![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of joint is the stifle?
What are the three articulations within it? |
Complex condylar synovial joint
Joints: Femorotibial Femoropatellar Proximal tibiofibular |
|
|
The joint capsule of the stifle is the largest in the body - what three synovial sacs does it have?
|
2 femorotibial joint sacs – medial and lateral
1 femoropatellar joint sac |
|
|
What separates the synovial and fibrous layers of the stifle joint capsule?
|
The infrapatellar fat pad.
|
|
|
Which meniscus of the stifle joint is thicker?
|
There are the medial and lateral menisci of the stifle joint. The lateral meniscus is slightly thicker.
|
|
|
How are the menisci of the stifle joint adhered to the tibia?
How is it adhered to the femur? |
Each meniscus has a cranial and caudal meniscotibial ligament - these bind the menisci tightly to the tibia.
The meniscofemoral ligament courses between the caudal part of the lateral meniscus and the medial femoral condyle. This is why the medial meniscus tears more easily - because it doesn't have this added stabilization. |
|
|
Where does the medial collateral ligament of the stifle course between?
|
Courses between the medial epicondyle of the femur and the medial border of the tibia distal to the medial tibial condyle
Fuses with the joint capsule and the medial meniscus |
|
|
Where does the lateral collateral ligament of the stifle course between?
|
Courses between the lateral epicondyle of the femur and the head of the fibula, with a few fibers going to the lateral condyle of the tibia
Courses over the tendon of origin of the popliteus m. |
|
|
Which of the collateral ligaments of the stifle are loose or taut on extension of the stifle? flexion?
|
Both ligaments are taut on extension of the stifle
The lateral collateral ligament loosens on flexion of the stifle |
|
|
What are the attachments and function of the cranial cruciate ligament?
|
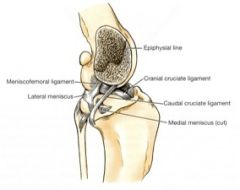
Attachments:
From the caudomedial part of the lateral condyle of the femur to the cranial intercondylar area of the tibia Function: Tightens on extension of the stifle Prevents the tibia from sliding cranially when the limb bears weight Limits medial rotation of the tibia when the stifle is flexed |
|
|
What are the attachments and functions of the caudal cruciate ligament of the stifle?
|
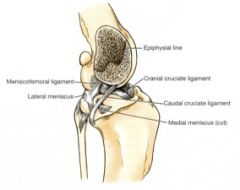
Attachments:
From the lateral surface of the medial femoral condyle to the medial edge of the popliteal notch of the tibia Function: Tightens on flexion of the stifle Prevents caudal movement of the tibia when the limb bears weight |
|
|
How do the collateral and cruciate ligaments of the stifle function together?
|
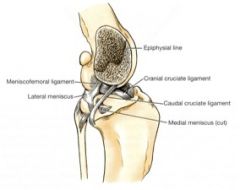
The collateral ligaments work together with the cruciate ligaments to limit internal rotation
In extension, the collateral ligaments are the primary check against internal rotation In flexion, the cruciates are the primary restraint against internal rotation of the tibia External rotation is limited only by the collateral ligaments in flexion and extension |
|
|
What tests can you use to diagnose cranial cruciate ligament rupture?
|
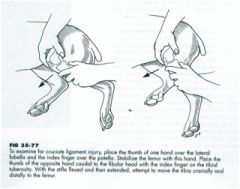
The cranial drawer test and tibial thrust.
Cranial drawer test is stabilizing the femur with one hand and with the other, try to move the tibia forward like moving a drawer out of a dresser. (pictured) Tibial thrust - when you flex the hock, the tibia will thrust cranially. |
|
|
What does the interosseus membrane of the crus connect?
What passes through its cranial opening? |
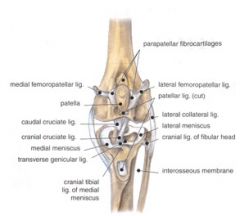
Connects the tibia and fibula – extends from the proximal to the distal tibiofibular joint capsule
An opening is present proximally for passage of the cranial tibial a. and v. |
|
|
How many joint sacs does the tarsus have?
|
3 lateral and 4 medial
|
|
|
Where does the tarsal joint capsule extend from?
|
from the periosteum proximal to the distal articular cartilage of the tibia and fibula to the proximal ends of the metatarsal bones
|
|
|
Where do the medial collateral ligaments of the tarsus course?
|
The medial malleolus of the tibia to the first tarsal bone.
|
|
|
Where do the lateral collateral ligaments of the tarsus course?
|
The lateral malleolus of the fibula to the base of metatarsal V, attaches to the calcaneus and fourth tarsal bones
|

