connected to a phone line should be without one. Many now come with one built in the strip |

|
|
|
Type A-B-C fire extinguisher Type C extinguisher |
Class A involve paper, cloth wood etc Class B involves flammable liquids or gases Class C involve electrical fires |
|
|
|
# Fuses |
A type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to provide overcurrent protection, of either the load or source circuit. |
|
|
|
Overvoltage |
Overvoltage occurs when the output voltage from the wall outlet is over the rated amount. AC from the wall is usually 110-130 volts, if it rises to 130 overvoltage occurs. It's harmful because too much DC can hurt the components and destroy electronic circuits |
|

