![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
etiology ?? |
varicella zoster virus |
|
|
varicella zoster virus
what ?? |
doubl-stranded DNA virus |
|
|
forms/types of varicella zoster infections |
1-primary
2-laten infection
3-secondary / reactivation
4-congenital |
|
|
primary varicella infection ??? |
chickenpox |
|
|
secondary varicella / reactivation |
shingle / Herpes zoster |
|
|
transmission methods ?? |
1-respiratory droplets
2-lesions / vesicles fluid |
|
|
transmissions via vesicles fluid ?? |
high viral load
less transmission rate than resp. droplets |
|
|
incupation period ?? |
10 - 21 day |
|
|
age of infection ??? |
most infection 90 % at age less than < 10 yrs |
|
|
prognosis ?? |
depends on : ___________________________ 1-age
2-immunity |
|
|
bad prognosis ?? |
old age ( any > 12 yo)
immunocopromized |
|
|
main method of Dx ? |
clinical : vesicular rash with different stages of maturation
in crops |
|
|
definitive method of Dx ?? |
vesicular fluid culture |
|
|
pathophysiology of 1ry infection |
1-replication at URT mucosa / Lymph N ((prodrom))
2-1ry viremia
3-2nd replication at liver / spleen
4- 2ry viremia
5-viral invasion of epidermis |
|
|
proliferation at URT mucosa and regional LN
timing ?? |
1st (( 2-4 )) days |
|
|
1ry viremia
timing ?? |
4-6 days |
|
|
2ry proliferation at liver and spleen
timing |
6-14 day |
|
|
2ry viremia timing ?? |
14-16 day |
|
|
viral invasion of skin ??
vesicle pathophysiology |
virus will invades the endothelium of capillaries and epidermis
it will cause intra and inter cellular edema .....vesicles formation |
|
|
clinical stages of disease
((history / symptomes )) |
1-prodrome
2-rash onset |
|
|
the prodrome ?? |
not common in children
in adolescent / adults is common : _________________________________ 1-nause 2-maylgia 3-anorexia 4-headache
|
|
|
stage of disease onset / rash
manifistation ?? |
1-itchy rash
2-malaise
3-fever |
|
|
fever in chickenpox charachteristic ??? |
low-grade |
|
|
infective period ?? |
1-2 days before the rash
4-5 days after onset // at time of crustation |
|
|
rash
area of involvement ?? starts at ??
|
at trunk / face |
|
|
rash
palms / soles ??
mucousa / oral ?? |
yes it does involve palms/soles / oral mucosa |
|
|
latent infection ?? |
after crustation of vesicles ..... virus will spread to local sensory nerves
and remain dormant at dorsal sensory ganglia till reactivation.......shingles |
|
|
chickenpox rash stages ?? |
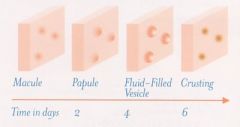
-red macules
-papules
-clear vesicle
-pustules
-central umbilication
-crustation |
|
|
chickenpox at oropharynx presentation ?? |
shallow painful ulcer |
|
|
most common complication of varicella |
2ry bacterial infection |
|
|
possible complications of chickenpox |
1-secondary infection
2-disseminated varicella ( varicella pneumonia)))
3-CNS
4-heamorrhagic complications
5-congenital varicella |
|
|
forms of varicella 2ry bacterial infections ?? organisms ?? |
1- staph & strep
2-impetigo / cellulitis / erysipelase
3-may result in scarring / sepsis |
|
|
disseminated varicella
manifestation |
- varicella pneumonia
- myocarditis
-gangrene
-hepatitis
-Glomerularnephritis |
|
|
CNS complications of varicella ??? |
-Ray syndrome
-Gullien- barie syndrome
-acute cerebellar ataxia
-encephalitis |
|
|
what are the heamorrhagic complications of varicella ?? |
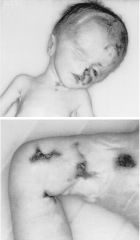
-rare
-unkown etilogy
-low plt and purpura
|
|
|
congenital varicella
% if mother infected ??
time of pregnancy ?? |
1-2 %
early-mid pregnancy |
|
|
congenital varicella presentation |
1-limbs aplasia
2-muscle atrophy
3-skin scarring
4-cortical atrophy
5-microceph
6-cataract
7-digital amputation |
|
|
DDx of chickenpox ?? |
-pemphigoid
-dermatitis herpitiformis
-drug eruption
-erythema multiformis
-H.simplex
-impetigo
-insect bite
-smallpox
-syphillis |
|
|
work up in chockenpox ?? |
- Tzank smear
-vesicular fluid Cx
-serology
-CXR |
|
|
Tzank smear |
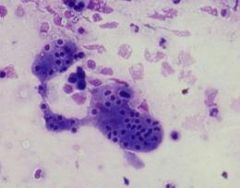
multinucleated giant cells |
|
|
manegment |

1-symptomatic
2-role of antiviral |
|
|
symptomatic Rx |
1-antihistamine
2-local creams / calamine lotion
3-acetaminophine |
|
|
indications for Antiviral / acyclovir use |
1-immunosuppressseds
2-older than 12 Yo
3-complication /disseminated / pneumonia |
|
|
acyclovir
oral vs Iv |
oral in adult immunocompetent as prophx for complications
IV for immunocopromized |
|
|
oral acyclovir as prophx in pt > 12 yo
dose frequency duration |
800 mg X 4
for 5 days |
|
|
immunocopromized IV dose frequency duration |
10-15 mg / Kg Q8 hrs
for 7 - 10 days |
|
|
other antiviral |
1 |
|
|
VZ immunoglobulin
post-exposure |
1 |
|
|
vaccination |
1 |
|
|
1 |

|

