![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Big things about Phylum arthropoda? |
-Largest phylum
-Only invertebrate phylum that has invaded terrestrial environment -Insects: only flying invertebrates -2/3 of all arthropods are insects |
|
|
tagmatization (See tagmatum)
|
fusion of segments into one discrete structure
|
|
|
What is the tagmatum of a lobster called?
|
carapace
|
|
|
arthropods have a reduced coelom in adult: body cavity consists mostly of _____ (______) filled with blood
|
hemocoel (spaces in tissue)
|
|
|
Arthropods have a _________ which contains protein, lipid, chitin, and often calcium carbonate secreted by underlying epidermins and shed (molted) at intervals; although chitin occurs in a few groups other than arthropods, its use it better developed in arthropods
|
cuticular exoskeleton
|
|
|
Arthropods have a _______ digestive system. their mouthparts are modified from ancestral appendages and adapted for different methods of feeding; gut tube shows great specialization by having chitinous teeth, compartments, and gastric ossicles
|
complete
|
|
|
Arthropods have a _________ MUSCULAR system, with ________ for attachment, _______________ for rapid actions, and _________ for visceral organs. Have no _____
|
complex, exoskeleton, striated muscles, smooth muscles, cilia
|
|
|
Well-developed ______ organs; behavioral patterns much more complex than those of most invertebrates
|
sensory
|
|
|
In arthropods, the sexes are usually ______, with paired reproductive organs and ducts
|
separate
|
|
|
oviparous
|
young are laid in eggs (not yet alive)
|
|
|
ovoviviparaous
|
a mixture of oviparity and viviparity
|
|
|
viviparous
|
young are born alive (not egg-lain)
|
|
|
Arthropods have paired _________ glands called _____, ____, or _____ glands.
|
excretory, coxal, antennal, maxillary
|
|
|
Other arthropods have excretory organs called ______ tubules.
|
Malpighian
|
|
|
How to arthropods respire?
|
by body surface, gills, tracheae (air tubes), or book lungs
|
|
|
arthropods have a(n) ______ circulatory system, with dorsal contractile heart, arteries and hemocoel (blood sinuses)
|
open
|
|
|
Subphylum Trilobita is so named because..?
|
it's body is formed into three lobes LONGITUDINALLY.
They represent some of the earliest forms of arthropods (all are extinct) |
|
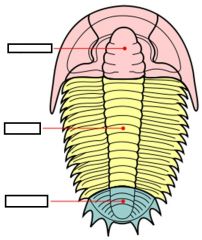
Label/Class?
|
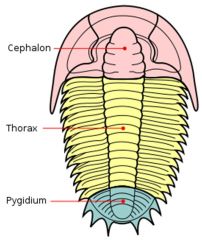
Subphylum Trilobita
|
|
|
Characteristics of Subphylum Chelicerata?
And what are the two classes associated with Chelicerata? |
Four pairs of legs
First pair of appendages are modified to form chelicerae*. No antennae. No mandibles. Cephalothorax and abdomen often with segments fused. Merostomata and Pycnogonida |
|
|
Characteristics of class Merostomata? (Subphylum?)
|
(Chelicerata)
Aquatic Compound lateral eyes appendages with gills |
|
|
Extinct "giant scorpion"?
|
(Class - Merostomata)
SUBCLASS** -> Eurypterids |
|
|
What subclass contains the Horseshoe crab? (What class?)
|
(Class Merostomata)
Subclass - Xiphosurida NOT EXTINCT** |
|
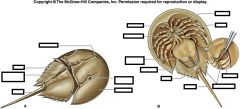
Label/Class?
|
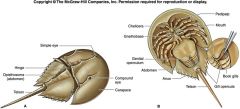
Class - Merostomata
Subclass - Xiphosurida |
|
|
A horseshoe crab uses its ______ to orient itself, provide extra defense, and locomote.
|
telson
|
|
|
Three classes of Chelicerata?
|
Merostomata
Pycnogonida Arachnida |
|
|
Sea spiders are a part of class ______, (Subphylum?)
|
(Subphylum Chelicerata)
Class Pycnogonida |
|
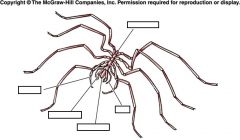
Label/Subphylum/Class
|
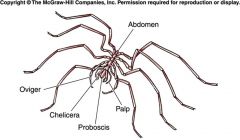
Celicerata/Pycnogonida
|
|
|
What organisms belong to class Arachnida? (Subphylum?)
|
(Subphylum: Chelicerata)
-scorpions, spiders, mites, ticks, and harvestmen |
|
|
Characteristics of Arachnida?
|
four pairs of legs;
segmented or unsegmented abdomen with or without appendages and generally distinct from cephalothorax respiration by gills, trachae, or book lungs excretion by Malpighian tubules or coxal glands dorsal bilobed brain connected to ventral ganglionic mass with nerves simple eyes sexes separate chiefly oviparous no true metamorphosis |
|
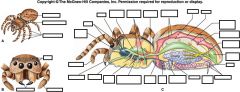
Label/Class?
|
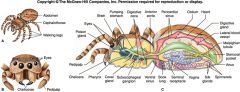
Arachnida (Subphylum Chelicerata)
|
|
|
What is it called whenever the spider injects its prey and returns later to suck out the dissolved organs?
|
saprozoic feeding
|
|
|
The cavity through which blood flows in an Arachnida and in which organs are located
|
hemocoel
|
|
|
The blood of an arthropod?
|
hemolymph
|
|
|
The communication of Arachnids in courtship rituals
|
semaphorant signaling
|
|
|
role of silk in spiders?
|
make web to catch stuff
wrap prey up ballooning (afixation to a stable structure that then flies away) |
|
|
The cover over the female gonopore on the anterior end of the epistosoma
|
epigynum
|
|
|
Unique structure that scorpions have located on ventral surface at the junction of prosoma and epistosoma.
For sexual recognition and feeding |
pectines
|
|
|
Sexual dimorphism in scorpions?
|
females are larger and have small pectines
males are smaller and have larger pectines |
|
|
Scorpions belong to what class?
|
Arachnida
|
|
|
Mites are a part of what class?
|
Arachnida
|
|
|
Ticks belong to what class?
|
Arachnida
|
|
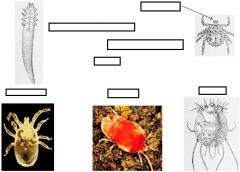
Label/Class?
|
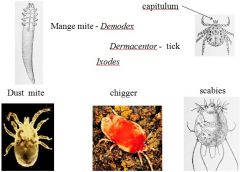
Arachnida
|
|
|
Crustaceans have a _______ larva stage
|
nauplius
|
|
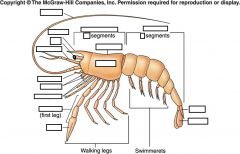
Label/What is it?
|
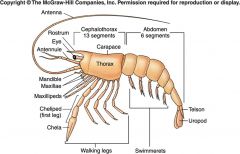
H.A.M. (Hypothetical Ancestral Malacostraca)
|
|
|
Shrimps, Crazyfishes, Lobsters, and crabs are part of class ________.
|
Malacostraca (soft + shell)
|
|
|
Other name for Hypothetical Ancestral Malacostraca (H.A.M.)?
|
caridoid facies
|
|
|
How many "Walking legs" do Malacostracans have?
|
TEN. (Also known as decapods). The first pair of legs is called the Cheliped with a Chela ("pincher") on the end.
|
|
|
Malacostracans have _______ which aid in holding eggs during development.
|
swimmerets
|
|
|
derived from the same embryonic tissue?
|
homology
|
|
|
repeated parts limbs/parts all derived from the same embryonic tissue
|
serial homology
|
|
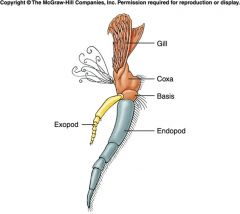
|
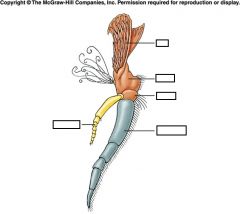
|
|
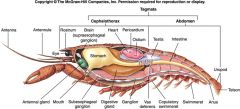
Label/Class?
|
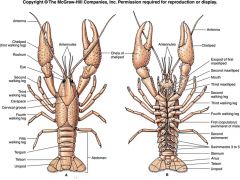
Malacostracan
|
|
|
ventral portion of the exoskeleton
|
sternum
|
|
|
dorsal portion of the exoskeleton
|
tergum
|
|
|
connection of dorsal and ventral portions of the exoskeleton
|
pleura
|
|
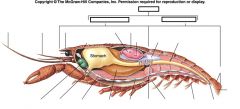
Label/Class?
|
Malacostracan
|
|
|
increase the surface area inside the exoskeleton of a Malacostracan for the muscles to attach to.
|
apodemes
|
|
|
The first two swimmerets of a Malacostracan are modified ONLY in _______ (for copulation).
|
males
|
|
|
6 segments of a Malacostracan mouth area anterior --> posterior?
|
mandible, first maxilla, second maxilla, 1st, 2nd, and 3rd, maxillapeds
|
|
|
Malacostracans have two stomachs: the _______ stomach and the _______ stomach.
|
Cardiac, Pyloric
|
|
|
A chitonized toothy structure between the cardiac and pyloric stomach
|
Gastric mill
|
|
|
Daphnia exhibit _________, changing their morphology depending on population densities.
|
cyclomorphosis
|
|
|
Leaf-like appendages on daphnia and fairy shrimp used for locomotion and respiration
|
phyllopodia
|
|
|
appendages of hexapoda are attached to the _______.
|
thorax
|
|
|
Kind of (hopping) locomotion that grasshoppers exhibit
|
saltatorial
|
|
|
Female grasshoppers have an ___________.
|
ovipositor
|
|
|
Describe respiration tract of insects..
|
spiracles --> trachea --> tracheoles
(Simple Diffusion) |
|
|
The metamorphological changes that take place in a butterfly are _________.
|
holometabolous
|
|
|
________ have two pair of appendages per somite.
|
diplopoda (millipedes)
|
|
|
________ have one pair of appendages per somite.
|
chilopoda (centipedes)
|

