![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Goals of Cancer Chemotherapy |
a. Curative therapy -Total eradication of cancer cells b. Palliative therapy -Alleviation of symptoms -Increased life span and improved quality of life c. Neoadjuvant therapy - Reduction of tumor burden before surgery or radiation d. Adjuvant therapy - Eradication of remaining cancer after surgery or radiation |
|
|
Detection Threshold |
확인할 수 있는 tumor size 1cm3. 이정도가 되려면 cancer cell 이 10^9개 있어야 됨. |
|
|
Tumor Evolution |
-mutation 이 계속 누적되는거. -Clonal selection 결과 dominant group in heterogeneous population. |
|
|
Three types of therapy |
a. Conventional therapy = targets cell growth & survival. b. Molecularly targeted therapy = oncogene addiction 을 target 으로. c. Anti-angiogenic therapy, immunotherapy = 미세환경 변화를 target으로. |
|
|
Target별 분류 |
Tumor targeting, vessel targeting, immune targeting, hormone targeting |
|
|
내성 기전 |
1. Single cell event: increased efflux, decreased influx, activation of detox system, activation of DNA repair, blocked apoptosis.
2. Group event |
|
|
Drug specific toxicities |
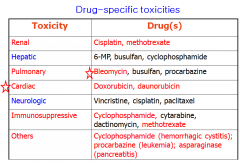
|
|
|
Cocktail therapy |
eg. breast cancer FAC or TAC |
|
|
Anticancer actions of alkylating agents |
DNA adduct/cross-linking – to block DNA replication DNA break – to stimulate cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis DNA repair – mutagenesis - carcinogenesis |
|
|
Resistance to alkylating agents |
-Decreased uptake of drugs -Increased nucleophilic substances like glutathione |
|
|
Toxicites of alkylating agents |
a. Bone marrow toxicity – immunosuppression, bleeding, anemia b. Mucosal toxicity – oral ulceration, intestinal denudation - sepsis c. Neurotoxicity – nausea/vomiting, mental change, seizure, ataxia d. Carcinogenesis (leukemogenic) – 5% of patients e. Others - pulmonary fibrosis by most alkylating agents - hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) by most alkylating agents - alopecia by alkylating agents - leakage from i.v. site – skin vesicle, ulcer - irreversible infertility - renal failure by platinum complexes and “acrolein” - hemorrhagic cystitis by “acrolein” |
|
|
Mesna (mercaptoethanesulfonate) |
Mesna에 의해 경감되는 약물: -cyclophosphamide -ifosfamide |
|
|
Nitrogen mustards |
대표적인 예: Cyclophosphamide *PO or IV *Hemorrhagic cystitis - w/ IV fluid but water intoxication due to ADH. *cadiac toxicity |
|
|
Nitrosoureas |
Streptozocin: pancreatic beta cell을 파괴해서 당뇨병을 유방할 수도 있다. |
|
|
Methylhydrazines
|
eg) procarbazine. -originally synthesized as a MAO inhibitor -methylates DNAs -side effects: common side effects of alkyating agents, hypertension due to MAOI, disulfiram-like action (숙취 더 심하게) |
|
|
Platinum Complexes |
cisplatin -Renal toxicity: pre-hydration to prevent toxicity (saline infusion). iv infusion of Pt drugs with diuretics. -ototoxicity -peripheral sensory, motor neuropathy -Amifostine reduces toxicities by donating SH group -avoid Al devices
Carboplatin: less toxic than cisplatin, but less effective in some tumors Oxaliplatin: wider range of anticancer activity
|
|
|
Topoisomerase Inhibitors |
-Topo 1: single strand 자름 -Topo 2: double strand 자름
|
|
|
Camptothecin analogues |
-inhibits topo I (cf. doxorubicin inhibits topo II) -toxic to cells at S-phase -drug resistance mech: efflux through MRP, alteration of Topo I, activation of DNA repair enz.
toxicities: -BM and GI toxicities -hepatitis, fever
uses: -radiation sensitizer -combined with other anticancer drugs |
|
|
Antimetabolites |
Folic acid analogues = Methotrexate (MTX) Pyrimidine analogues = 5 Fluorouracil (5FU), Cytarabine (Ara-C) Purine analogues = 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP), 6-thioguanine (6-TG) |
|
|
Methotrexate (MTX) |
Mode of action: -reduce the FH4 level by inhibiting FH2 reductase -block DNA/RNA synthesis -kill cells during the S phase
Drug resistance mechanism: -impaired transport of drug -alteration of target structure (FH2 reductase) -overexpression of the target gene -less conjugation of glutamates -increased drug efflux (MRP, multidrug resistance protein)
Toxicity: -acute: injure BM and GI cells, pneumonitis -chronic: liver cirrhosis, dermatitis, renal toxicity.
Uses: -hematological malignany/solid tumor -non-cancer: anti prolif action = psoriasis immunosupp action = graft rejection, RA, Crohn's disease (면역 억제 시킴)
|
|
|
Leucovorin rescue after high dose MTX |
-resume do novo synthesis of deoxynucleosides -recover normal cells from MTX toxicity |
|
|
5FU |
Kill cells during the S phase.
Toxicity: dermatitis (hand foot syndrome, CNS & heart toxicity Uses: radiation sensitizer 5FU + Leucovorin: potentiate 5-FdUMP inhibition of TS. |
|
|
Cytarabine (Ara-C) |
incorporate into DNA and RNA strands. Uses: leukemia. solid tumor X |
|
|
Purine Analogues |
Immunosuppressant = Azathioprine Anti-viral = Acyclovir Anti-cancer = 6MP Anti-gout = allopurinol |
|
|
6MP (mercaptopurine) |
-blocks de novo synthesis of purine as a pseudo-substrate -short half life due to rapid metabolism. So reduce 6MP dose by 75 % in patients taking allopurinol.
Toxicity -hyperuricemia; controlled by allopurinol --> reduce 6MP dose
Uses: -hematological malignancy -non-cancer: psoriasis, polycythemia vera. -immunosuppressive action: RA, Crohn's disease |

