![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the major families of receptors?
|
Ion channels
G-protein coupled receptors Receptor enzymes Cytosolic nuclear receptors |
|
|
What is affinity and intrinsic efficacy of a drug?
|
Affinity: Chemical forces that cause the drug to associate with the receptor
Intrinsic Efficacy: the extent of functional change imparted by a drug to a receptor upon binding of a drug |
|
|
What is the difference between potency and magnitude of effect (aka efficacy) of a drug?
|
Potency: Dose of drug necessary to produce a specified effect. (dependent on receptor density, efficiency of the stimulus-response mechanism, affinity, and efficacy)
Magnitude of effect: asymptotic maximal response |
|
|
What are spare receptors?
|
Receptors left over after a max response. (i.e. a drug with high intrinsic efficacy will have a lot of spare receptors)
|
|
|
What is a drug that binds to a receptor to produce an effect opposite that of an agonist by stabilizing all receptors in the inactive state called?
|
Hah! Dumbass! Its an Inverse agonist!
|
|
|
What is a drug that binds to receptors but cannot initiate a cellular response, but prevent agonists from producing a response (ie affinity but no efficacy)?
|
Antagonists! Hah Dumbass! oh wait...! Nevermind! LOL ahhahahaah I'm losing it
|
|
|
What is a physiologic antagonist?
|
Its another drug that has the opposite effect but through a different mechanism as the agonist (ie. different channel or receptor - possibly on different tissues)
|
|
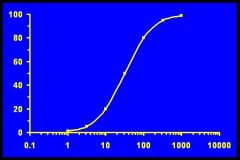
Where would the Threshold, ED50, and Ceiling for a drug be on this dose response curve?
|
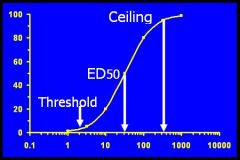
Look at the picture stupid
|
|
|
If an agonist cannot reach maximal effect what is that agonist referred to as?
|
partial agonist
|
|
|
What would happen if you added a full agonist and a partial agonist for the same receptor?
|
You would have a competitive inhibition between the two drugs yeilding an equilibrium level of response that is submaximal. (ie. the partial agonist function similar to an antagonist and prevents maximal response from the full agonist)
|
|
|
How can you calculate relative potency between two drugs?
|
Take the ED50 of one and divide by the ED50 of the other. (eg. ED50B/ED50A = relative potency... 320/3.2 = 100 meaning 100X less of drug A than drug B is the same response)
|
|
|
How is the safety index of a drug determined?
|
Take the 1% lethal dose and divide by the 99% effective dose. (eg. LD1/ED99 if this number is low the drug is not safe) This index is more important than potency!
|
|
|
How is Therapeutic index determined?
|
LD50/ED50
|

