![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define phylogeny |
Evolutionary relationship between organisms |
|
|
Taxonomy |
Classification of organisms |
|
|
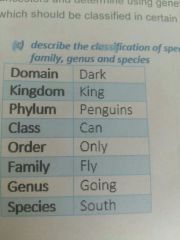
What is the taxanomic hierachy |
|
|
|
What are the 5 kingdoms. Description |
Prokaryotae. Single cell .No nucleus. Respiration on cell surface membrane. Bacteria Protoctista. Single celled. Rejects from all Kingdom. Plant like and animal like Fungi. Multi nuclei. Chitin cell wall.saprotrophic . Plants. Autotrophic. Cellulose. Animal. Heterotrophic. Fertilised eggs develop into blastula |
|
|
What is the naming system and why |
Binomial. Genus species Homo sapiens Universal name
|
|
|
What is the name of the key that uses a series of questions to identify the species |
Dichotomous key |
|
|
Difference between old and new classification system |
Based only on anatomy and appearance Mitochondrial and dna evidence. Fungi has hyphae like root of plant but doesn't photosynthesis |
|
|
2 biochemical ways to determine phylogenetic relationships |
Amino acid sequencing of Cytochrome c used in respiration.
Genome sequencing |
|
|
Compare 5 Kingdom system with 3 domain system |
Molecular evidence suggests bacteria fundementally different from eukaryotes and archaea. Archaea more closely related to eukaryotes than eubacteria: Similar rna polymerase Similar dna replicate mechanism Produce protein that binds to dna Eubacteria Archaea Eukaryotes |
|
|
Reasons for classification |
Easier study of living things Easier identification Relationship between species |
|
|
What are bacteria cell wall made of |
Peptidoglycan |
|
|
2 types of evolution |
Divergent. Original common ancestor
Convergent. Same environment so similar characteristic . Marsupial moles and placental mole. |
|
|
What are the conclusion Darwin and Wallace came up with that led to the theory of natural selection |
Similar appearance to parents No 2 induiduals identical Struggle to survive Survival of the fittest Over time large number of changes = new species |
|
|
Evidence for evolution |
Fossil evidence Molecular evidence |
|
|
Variation |
Presence of variety |
|
|
Intraspecific variation |
Variation between members of the same species |
|
|
Interspecific variation |
Variation between species |
|
|
Continuous variation |
2 extremes and range in between |
|
|
Discontinuous variation |
Distinct categories and no inbetween Controlled by only few genes |
|
|
2 causes of variation |
Genetic Environmental |
|
|
What is used to show the relationship between two variables |
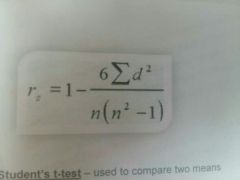
Spearman's rank correlation coefficient |
|
|
3 types of adaptation |
Anatomical Physiological/ biochemical Behavioural |
|
|
Describe natural selection |
Mutation cause genetic variation Selective pressure Advantageous characteristics survive; survival of the fittest Pass on advantage gene Next generation has more individual w// advantageous genes. |
|
|
Example of evolution |
Incecticide resistant MRSA |
|
|
Speciation |
Formation of new species from pre existing ones |
|
|
Describe speciation |
Reproductive barrier Variation spreads down generations Change occur to only part of group; no longer interbreed |
|
|
2 reasons for speciation |
Allopatric. Geographic separation
Sympatric. Biochemical. Behavioural . Physical change that prevents fertilisation |

