![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
120 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
study types:
observational retrospective observational prospective observational |
case-control
cohort cross-sectional |
|
|
what measures are used for these studies?
case-control cohort cross-sectional |
odds ratio
relative risk prevalence |
|
|
what kind and number of people are in phase 1 and phase 2 clinical trials?
|
small # of healthy volunteers
small # with the disease |
|
|
phase 1 purpose
|
SToP
safety toxicity pharmacokinetics |
|
|
phase 2 purpose
|
AED
adverse effects efficacy dosing |
|
|
sensitivity
specificity PPV NPV |
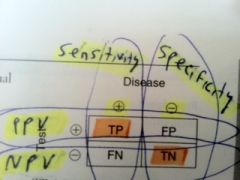
sensitivity = TP/(TP+FN)
specificity = TN/(TN+FP) PPV = TP/(TP+FP) NPV = TN/(TN+FN) |
|
|
sensitivity in words
|
true positives / everyone with disease
|
|
|
specificity in words
|
true negatives / everyone without disease
|
|
|
positive predictive value in words
|
probability that a person actually has the disease
given a positive test result |
|
|
negative predictive value in words
|
probability that someone is disease free
given a negative test result |
|
|
point prevalence =
incidence = |
total cases / total population
new cases / total population |
|
|
prevalence ~ =
|
incidence x disease duration
|
|
|
for acute disease,
prevalence = |
incidence
|
|
|
odds ratio approximates _ if _
|
relative risk
if prevalence is not too high |
|
|
odds ratio vs. relative risk, defined in words
|
odds of having disease in exposed group / odds in unexposed group
percent with disease in exposed group / percent with disease in unexposed group |
|
|
formulas
--odds ratio --relative risk --attributable risk |
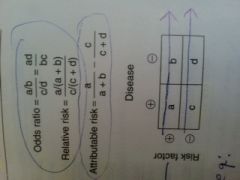
|
|
|
number needed to treat =
number needed to harm = |
1/absolute risk reduction
1/attributable risk |
|
|
selection bias
|
nonrandom assignment to study group
|
|
|
recall bias
|
knowledge of presence of disorder alters recall
|
|
|
late-look bias
|
information gathered at an inappropriate time
e.g. survey to study a fatal disease (only pts alive will be answer survey) |
|
|
procedure bias
|
pts in different groups are not treated the same --
e.g. more attention is paid to treatment group |
|
|
confounding bias
|
occurs with 2 closely associated factors
effect of 1 factor distorts effect of the other |
|
|
lead-time bias
|
early detection is confused with ^ survival
|
|
|
pygmalion effect
|
researcher's belief in the efficacy of a treatment changes the outcome of treatment
|
|
|
hawthrone effect
|
group changes its behavior due to knowledge of being studied
|
|
|
ways to reduce bias
|
--blind studies
--placebo responses --crossover studies (each subject acts as own control) --randomization |
|
|
skew means...
|
skew, like screw, asks "where's the tail?"
e.g. positive skew has the tail toward positive x axis |
|
|
R skew =
|
positive skew
= mean > median > mode |
|
|
type I error (3 definitions)
|
finding a difference when none exists
(convicting an innocent man) mistakenly rejecting Ho |
|
|
type II error (3 definitions)
|
not finding a difference when one exists
(letting a guilty man go free) mistakenly accepting Ho |
|
|
probability of making a type I error
probability of making a type II error |
p, alpha
beta |
|
|
type I error is a false _
type II error is a false _ |
false positive
false negative |
|
|
square diagram of
alpha error (type I) beta error (type II) power |
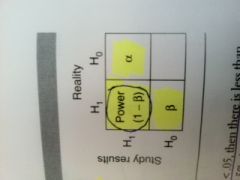
|
|
|
power =
|
1 - beta
|
|
|
power means, in words
|
probability of rejecting null hypothesis when you should
= probability of finding a difference if in fact one exists |
|
|
power depends on
|
^ sample size --> ^ power
--total number of end points --difference in compliance (mean values) between treatment groups --size of expected effect |
|
|
standard error of the mean
|
standard deviation / sqrt(n)
|
|
|
confidence interval, in words:
|
range in which a specified probability of the means of repeated samples are expected to fall
|
|
|
in what cases specifically...if a confidence interval includes
--0 --1 --> Ho is not rejected |
CI for a mean difference includes 0
CI for odds ratio or relative risk includes 1 |
|
|
if the CI between 2 groups overlaps...
|
then they're not significantly different
|
|
|
CI interval formula
|
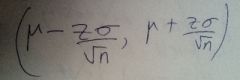
|
|
|
t test
ANOVA chi^2 check... |
difference between means of 2 groups
difference between means of 3 or more groups difference between percentages or proportions of categorical outcomes |
|
|
r^2
vs. r |
coefficient of determination
coefficient of correlation |
|
|
disease prevention 1, 2, 3
|
prevent
early detection reduce disability |
|
|
reportable diseases
|
Hep Hep Hep Horray, the
SSS MM ART Chick is Gone! --in all states [vary by state] --Hep A --Hep B [Hep C] [HIV] --Salmonella --Shigella --Syphilis --Measels --Mumps --AIDS --Rubella --Tuberculosis --Chickenpox --Gonorrhea |
|
|
leading causes of death:
infants |
congenital
SIDS respiratory distress syndrome |
|
|
leading causes of death:
age 1-14 |
ICCHH:
injuries cancer congenital homicide heart disease |
|
|
leading causes of death
age 15-24 |
injuries
homicide suicide |
|
|
leading causes of death
age 25-64 |
cancer
heart disease injuries |
|
|
leading causes of death
age 65+ |
heart disease
cancer stroke |
|
|
medicare is available to...
|
> 65
ppl w. certain disabilities ESRD pts |
|
|
medicare parts
|
A
--inpatient hospital care --skilled nursing --hospice --home health B --outpatient care --doctors --PT/OT C --combination of A & B D --prescription drug coverage |
|
|
informed consent requires
|
--discussion of information (risks, benefits, alternatives -- no intervention)
--pt agreement to plan of care --freedom from coercion |
|
|
exceptions to informed consent
|
--lacks capacity
--legally incompetent --emergency implied consent --therapeutic privilege --waiver |
|
|
therapeutic privilege exception to informed consent =
|
withholding information when disclosure would severely harm pt
or undermine informed decision-making capacity |
|
|
emancipation (4)
|
married
self-supporting has children military |
|
|
parental consent is not required... (5)
|
emergency
contraceptives STD treatment care during pregnancy drug addiction treatment |
|
|
capacity vs. competence
|
psychological decision-making ability
legal competence |
|
|
decision-making capacity (5)
|
makes and communicates a choice
is informed decision is stable over time d. is consistent with patient's values d. is not a result of delusions or hallucinations |
|
|
oral advance directives are more valid if (4)
|
informed
specific choice repeated --pt was informed --directive is specific --pt made a choice --decision was repeated over time |
|
|
confidentiality respects _
|
privacy
autonomy |
|
|
exceptions to confidentiality
|
potential serious harm to others
high likelihood of harm to self no alternative means exist to warn or protect physician can take steps to prevent harm |
|
|
examples of how physicians may need to violate confidentiality
|
infectious diseases... tell
--public officials --people at risk Tarasoff decision: law requires physician to inform and protect potential victim child/elder abuse impaired automobile drivers suicidal/homicidal patients |
|
|
negligence civil suit requires
|
duty (the physician to the pt)
dereliction (breach of duty) damage (to patient) direct (the breach of duty caused the harm) |
|
|
APGAR
= |
appearance
pulse grimace activity respiration |
|
|
apgar
appearance |
0 blue
1 trunk pink 2 all pink |
|
|
apgar
pulse |
0 -- 0
1 -- < 100/minm 2 -- > 100/min |
|
|
apgar
grimace |
0
none 1 grimace 2 grimace + cough |
|
|
apgar
activity |
0 -- limp
1 -- some 2 -- active |
|
|
apgar
respiration |
0 -- none
1 -- irregular 2 -- regular |
|
|
low birth weight is
|
< 2500 g
|
|
|
milestones
birth-3 months |
rooting reflex
orients to voice |
|
|
milestones
3 months |
holds head up
Moro reflex disappears social smile |
|
|
milestones
7-9 months |
sits alone
crawls stranger anxiety |
|
|
milestones
15 months |
walks
babinski disappears a few words separation anxiety |
|
|
toddler =
|
12-36 months
|
|
|
milestones
12-24 months |
climbs stairs
stacks 3 blocks at 1 year 6 blocks at 2 years ------------------------------------- object permanence 200 words 2 word sentences at 2 yrs old |
|
|
24-36 months
milestones |
-----------------------------
core gender identity parallel play |
|
|
milestones
30-36 months |
stacks 9 blocks
toilet training (pee at 3) |
|
|
milestones
3 yrs |
rides tricycle
copies line or circle 900 words complete sentences |
|
|
milestones
4 years |
simple drawings
hops on 1 foot -------------------------------- cooperative play imaginary friends grooms self brushes teeth buttons & zips |
|
|
tanner stage 1
|
1
childhood |
|
|
tanner stage 2
|
2
--pubic hair appears (adrenarche) --breasts enlarge |
|
|
tanner stage 3
|
3
pubic hair darkens, becomes curly penis size/length ^ |
|
|
tanner stage 4
|
4
penis width ^ darker scrotal skin development of glans raised areolae |
|
|
tanner stage 5
|
5
adult areolae are no longer raised |
|
|
sexual changes in the elderly
|
slower erection/ejaculation
longer refractory period vaginal --shortening --thinning --dryness |
|
|
sleep changes in the elderly
|
v REM
v slow-wave sleep (3 & 4) ^ latency ^ awakenings |
|
|
psychiatric changes in the elderly
|
v psychiatric disorders
^ suicide rate |
|
|
highest suicide rate is in...
|
males 65-74
|
|
|
physical changes in the elderly
|
decreased:
vision hearing immune response bladder control renal pulmonary GI function muscle mass ^fat |
|
|
normal bereavement can last _
includes _ can include _ |
up to 2 months
shock denial guilt somatic symptoms can include: illusions |
|
|
pathologic grief
|
excessively intense
> 2 months delayed, inhibited, denied depression delusions hallucinations |
|
|
grief stages
|
denial
anger bargaining grief (depression) acceptance |
|
|
stress effects
|
production of free fatty acids
lipids cholesterol 17-OH corticosteroids catecholamines affects --water absorption --muscular tonicity --gastrocolic reflex --mucosal circulation |
|
|
4 notable drugs that affect sexual performance
|
you're not SANE if you trade drugs for sex...
SSRIs antihypertensives neuroleptics ethanol |
|
|
BMI threshold values
|
<18.5 underweight
>25 overweight >30 obese >40 morbidly obese |
|
|
EEG waveforms
awake (eyes open) awake (eyes closed) stage 1 stage 2 stages 3-4 REM |
at night, BATS Drink Blood
beta alpha theta sleep spindles, K complexes delta beta |
|
|
sleep stages % of total sleep time in young adults
|
1 -- 5%
2 -- 45% 3-4 -- 25% REM -- 25% |
|
|
sleep stages 3-4 feature...
|
slow-wave sleep
deepest non-REM sleep sleepwalking night terrors bedwetting |
|
|
sleep stage 1 & 2 feature...
|
1: light sleep
2: deeper sleep; bruxism |
|
|
REM sleep features
|
dreaming
loss of motor tone possibly memory processing erections ^ brain O2 use |
|
|
the two most extreme EEG waveforms
|
beta
--highest frequency --lowest amplitude delta --lowest frequency --highest amplitude |
|
|
EEG waveform in sleep stage 2
|
sleep spindles
k complexes |
|
|
things that reduce REM sleep
some of them also reduce _ sleep |
v with age
NE reduces REM sleep v REM and v delta: --alcohol --benzodiazepines --barbiturates |
|
|
_ is key to initiating sleep
|
serotonergic predominance of raphe nucleus
|
|
|
extraocular movements during REM sleep are due to _ in the brain
|
PPRF aka conjugate gaze center
|
|
|
_ is used to treat enuresis because it
|
imipramine
v stage 4 sleep |
|
|
imipramine is a _
|
TCA
|
|
|
benzos are useful for _ sleep disorders
|
night terrors
sleepwalking |
|
|
REM cardiovascular effects
|
^ and variable pulse
^ and variable BP |
|
|
sleep changes in depressed patients
|
v slow-wave
v REM latency ^ REM early in sleep cycle ^ total REM nighttime awakeneings early-morning awakening |
|
|
REM sleep occurs every ... minutes
REM sleep duration ^ / v throughout the night |
^
|
|
|
narcolepsy features (5)
|
1^ characteristic: excessive daytime sleepiness
hypnagogic or hypnopompic hallucinations start off with REM sleep cataplexy strong genetic component |
|
|
cataplexy
|
loss of all muscle tone following a strong emotional stimulus
|
|
|
rx for narcolepsy
|
mnemonic: "SOMA"
sodium oxybate modafinil amphetamines |
|
|
circadian rhythm is driven by _
|
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of hypothalamus
|
|
|
circadian rhythm controls
|
ACTH
prolactin melatonin nocturnal NE release |
|
|
circuit that releases melatonin
|
~ light cycle ~ --> SCN --> NE release --> pineal gland --> melatonin
|
|
|
sleep terror occurs during _
what does kid recall? |
slow-wave sleep
no memory of it |

